Syslog-ng log-forwarding configuration – HP Linux Server Management Software User Manual
Page 48
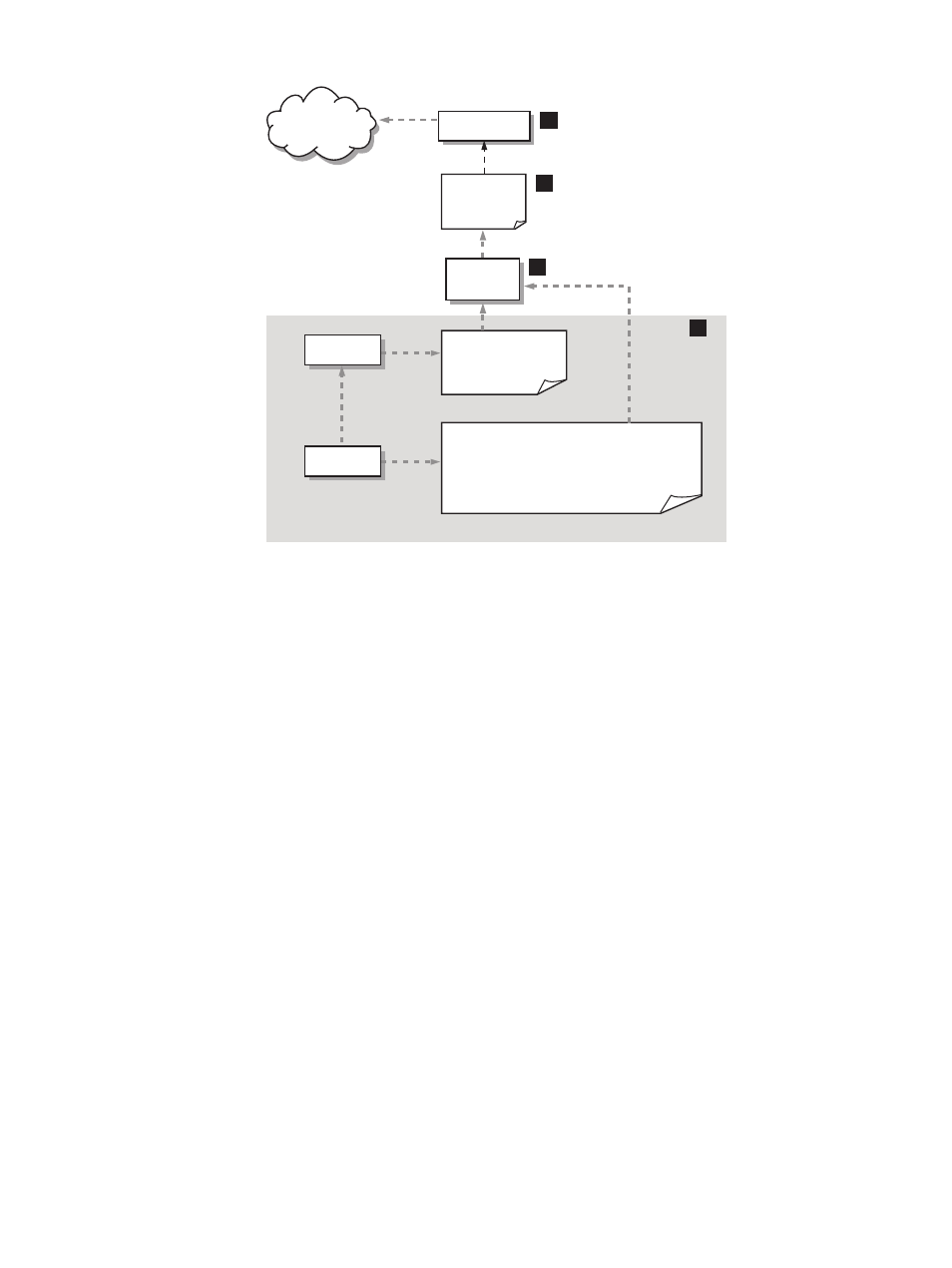
Figure 3-1 syslog-ng Log-Forwarding Configuration
1
4
3
2
syslog-ng
fifo
syslog-ng
syslogd
cmcld
TCP/IP
or UDP
Log
reader
+/var/log/
messages
maillog
+ /usr/local/cmcluster/conf/
-clog.log
-csync.log
-xclock.log
NOTE: Actual path for cmcluster may be different
1.
The gray area represents standard syslogd operation. Applications such as Serviceguard’s
cmcld
daemon call syslog (see syslog(3C)) to send messages to syslogd. syslog writes
messages to the local system’s /var/log/messages and related files. Applications also
frequently have application-specific log files. In this example, Serviceguard maintains a log
of package operations in $SGCONF/
2.
The clog_tail daemon of DSAU, labeled “Log reader” in the diagram, monitors text-based
logs and sends new log lines to syslog-ng for processing. In a Serviceguard cluster,
clog_tail
defaults to monitoring all the package logs.
3.
The log_reader sends all new log messages to a named pipe
(log_consolidation_fifo), which is one of the log sources for syslog-ng.
4.
The syslog-ng reads any new data from the named pipe and forwards it to the log
consolidation server.
illustrates the configuration on the log consolidation server.
48
Consolidated Logging
