Applications, Advantages of wt1800, N harmonic distortion factor – Atec Yokogawa-WT1800 User Manual
Page 8: Measurement, N immediately print out screens, N tube current measurements of fluorescent lamps
Advantages of WT1800
Applications
Applications
Applications
Product Featur
es
Functions/Displays
Applications
Softw
ar
e
Comparisons
Explanations
Specifications
n Ripple factor and power loss measurements using
user-defined function
A user-defined function makes it possible to compute not only the conversion efficiency but
also the power loss, DC voltage and DC current ripple factors between the input and output.
This is helpful in multiplying a factor or slightly changing the arithmetic expression according
to the purpose. Up to 20 arithmetic expressions can be set. Display names for the arithmetic
operations F1, F2, and so on can be changed freely.
Voltage fluctuations and harmonic flow into the power system
due to reverse power flow. A harmonic measurement function
makes it possible to compute and display the harmonic distortion
factor (THD) by measuring harmonic components.
Multiple engineers may want to verify detailed data during a test.
A built-in printer makes it possible to print data immediately on
the spot and for multiple engineers to verify the data
simultaneously.
s
n Harmonic distortion factor
(THD)
measurement
(/G5 and /G6 options)
n Immediately print out screens
(/B5 option)
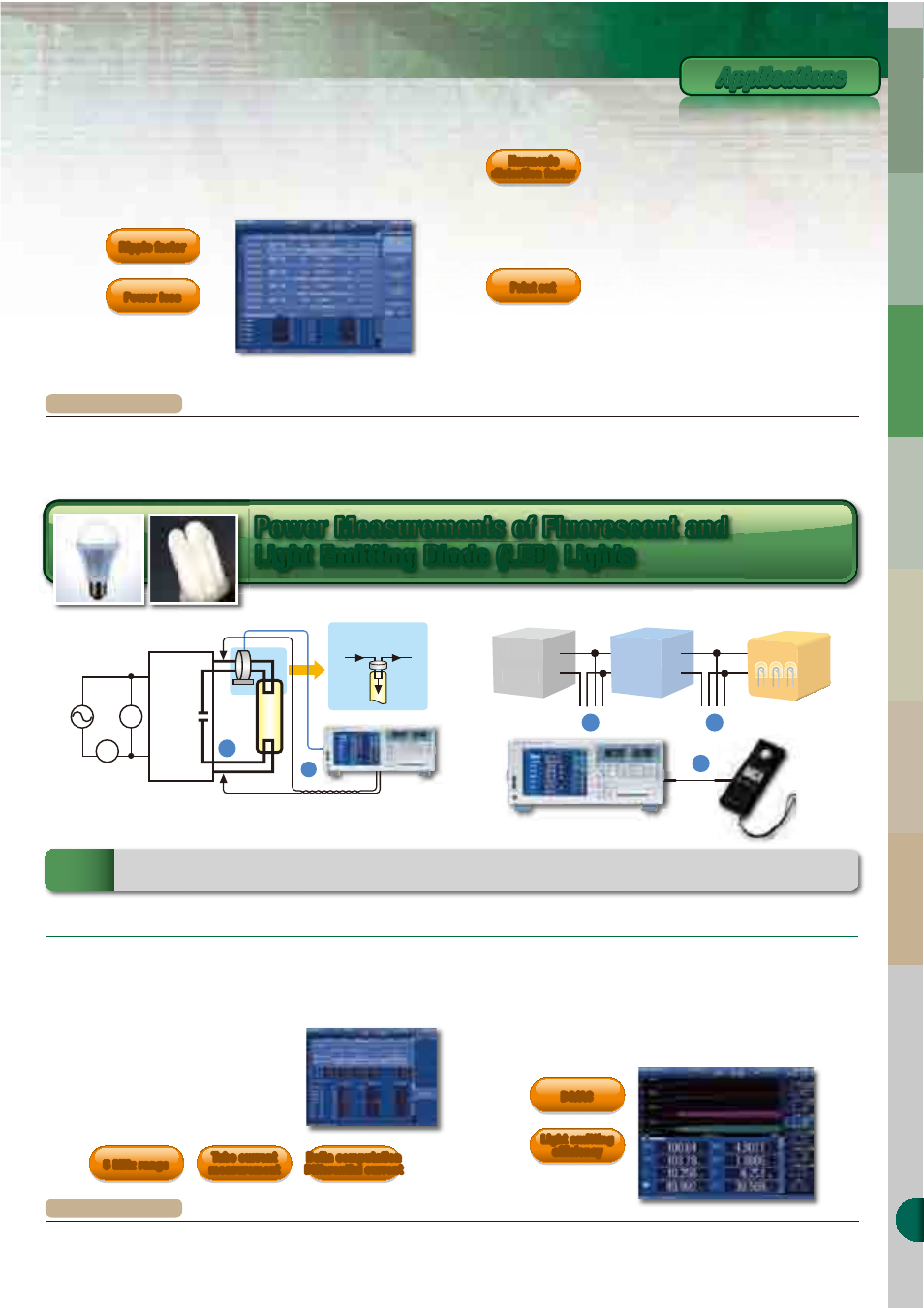
Ballast
Connected by general
power wire connection
on the primary side
I1
I1
I2
I2
Twisted wire for voltage measurement
Lamp current = I1−I2
LED
* Be careful of the current range. Since the current value is
generally small, use the 5A input element (in the 10 mA to 5 A range).
n Light emitting efficiency and power measurements
of LED lights
(/AUX option)
n Tube current measurements of fluorescent lamps
(/DT option)
A ballast uses harmonic frequency signals to illuminate the fluorescent lamp.
The frequency is generally as fast as tens of kHz. A wide range capability of
power measurement is important to reliably
capture the signals. Also, since tube current
cannot be measured directly, it is obtained either
by measuring the difference between the output
current of the ballast and the cathode current
using a current sensor, or by using the delta
computation of the WT1800 (/DT option).
It is important for LED lights to increase the light emitting efficiency while at the
same time reducing the current and power consumption.
The WT1800 allows you to measure voltage, current, and power, as well as
compute the light emitting efficiency (lamp efficiency) by connecting the output
of an illuminance meter, etc. to the external signal input terminal (/AUX option).
Note: Tube current is obtained by the computation of a difference in the
instantaneous values instead of the effective current values.
A
1
2
A
I
U
* Lamp current can be obtained either by measuring the output of a wide range current sensor as shown in the
figure, or by obtaining the differential current using computation (delta computation function).
AC pow
wer
supply
Switching
regulato
or
ak value ( ))/2
DC voltage value (mean)]
10
Power Measurements of Fluorescent and
Light Emitting Diode (LED) Lights
Power Measurements of Fluorescent and
Light Emitting Diode (LED) Lights
*Also refer to the features of other applications.
*Also refer to the features of other applications
1
.
minance
um
Ill
ter
et
m
Overview
Since the switching frequency of fluorescent lamp is sometimes as fast as approximately tens of kHz, a wide range power measurement is required. Also, sometimes dimming control
by a PWM modulation circuit is performed for the LED lights. The WT1800 provides a wide range from DC to up to 5 MHz to allow you to evaluate these kinds of harmonic signals.
Example of fluorescent lamp
orescent lamp
Example of fluo
oresce
wire connection
* An external input terminal (EX) allows you to perform both direct input measurement and clamp measurement.
Harmonic
distortion factor
Harmonic
distortion factor
Tube current
measurement
Tube current
measurement
Light emitting
efficiency
Light emitting
efficiency
Delta computation
Differential current
Delta computation
Differential current
Ripple factor
Ripple factor
Power loss
Power loss
5 MHz range
5 MHz range
DC/AC
DC/AC
Print out
Print out
*For detailed specifications, see the page on the specifications. You need to provide a cable for voltage measurements when wiring.
Direct input measurements at less than 50 A: WT1806-06-F-HE/EX6/B5/G6/AUX
6 power inputs, current measurement range 10 mA to 55 A, or clamp measurement (with clamp input terminals), built-in printer, dual harmonic, auxiliary input
Measurement at more than 50 A using a current sensor: WT1806-60-F-HE/EX6/B5/G6/AUX
6 power inputs, current measurement range 100 μA to 5.5 A (measure AC/DC current sensor output), external current sensor input (for clamp measurement), built-in printer, dual harmonic, external signal input
*Direct input and current sensor input cannot be connected simultaneously.
Typical Product Configuration
*For detailed specifications, see the page on the specifications. You need to provide a cable for voltage measurements when wiring.
WT1806-06-H-HE/EX6/G6/DT/DA: 6 power inputs, current input range 10 mA to 55 A, or clamp measurement (with a clamp input terminal), dual harmonic, delta computation (differential current
measurement), DA output
*Direct input and current sensor input cannot be connected simultaneously.
Typical Product Configuration
9
