3 operating sequence, 1 sampling sequence, Operating sequence – Campbell Scientific CVS4200 / BVS4300 Stationary Samplers User Manual
Page 36: Sampling sequence
CVS4200 / BVS4300 Stationary Samplers
7.3 Operating Sequence
7.3.1 Sampling Sequence
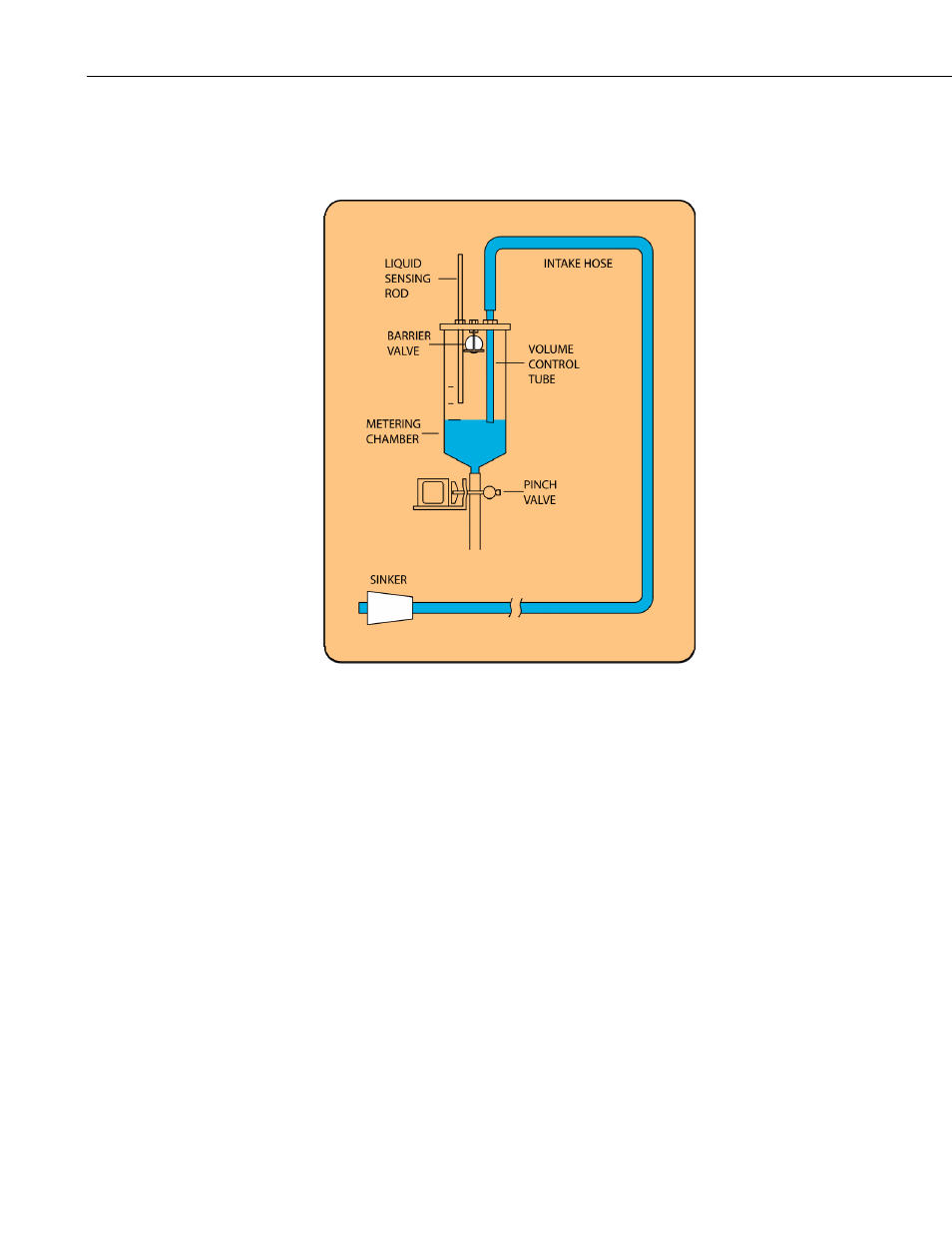
SAMPLING PROCESS:
1. High pressure air purge of intake hose.
2. Liquid is drawn into the metering chamber, up to the liquid sensing rod.
3. All excess liquid is purged from the system down to the level set by the
volume control tube.
4. The sample is then released into either one composite container or one of
several discrete containers.
The sampling sequence begins with a high pressure air purge of the intake
assembly to remove residual liquid and obstructions. Upon completion of the
pre-purge cycle, the system converts to a vacuum state, drawing the sample
through the intake hose into the metering chamber. The system then
pressurizes, ejecting excess fluid back through the intake line until the
predetermined sample volume is achieved. The sample is then deposited under
pressure into the sample container while the post purge again clears the intake
line of any residual liquid.
Should the sampler, for any reason, not be able to draw a sufficient volume of
fluid to obtain a sample, the unit automatically initiates a second attempt.
Should a sample still not be delivered, the sequence will be abandoned and the
unit will await the next initiation. Upon two consecutive failures, the sampler
will suspend the sampling program until manually RESTARTed.
28
