Principle of thermal imaging – LumaSense Technologies MCS640 Manual User Manual
Page 15
11
4
Section
Principle of Thermal
Imaging
All materials above 0 degrees Kelvin (-273 degrees C) emit infrared energy. The infrared
energy emitted from the measured object is converted into an electrical signal by the
imaging sensor (microbolometer) in the camera and displayed on a monitor as a color or
monochrome thermal image. The basic principle is explained in the following sections.
4.1 Infrared Radiation
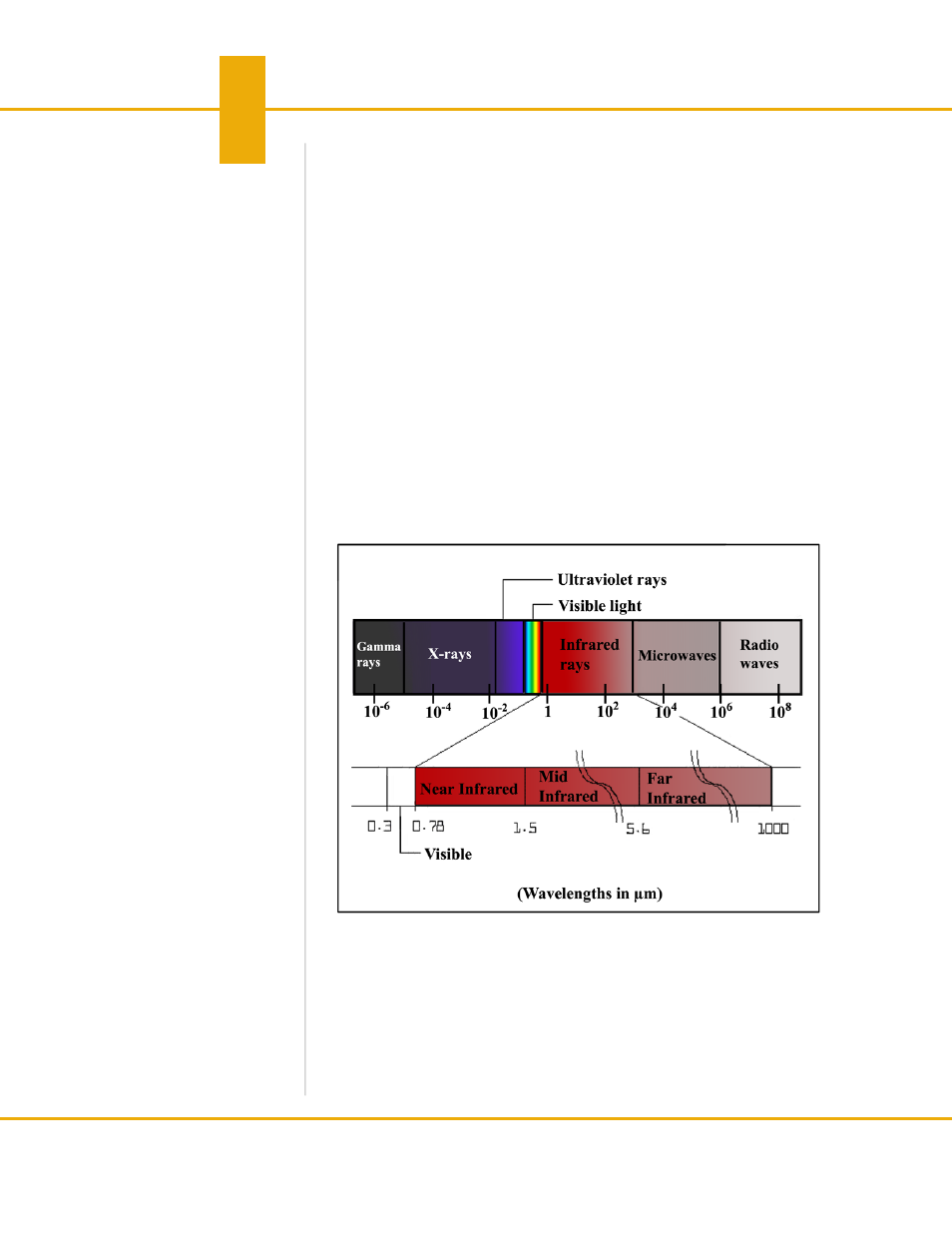
The infrared ray is a form of electromagnetic radiation the same as radio waves,
microwaves, ultraviolet rays, visible light, X-rays, and gamma rays. All these forms,
which collectively make up the electromagnetic spectrum, are similar in that they emit
energy in the form of electromagnetic waves traveling at the speed of light. The major
difference between each ‘band’ in the spectrum is in their wavelength, which correlates to
the amount of energy the waves carry. For example, while gamma rays have wavelengths
millions of times smaller than those of visible light, radio waves have wavelengths that
are billions of times longer than those of visible light.
The wavelength of the infrared radiation ‘band’ is 0.78 to 1000µm (micrometers). This is
longer than the wavelength of visible light yet shorter that radio waves. The wavelengths
of infrared radiation are classified from the near infrared to the far infrared.
a spectrum of electromagnetic
radiation
