Table 8 continuous access xp suspend types, 8 continuous access xp suspend types, Continuous access xp asynchronous suspension – HP XP Continuous Access Software User Manual
Page 29: Table 8, Continuous access xp asynchronous
Continuous Access XP user guide for the XP1024/XP128
29
When a Continuous Access XP Asynchronous (Continuous Access XP Async) pair is suspended, the MCU
stops performing Continuous Access XP Async recordset operations for the pair. The MCU continues
accepting write I/Os for the suspended P-VOL and tracks P-VOL cylinders updated while the pair is
suspended. The MCU and RCU also tracks recordsets discarded during the pair suspension. When a
suspended Continuous Access XP Async pair is resumed, the RCU sends the S-VOL cylinder bitmap to the
MCU, and the MCU merges the P-VOL and S-VOL bitmaps to determine which cylinders are out-of-sync.
This method ensures that all cylinders containing recordsets discarded at the RCU are resynchronized at
this time.
A suspended (or split) Continuous Access XP Async S-VOL has an additional status called consistency
status. Consistency status is displayed only at the RCU and indicates the S-VOL’s update sequence
consistency with respect to other S-VOLs in the same group. See
on page 28 for a description of
consistency status for suspended/split Continuous Access XP Async S-VOLs.
Continuous Access XP Asynchronous suspension conditions
Continuous Access XP Asynchronous operations involve additional suspension conditions related to
recordset operations. The MCU and RCU detect Continuous Access XP Async suspension conditions and
suspend Continuous Access XP Async pairs. When a Continuous Access XP Async pair is suspended,
cylinders containing the following records are marked in the cylinder bitmap as modified (to be copied
during the pairresync operation):
•
Recordsets created by the MCU, but not yet sent to the RCU. After marking these P-VOL cylinders as
modified, the MCU discards these recordsets.
•
Recordsets sent to the RCU, but not acknowledged by the RCU. The MCU marks these P-VOL cylinders
as modified and discards these recordsets, ensuring that recordsets lost during transmission to the RCU
are identified and marked.
•
Recordsets that reached the RCU, but have not yet been settled. After marking these S-VOL cylinders
as modified, the RCU discards these recordsets.
•
P-VOL records updated by host-requested write I/Os after the pair was suspended (same function as
for Continuous Access XP Synchronous pairs).
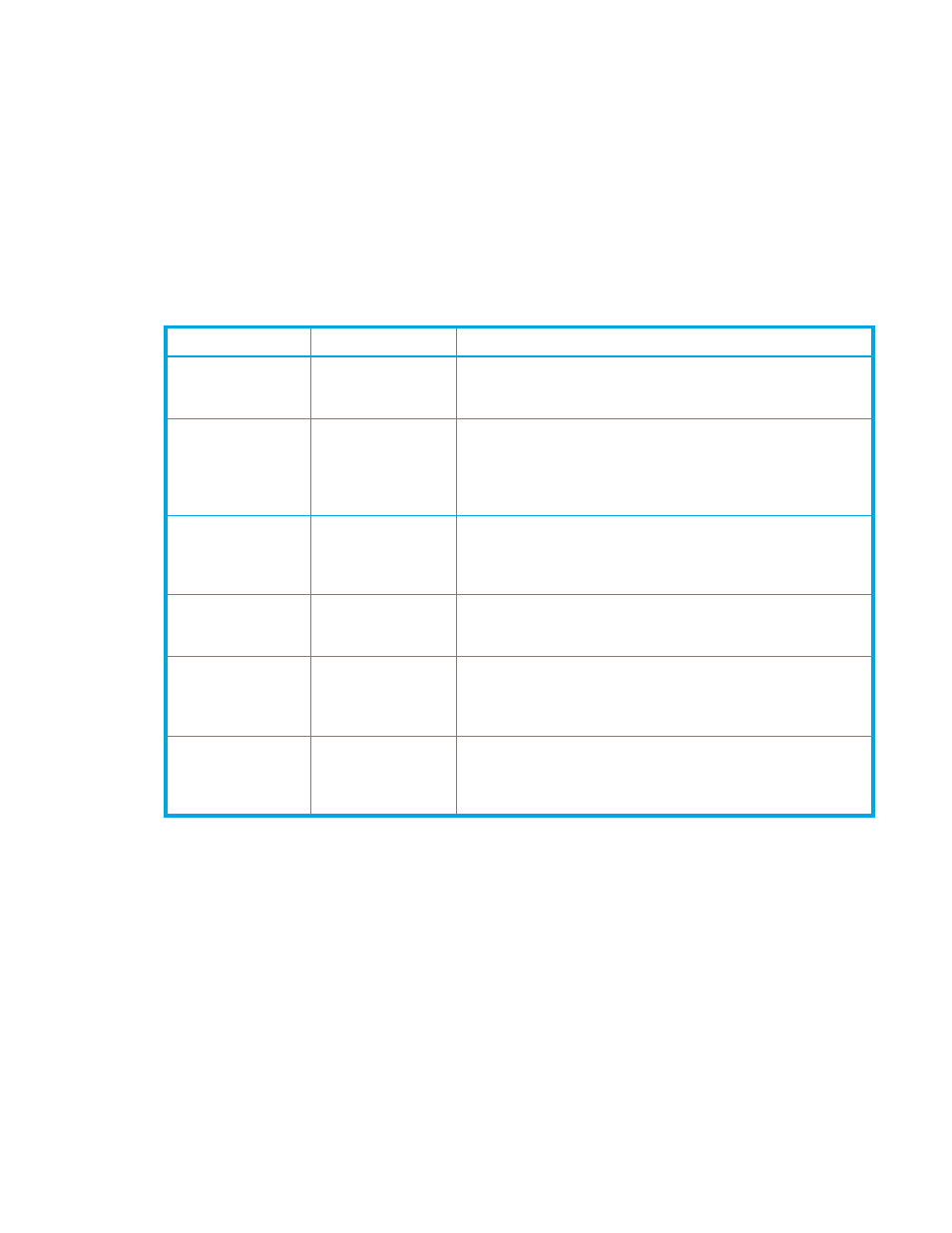
Table 8
Continuous Access XP suspend types
Type
Applies to
Description
PSUE,
by RCU
P-VOL, S-VOL
The MCU detected an error condition at the RCU causing the MCU
to suspend the Continuous Access XP volume pair. S-VOL suspend
type is PSUE-S-VOL Failure.
PSUE,
S-VOL Failure
P-VOL, S-VOL
The MCU detected an error during RCU communications or update
copy. In this case, S-VOL suspend type is usually PSUE-S-VOL
Failure. This suspend type is also used when the number of paths
falls below the minimum number of paths setting on the RCU
Option pane.
PSUE,
MCU IMPL
P-VOL, S-VOL
The MCU could not find valid control information in its nonvolatile
memory during IMPL. This condition occurs only if the MCU is
without power for more than 48 hours (power failure and fully
discharged backup batteries).
PSUE,
Initial Copy Failed
P-VOL, S-VOL
The
Continuous Access XP
pair was suspended before the initial
copy operation was complete. Data on the S-VOL is not identical to
data on the P-VOL.
PSUE,
MCU P/S OFF
S-VOL
(
Continuous Access
XP
Async only)
The RCU received a request from the MCU to suspend the S-VOL
due to MCU power-off. The RCU stops expecting recordsets from
that MCU. The P-VOL status does not change due to MCU
power-off.
PSUS,
Sidefile overflow
(
Continuous Access
XP
Async only)
P-VOL, S-VOL
The amount of sidefile exceeds the specified “current pending
update data rate,” and the RCU data is not transferred within the
specified “offloading timer.”
