Figure 2-2. aar processing, Figure 2-2. aar processing number, Extension – AT&T DEFINITY 7200 series User Manual
Page 84: Node (system 85 and generic 2 only)
2-12
COMMUNICATION SYSTEM NETWORKING — AN OVERVIEW
_
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
_
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
_
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
16-28, 120
40-49, 108, 109, 120
TRUNK TYPES
PUBLIC NETWORK
(NPA) NNX
−
XXXX
PRIVATE NETWORK
(RNX) - XXXX
PREFERENCE
DATA
OBTAIN
PREFERENCE
FROM
PATTERN
CONDITIONAL
ROUTING
COUNT
OBTAIN
PATTERN
EXT + NODE + RNX
MATCH RNX
TO
NODE
FROM
INTERNAL
DIAL
PLAN
EXT + RNX
EXT + NODE
UNIFORM
DIAL PLAN
FUNCTION
MATCH EXT
TO
RNX
EXTENSION
NUMBER
PORTABILITY
EXT + (NODE) + RNX
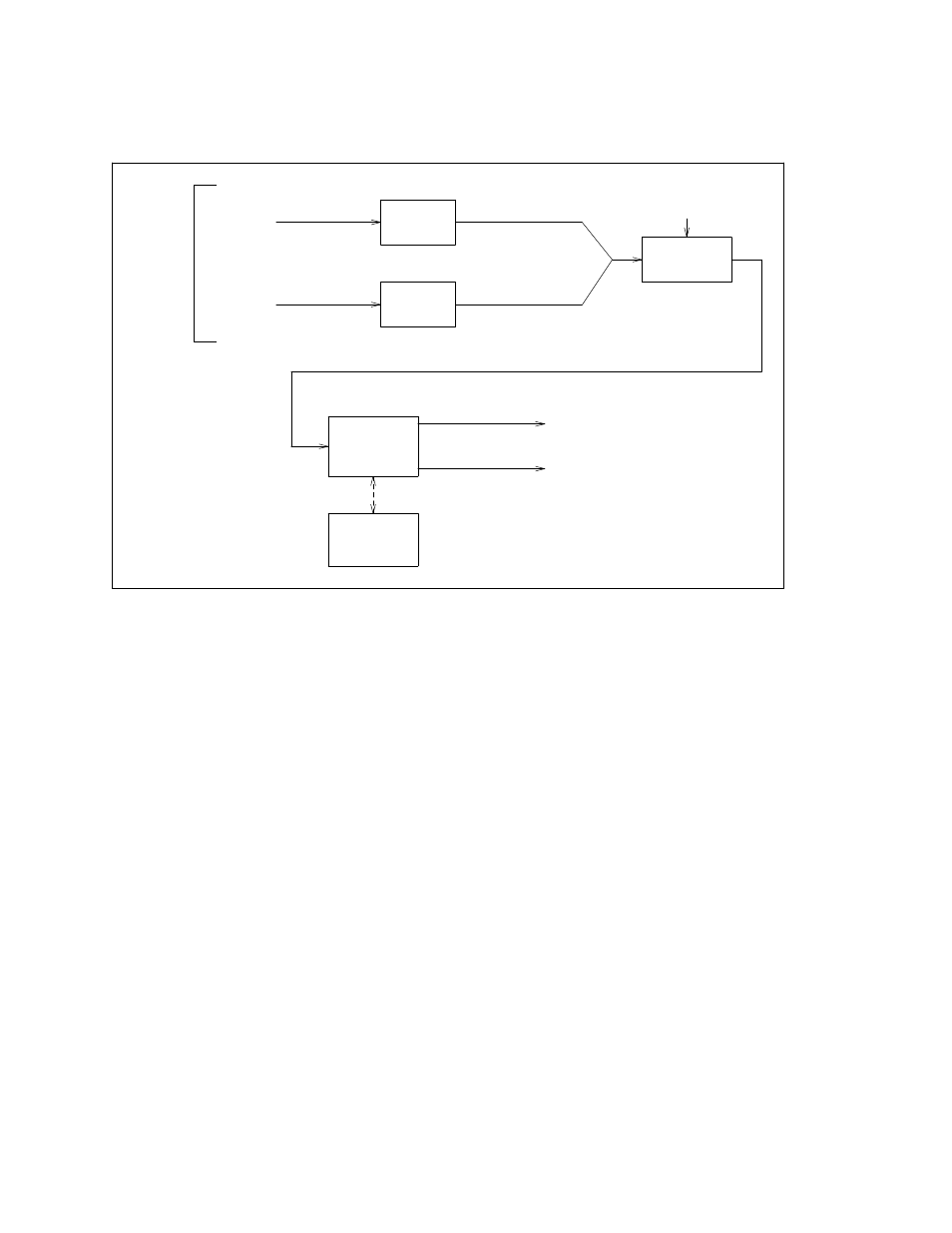
Figure 2-2. AAR Processing
number.
•
If the Uniform Dial Plan function is effective in the switch, AAR receives the RNX number of the
destination switch and the destination extension number.
For extension number portability calls, AAR then finds the RNX of the destination switch in a table that
cross-references the extension to the RNX. When the Uniform Dial Plan function is active on the System
85 or Generic 2, AAR finds the node number of the destination switch in a table that cross-references the
RNX to the node number. On the System 75 and Generic 1, the internal dial plan provides only the RNX
for further AAR processing.
At this point in call processing, AAR has either received or derived the following information on the
destination of each call:
•
Extension
•
Node (System 85 and Generic 2 only)
•
RNX
On the System 85 and Generic 2 communications system, AAR uses the node number and conditional call
routing count, to find the routing pattern that is most appropriate for the call. It does this by finding the
node number in a table that cross-references the node number to a routing pattern. The pattern lists the
trunks groups (preferences) over which it is possible to send the call. On the System 75 and Generic 1
communications systems, only the RNX is used to find the routing pattern that is most appropriate for the
call.
