Measurement principle – KYORITSU 4106 User Manual
Page 18
14
7. Measurement Principle
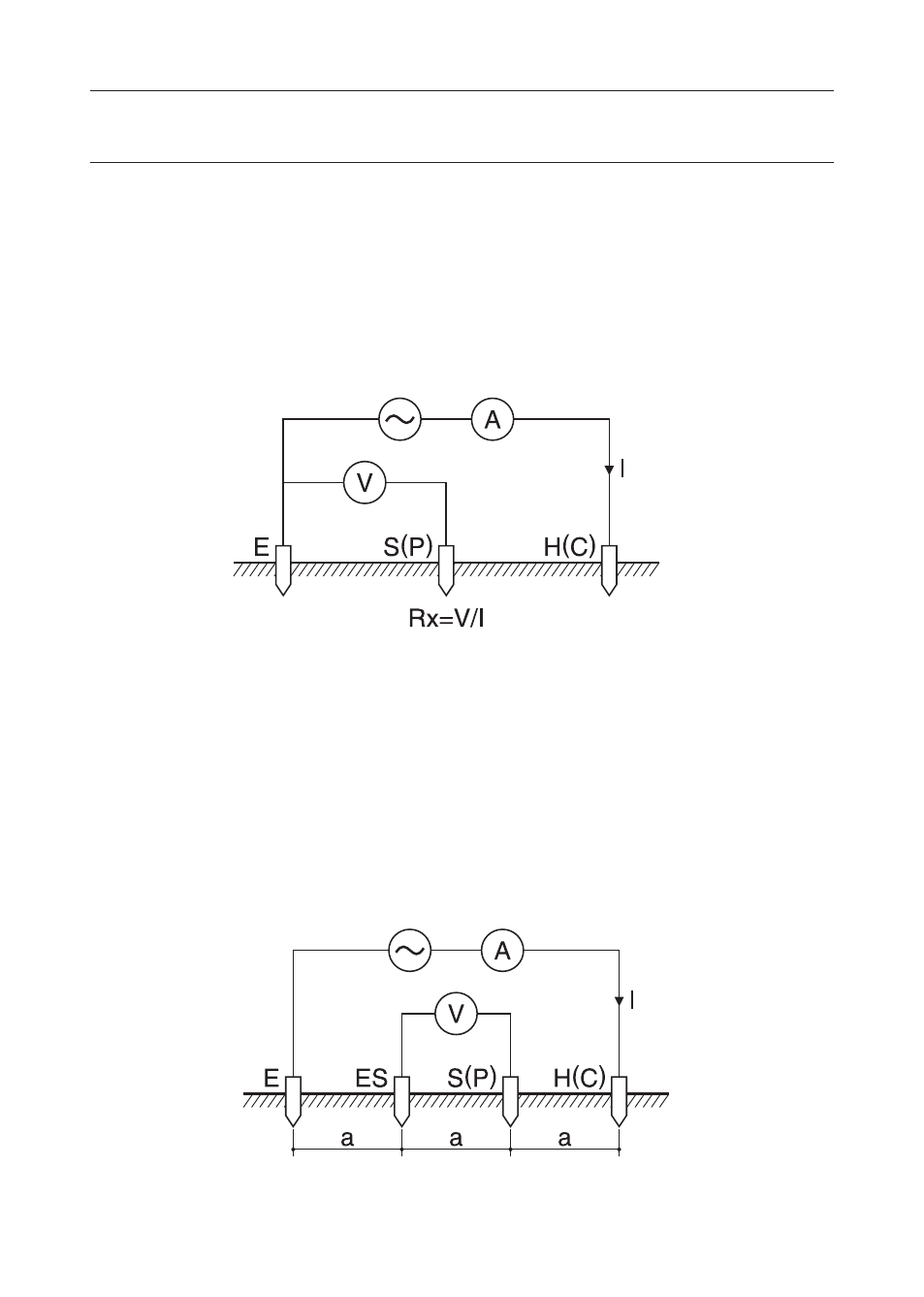
7-1 Principle of Earth Resistance Measurements
This instrument makes earth resistance measurements with fall-of-potential
method, which is a method to obtain earth resistance value “Rx” by applying
AC constant current “I” between the measurement object “E” (earth
electrode) and “H(C)” (current electrode), and finding out the potential
difference “V“ between “E” (earth electrode) and “S(P)” (potential
electrode). See Fig.3.
7-2 Principle of Earth Resistivity (ρ) Measurements
According to the Wenner 4-pole method, apply AC current “I” between the
“E” (earth electrode) and “H(C)” (current electrode) to find out the potential
difference “V” between the potential electrode “S(P)”and auxiliary earth
electrodes “ES”. (Fig.4)
To obtain the earth resistance “Rg(Ω)”, devide the potential difference “V”
by AC current “I”; where the interval between electrodeds is “a”(m). Then
use a formula: ρ= 2・π・a・Rg(Ω・m)
Fig. 3
Fig. 4
