2 troubleshooting flowcharts, Troubleshooting flowcharts -5 – Yokogawa EJX118A User Manual
Page 40
<8. Maintenance>
7-5
IM 01C25H01-01E
This transmitter is equipped with a self-diagnostic
function which will be useful in troubleshooting,
and the transmitter equipped with an integral
indicator will show an alarm code as a result of self-
diagnosis.
See subsection 7.5.3 for the list of alarms.
See also each communication manual.
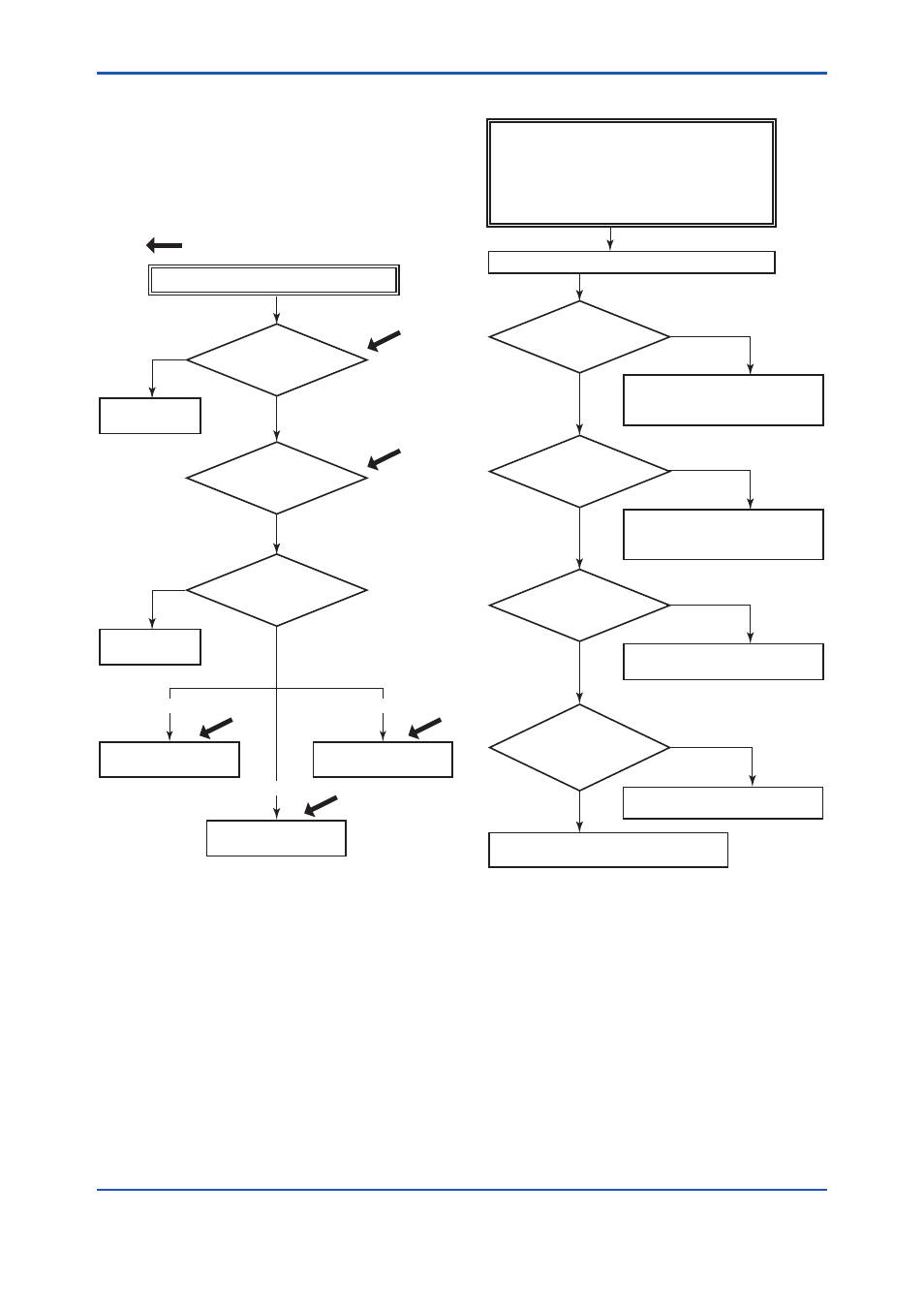
Abnormalities appear in measurement.
: Areas where self-diagnostic offers support
Is process variable
itself abnormal?
Inspect the
process system.
Isolate problem in
measurement system.
Does problem exist in
receiving instrument?
Check/correct
environmental conditions.
Inspect receiver.
Check transmitter.
Check/correct operating
conditions.
Measurement system problem
F0704.ai
YES
NO
NO
YES
Environmental conditions
Operating conditions
Transmitter itself
Figure 7.5 Basic Flow and Self-Diagnostics
7.5.2 Troubleshooting Flowcharts
Connect communicator and check self-diagnostics.
Does the self-diagnostic
indicate problem location?
Contact Yokogawa service personnel.
F0705.ai
The following sorts of symptoms indicate that the
transmitter may not be operating properly.
Example : • There is no output signal.
• Output signal does not change even though
process variable is known to be varying.
• Output value is inconsistent with value
inferred for process variable.
Is power supply
polarity correct?
Are power
supply voltage and load
resistance correct?
Refer to Section 5.3 to check/correct
polarity at each terminal from power
supply to the terminal box.
Refer to Section 5.6 for rated voltage
and load resistance.
Find/correct broken conductor or
wiring error.
Is there
continuity through the
transmitter loop wiring?
Do the loop numbers
match?
YES
NO
NO
YES
NO
YES
NO
YES
Refer to error message summary in
Subsection 7.5.3 or in each
communication manual to take actions.
