3 log consolidation configuration, Syslog-ng log consolidator configuration – HP Linux Server Management Software User Manual
Page 49
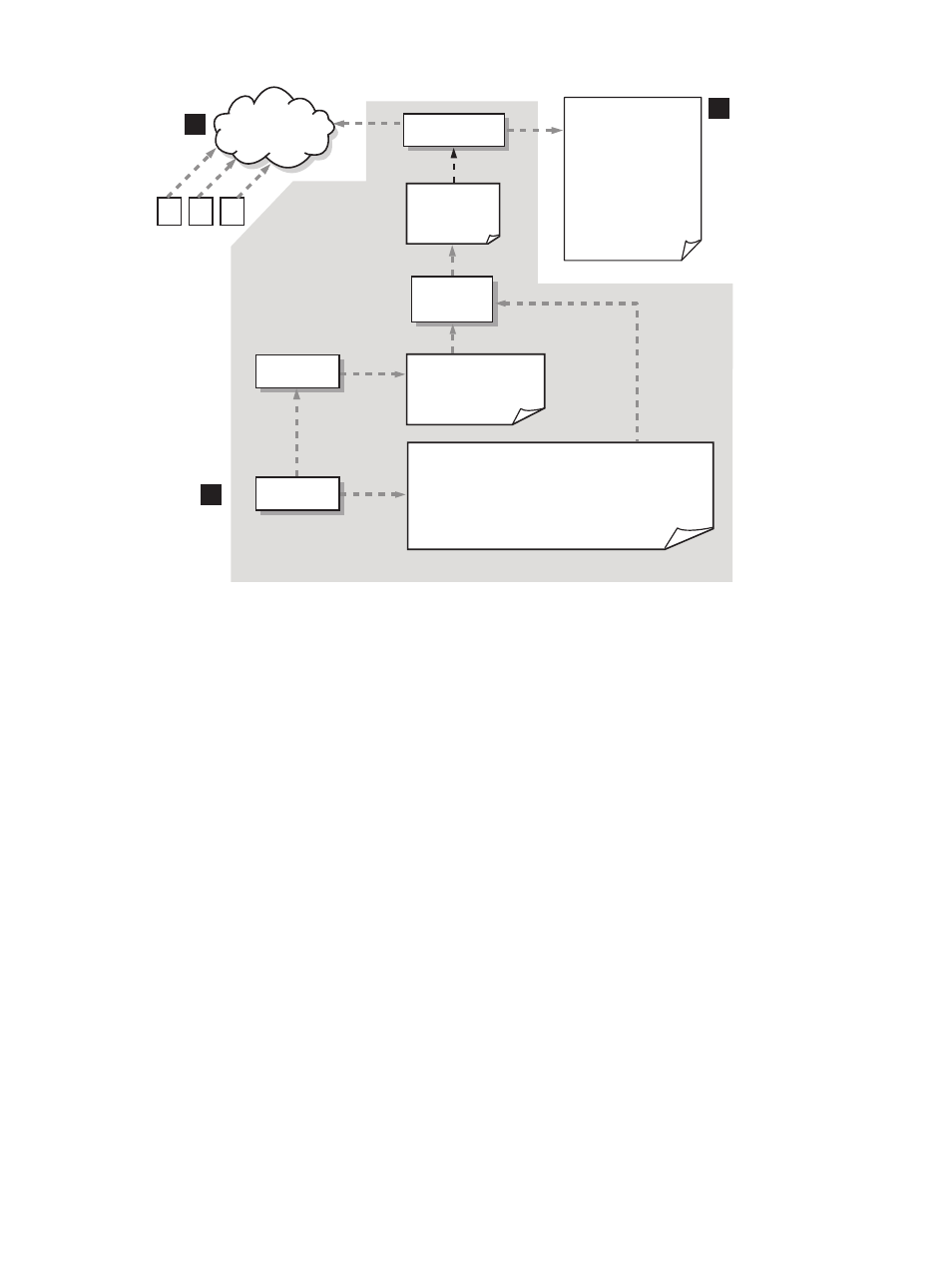
Figure 3-2 syslog-ng Log Consolidator Configuration
1
3
2
syslog-ng
fifo
syslog-ng
syslogd
cmcld
TCP/IP
or UDP
Log
reader
+/var/log/
messages
mail log
A
B
C
Consolidated Logs:
+ /clog/syslog
-syslog.log
-mail.log
-syslog-ng.log
+/clog/packages
-clog.log
-csync.log
-xclock.log
NOTE: Actual path for cmcluster may be different
+ /usr/local/cmcluster/conf/
-clog.log
-csync.log
-xclock.log
1.
The syslog-ng server reads the incoming log data from the UDP or TCP connected clients.
Note: gray arrows indicate a read operation; black arrows, a write.
2.
The gray area is identical to the client configuration in
Figure 3-1: “syslog-ng Log-Forwarding
. In terms of the local system, syslog-ng acts as client and is processing
locally forwarded clog_tail messages.
3.
The syslog-ng server processes all messages and filters them into the appropriate
consolidated log files. In this specific example, the administrator has created a filesystem
named “/clog” to house the consolidated logs. /clog/syslog/ would contain the
consolidated syslog-related file. /clog/packages would contain consolidated package
logs for a Serviceguard cluster.
3.3 Log Consolidation Configuration
The following sections describe how to configure log consolidation servers and log forwarding
clients. Configuring a consolidation server is a multi-step process. The clog_wizard tool vastly
simplifies the configuration process. If you choose not to use the wizard, the manual configuration
steps are also described below.
3.3 Log Consolidation Configuration
49
