Cache logical partition (clpr), Figure 1 – HP StorageWorks XP Remote Web Console Software User Manual
Page 14
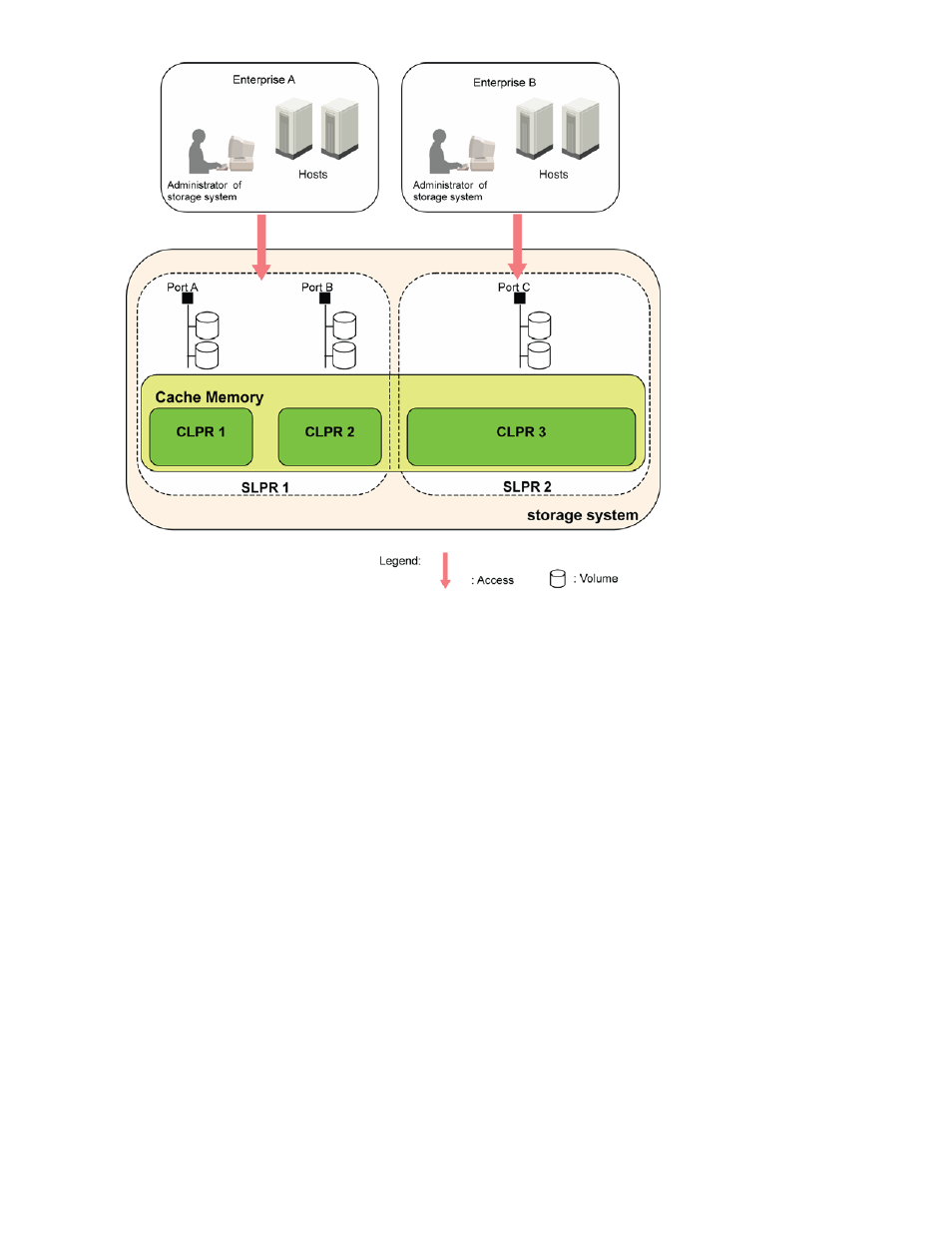
Figure 1 An Example of Storage Management Logical Partition Function
To create SLPR, allocate the resources of storage system, that is, ports and CLPRs. For instructions on
allocating the resources of storage system, see “
Performing Disk/Cache Partition Operations
To create a CLPR and manage it, you need a user authority for storage sys-
tem, that is, Storage Administrator. For details on a Storage Administrator, see
Storage Administrator and Storage Partition Administrator Privileges
” on page 17 in this manual and the
HP StorageWorks XP24000 Remote Web Console User’s Guide.
•
SLPR and LDKC
You can allocate storage system resources that belong to the optional LDKC to an SLPR.
Cache Logical Partition (CLPR)
If one storage system is shared with multiple hosts, and one host in these hosts reads or writes a large
amount of data, the read and write data of the host may occupies the large area in the cache memory
of the storage system. Under this circumstances, other hosts slow down the read/write speed since
other hosts must wait for a chance to write into the cache memory. The cache logical partition function
of Disk/Cache Partition can partition the cache memory of the storage system. The partitioned cache
memories are used as the virtual cache memories, and each of them is allocated to each host. As a
result, the situation that the specified host exclusively uses most area of cache memory can be prevented.
on page 15 shows an example of use for the network within a corporation. The cache memory
is partitioned to three virtual cache memories. Each virtual cache memory is allocated to each host of
three branch offices. The host of branch A is inputting and outputting a large amount of data to or from
storage system. However, the read and write data of the host of branch A does not occupy the cache
memory because the capacity of cache that the host of branch A can use is limited to 40 Gbytes. Even
if the host of branch A accesses a large amount of data, the hosts of other branches does not slow
14
About Disk/Cache Partition Operations
