GW Instek SPS Series User Manual
Page 20
16
Similarly, crossover from the constant current to the constant voltage mode automatically occurs from a decrease in
load, a good example of this would be seen when charging a 12 volt battery. Initially, the open circuit voltage of
the power supply may be preset for 13.8 volts. A low battery will place a heavy load on the supply and it will
operate in the constant current mode, which may be adjusted for a 1 amp charging rate. As the battery becomes
charged, and its voltage approaches 13.8 volts, its load decreases to the point where it no longer demands the full 1
amp charging rate. This is the crossover point where the power supply goes into the constant voltage mode.
6-4. Operation mode: Voltage Operation Mode
A. Set Power switch to “OFF” position.
B. Make sure that line voltage is correct for the input power voltage.
C. Plug power cord into the power outlet.
D. Set Power switch to “ON” position.
E. Adjust “Voltage” and “Current” control to the desired output voltage and current.
F. Connect the external load to the output binding posts. Make sure both “+” and “-” terminals are connected
correctly.
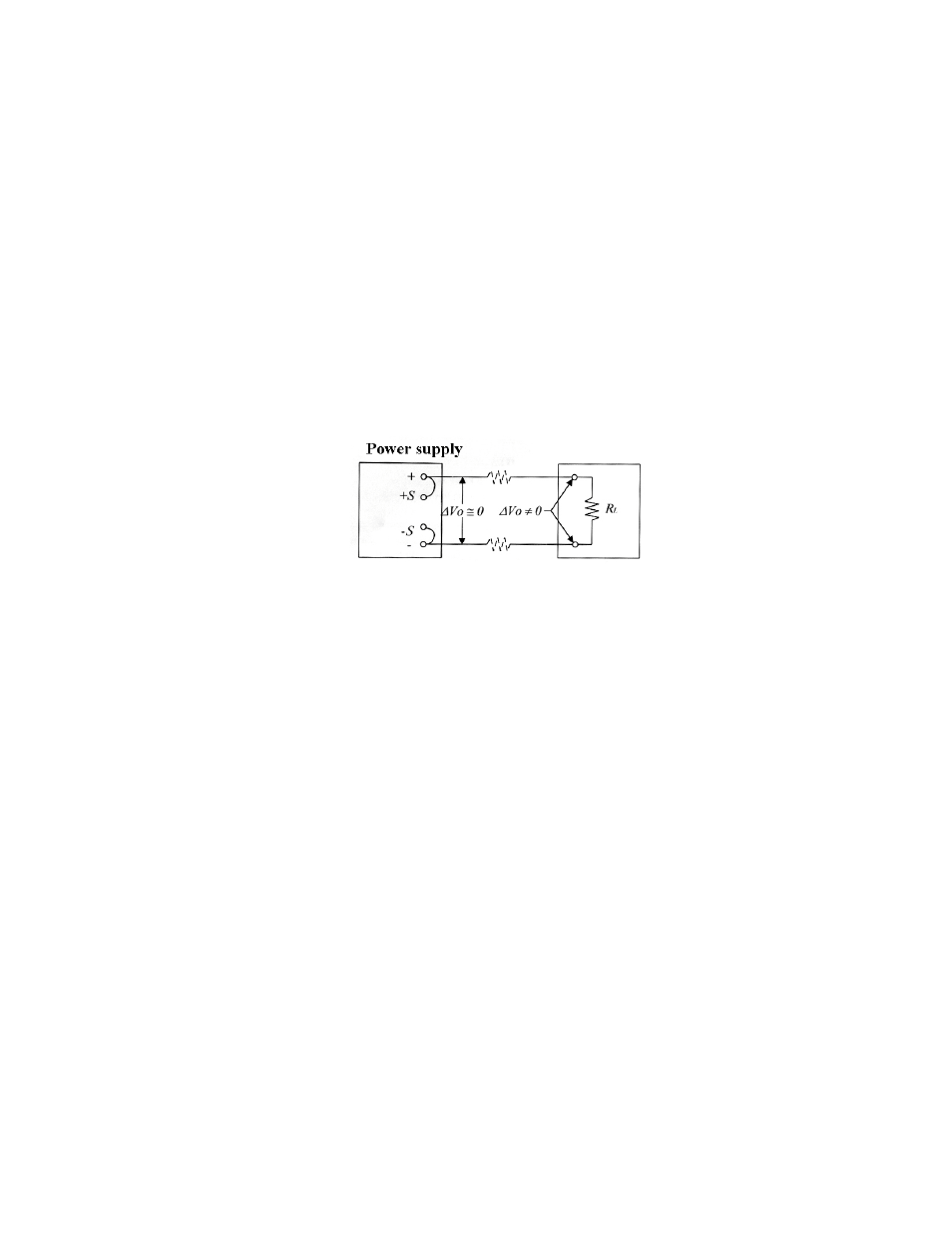
6-5. Remote Error Sensing
A normal power supply can perform its best load regulation, line regulation, low output impedance, and low output
ripple and noise, as well as the rapidly transient recovery response. Please refer to figure 6-2. If there is any test lead
connected between load and output terminal, the best characters of power supply can not be shown up on the load
terminal.
Figure 6-2 The power supply with local error sensing
