Appendix – System Sensor FAAST Networking User Manual
Page 38
User Guide: FAAST Fire Alarm Aspiration Sensing Technology® Networking
38
Appendix
Glossary
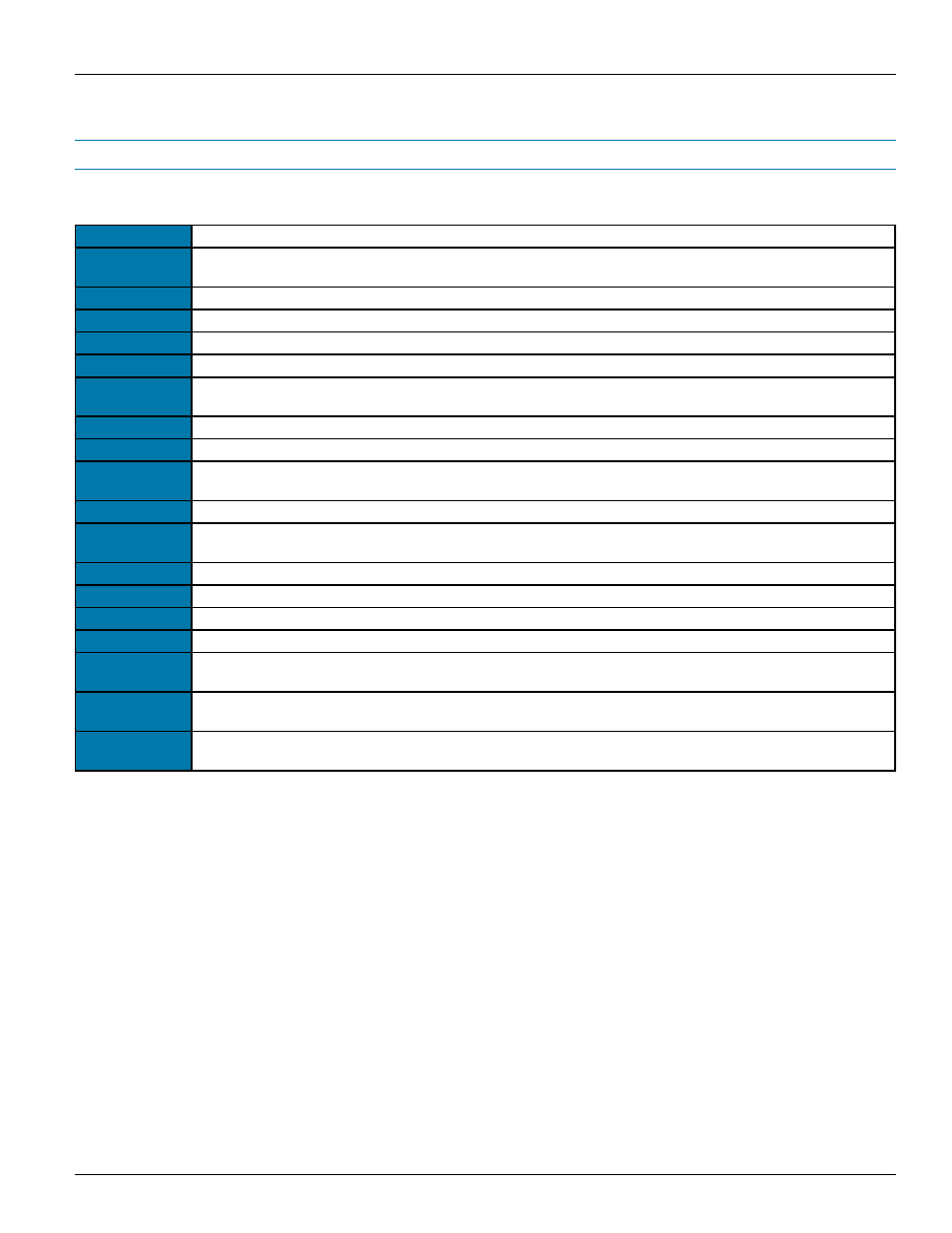
Authentication
A process to confirm the identity of an individual, often using a password
DHCP
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol - A network protocol for automatically assigning IP addresses to host
devices
DNS
Domain Name System - A hierarchal system of naming networks and devices on the Internet
Domain
A name that uniquely identifies a network and a sphere of administrative authority
Ethernet
A collection of wired local area network technologies
FAAST
Fire Alarm Aspiration Sensing Technology
FQDN
Fully Qualified Domain Name - The concatenation of a hostname and domain name with a period such as:
hostname.domain.com
Hostname
A human-readable label assigned to a device on a network and mapped to an IP address
IT
Information Technology
IP Address
A 32-bit number assigned to each device in an IP network – usually represented as four decimal numbers
such as: 192.168.1.10
LAN
Local Area Network
MAC Address
Media Access Control Address - A unique address assigned to every Ethernet interface by the device manu-
facturer.
NetBIOS
An alternative name resolution system found on Microsoft Windows networks
PipeIQ
A desktop software application for managing aspiration smoke detectors
SMTP
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol - A protocol used by clients and servers to transmit e-mail messages
SMTP Client
A device that connects to a mail server in order to send e-mail messages
SMTP Server
A computer that accepts incoming e-mail messages from clients and delivers them to other e-mail servers or
e-mail recipients
TCP/IP
Transport Control Protocol / Internet Protocol - A common suite of addressing and routing protocols used on
the Internet
TLS/SSL
Transport Layer Security/Secure Sockets Layer - Protocols that use encryption to provide secure communica-
tions over the Internet
