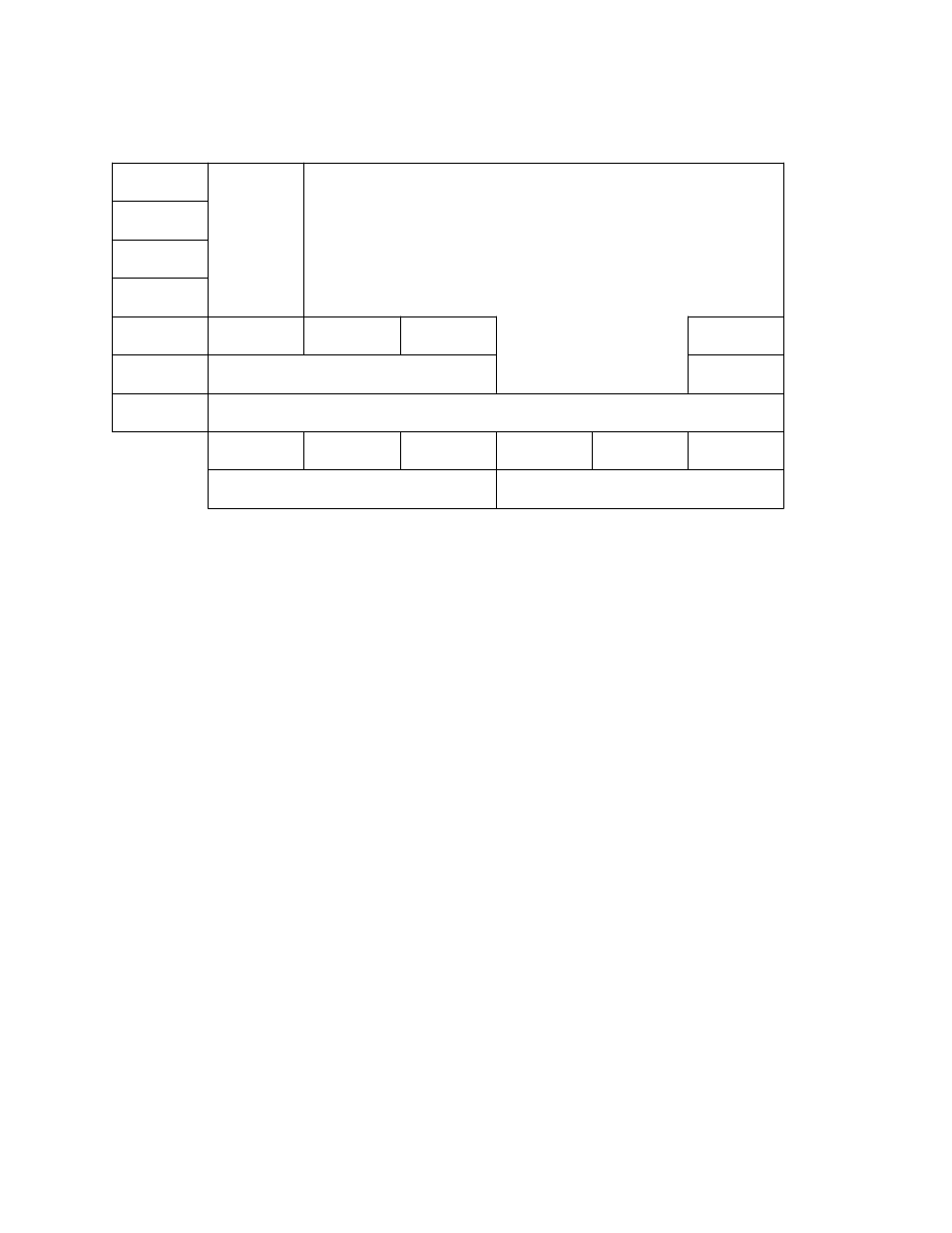
Figure d-2. isdn protocols – AT&T DEFINITY 7200 series User Manual
Page 281
COMMUNICATIONS PROTOCOLS
D-9
_
______________________________________________________________________________________
_
______________________________________________________________________________________
_
______________________________________________________________________________________
Further
study
( )
B Channel
Packet
switching
CCITT-ISO
OSI-related protocols
Leased
circuit
Circuit
switching
Telemetry
D Channel
Packet
Signal
X.25
LAP-B
Layer 1 (I.430, I.431)
LAP-D (I.441)
X.25
Packet level
X.25
Packet level
Call control
I.451
End-to-end
user
signaling
Physical
Data link
Network
Transport
Session
Presentation
Application
Adapted from: Data and Computer Communications, by William Stallings, Macmillan Publishing Co., N.Y., 1988
Figure D-2. ISDN Protocols
Other Common Standards
In addition to standards formulated by the CCITT, many other standards are common. Most notable among
these non-CCITT standards are some of the most popular protocols at layers 1 and 2.
Layer 1 protocols include:
•
RS-232C — A common physical interface used to connect DTE devices to voice-grade modems for use
in the public network.
•
RS-449 — A replacement specification for the RS-232C specification. It was devised to overcome the
RS-232C distance restrictions and the lack of modem control that RS-232C procedures afford.
•
RS-366A — A physical interface between a DTE and automatic calling equipment for data
communications.
Layer 2 protocols include:
•
SDLC (Synchronous data link control) — An IBM protocol that has a 1 byte addressing field and is
capable of transmitting messages in multiple frames.
•
HDLC (High-level data link control) — A very common bit-oriented standard issued by the ISO. It
features a multi-byte addressing field, but otherwise, is quite similar to SDLC, from which it was
derived.
•
BSC (Binary synchronous communications) — An early IBM character-oriented, half-duplex protocol
that transmits messages consisting of strings of characters. Control information is provided by special
non-printing characters.
