2 quarter bridge strain with 2 wire element, 1 quarter bridge strain with 2 wire element wiring – Campbell Scientific 4WFBS120, 4WFBS350, 4WFBS1K 4 Wire Full Bridge Terminal Input Modules User Manual
Page 23
4WFBS120, 4WFBS350, 4WFBS1K 4 Wire Full Bridge Terminal Input Modules (TIM)
4.2 Quarter Bridge Strain with 2 Wire Element
Although a two wire gage can be used with the 4WFBS TIM,
due to the issues outlined in Section 4.4.3, it is not
recommended. An exception may be applications with short
leads in a stable temperature environment.
NOTE
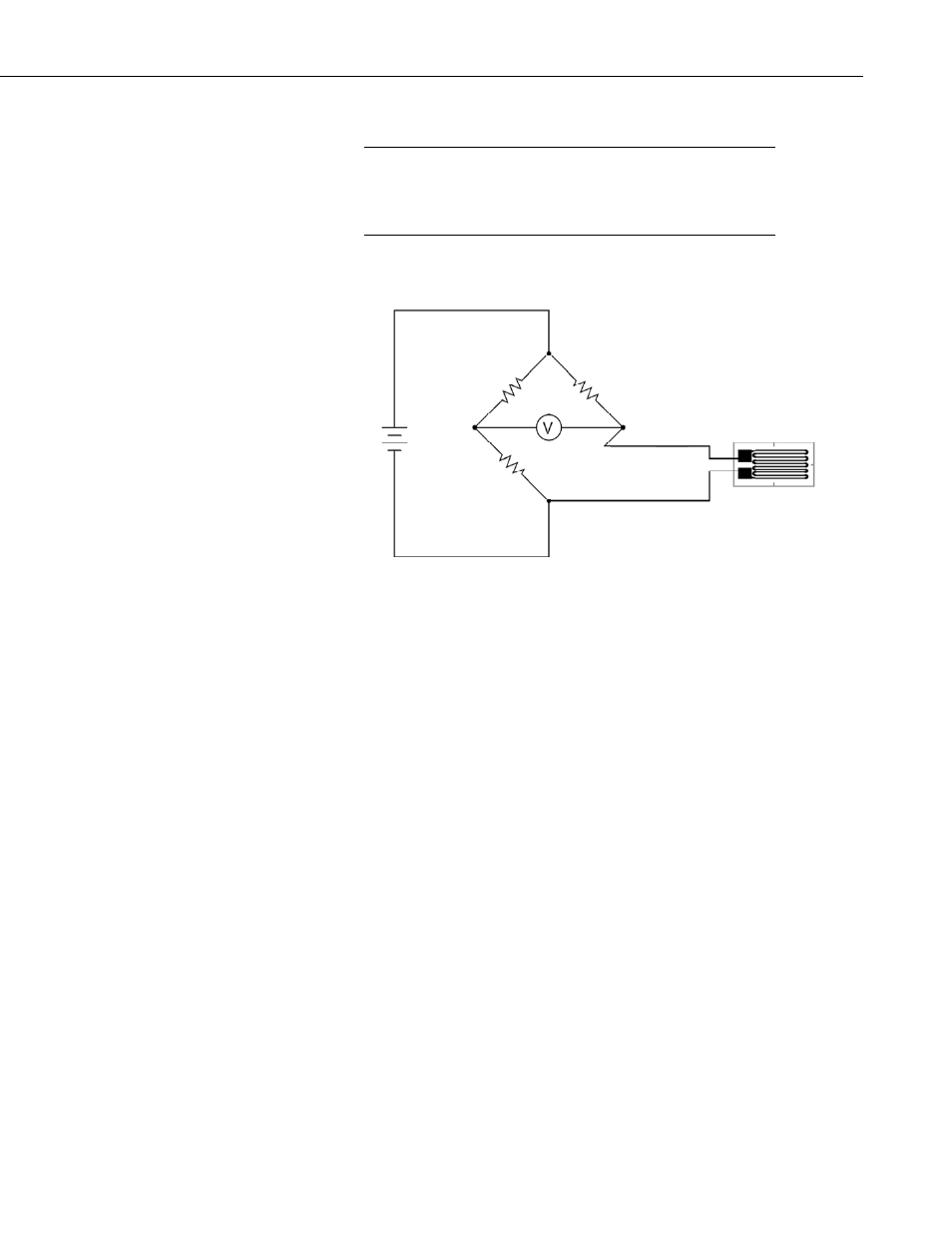
A 2-wire quarter bridge strain circuit is shown in figure 4.2-1.
R
D
R
1
=1K
Ω
R
2
=1K
Ω
R
4
=Gauge
+
-
Excite V
FIGURE 4.2-1. Two wire quarter bridge strain circuit
In this circuit, R1 and R2 are 1000 ohm resistors making up the back plane of
the Wheatstone bridge, as is done in the TIM design. R
D
is the complementary
resistor, or Dummy Resistor, that has a nominal resistance of the un-strained
gage. The 4
th
resistive element is the active strain gage. Strain gages are
available in nominal resistances of 120, 350, and 1000 ohms. The 4WFBS
model must match the nominal resistance of the gage (e.g., the 4WFBS120 is
used with a 120 ohm strain gage).
As can be seen in Figure 4.2-1, both sensor leads are in the same arm of the
Wheatstone bridge. Not only does this affect the sensitivity of the gage, the
output from this circuit will include temperature induced line resistance errors.
See Section 4.4.3, Lead Compensation using ¼ Bridge Strain with 2 Wire
Element for more information on issues with using 2 wire gages.
4.2.1 Quarter Bridge Strain with 2 Wire Element Wiring
To use a two wire element strain gauge with the 4WFBS TIM requires a
jumper wire be placed between the H and L terminal of the TIM module as
shown in Figure 4.2-2.
17
