Exact method – PASCO ME-6831 Ballistic Pendulum_Projectile Launcher User Manual
Page 11
®
M o d e l N o . M E - 6 8 3 0 , M E - 6 8 3 1
B a l l i s t i c P e n d u l u m T h e o r y
0 1 2 - 0 5 3 7 5 C
7
This momentum equal to the momentum of the ball just before the collision:
Setting these two equations equal to each other and replacing KE with our known potential energy gives:
Solve this for the ball’s velocity and simplify to get:
Exact Method
The potential energy is found in a way identical to the way
shown previously:
For the kinetic energy, you can use the equation for angular
kinetic energy instead of linear kinetic energy, and substitute
into it the equation for angular momentum:
where I is the moment of inertia of the pendulum/ball combination, and
is the angular velocity immediately after
the collision.
As you did previously, solve this last equation for angular momentum:
This angular momentum is equal to the angular momentum of the ball before the collision, as measured from the
pendulum pivot point:
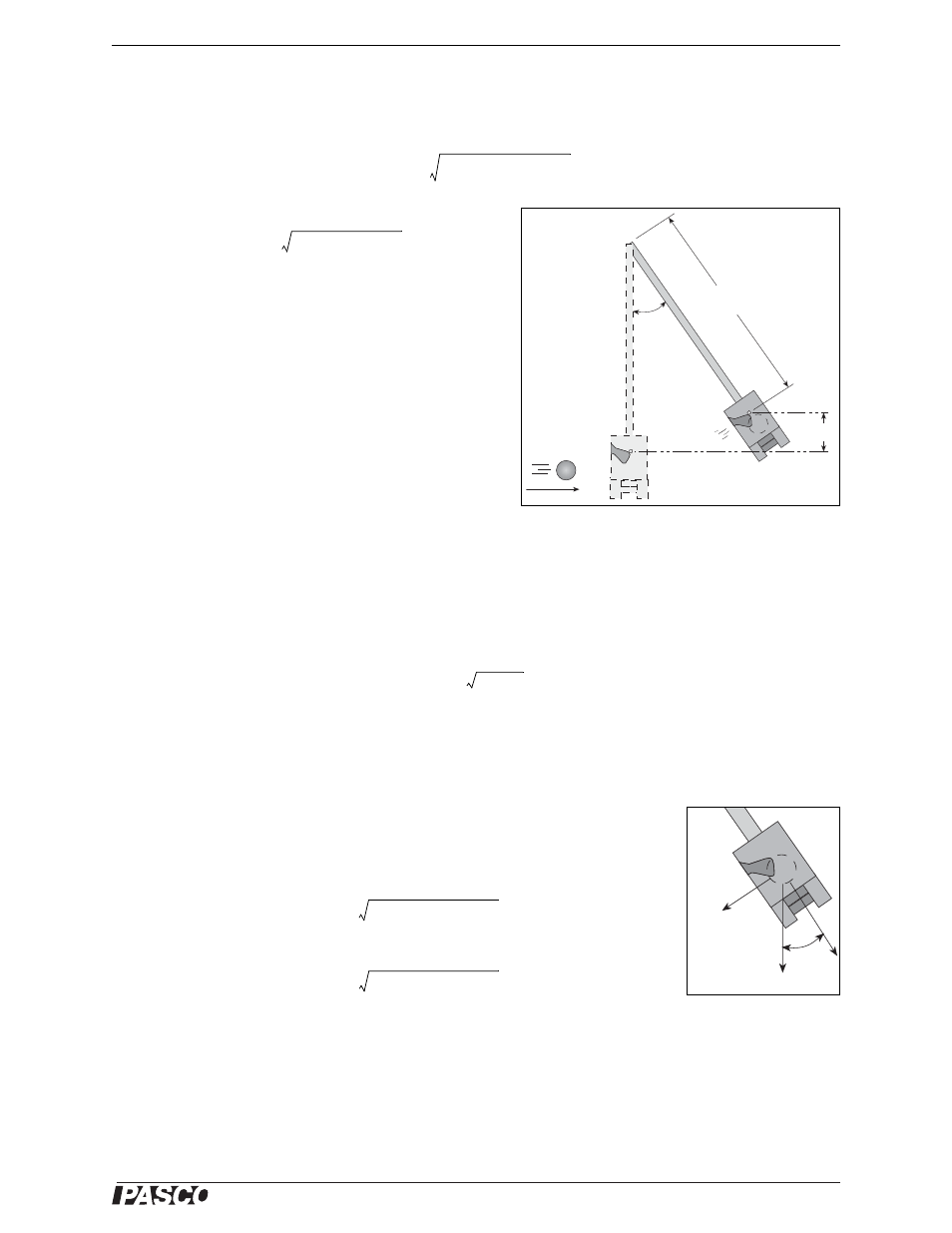
where R
b
is the distance from the pendulum pivot to the ball. (NOTE: This radius is not in
general equal to R
cm
, which is the distance from the pivot point to the center of mass for
the pendulum/ball system.)
These two angular momenta are equal to each other, so:
Solve for v:
Now you need to find I, the moment of inertia of the pendulum and ball. To do this, start with the rotational equiv-
alent of Newton’s Second Law:
where
is torque, I is moment of inertia, and is angular acceleration. The force on the center of mass of the pen-
dulum is Mg, and the component of force directed towards the center of the pendulum swing is F = -Mg sin
See
Figure 2.)
P
b
mv
b
=
mv
b
2M
2
gR
cm
1
cos
–
=
R
cm
cm
cm
h
cm
m
v
Figure 1
v
b
M
m
----- 2gR
cm
1
cos
–
=
PE
MgR
cm
1
cos
–
=
KE
1
2
---I
2
=
L
p
I
=
KE
L
p
2
2I
--------
=
L
p
2I KE
=
L
p
mR
b
2
mR
b
v
=
=
-Mg sin
-Mg
Figure 2
mR
b
v
2IMgR
cm
1
cos
–
=
v
1
mR
b
---------- 2IMgR
cm
1
cos
–
=
I
=
