2 emissivity – LumaSense Technologies MCS640 Manual User Manual
Page 16
12
Section 4
Principles of Thermal Imaging
4.2 Emissivity
Infrared radiation is energy radiated by the motion of atoms and molecules on the surface
of object, where the temperature of the object is more than absolute zero. The intensity
of the emittance is a function of the temperature of the material. In other words, the
higher the temperature, the greater the intensity of infrared energy that is emitted. As
well as emitting infrared energy, materials also reflect infrared, absorb infrared and, in
some cases, transmit infrared. When the temperature of the material equals that of its
surroundings, the amount of thermal radiation absorbed by the object equals the amount
emitted by the object.
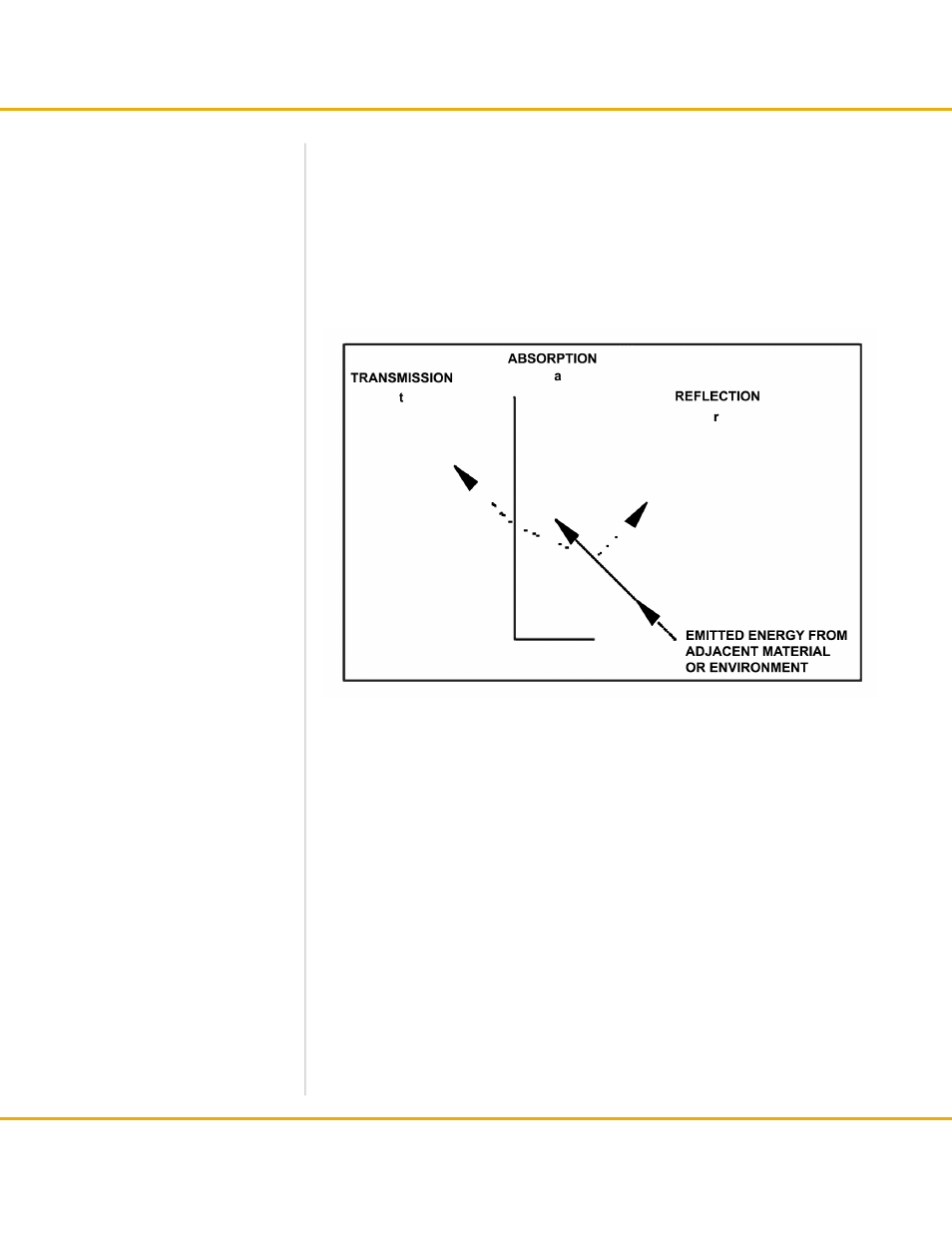
The figure above shows the three modes by which the radiant energy striking an object
may be dissipated. These modes of dissipation are:
a = absorption
t = transmission
r = reflection
The fractions of the total radiant energy, which are associated with each of the above
modes of dissipation, are referred to as the absorptivity (a) transmissivity (t) and the
reflectivity (r) of the body. According to the theory of conservation of energy, the extent
to which materials reflect, absorb and transmit IR energy is known as the emissivity of
the material.
transmission, absorption, and
reflection of Infrared energy
