2 sensor, 4 start sequence – Rainbow Electronics AT77C102B User Manual
Page 11
11
5364A–BIOM–09/05
AT77C102B
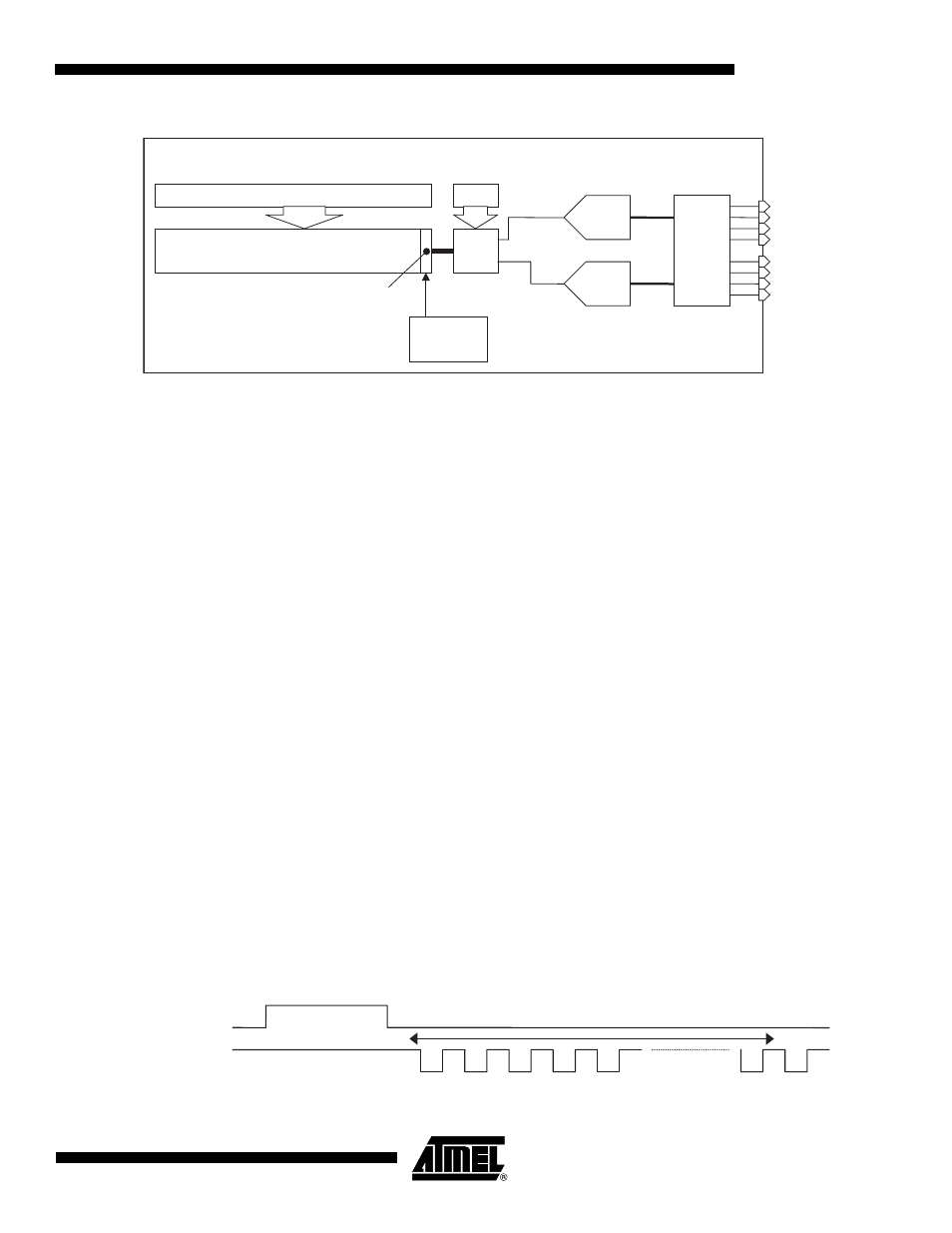
Figure 3-6.
Functional Description
3.2
Sensor
Each pixel is a sensor in itself. The sensor detects a temperature difference between the begin-
ning of an acquisition and the reading of the information: this is the integration time. The
integration time begins with a reset of the pixel to a predefined initial state. Note that the integra-
tion time reset has nothing to do with the reset of the digital section.
Then, at a rate depending on the sensitivity of the pyroelectric layer, on the temperature varia-
tion between the reset and the end of the integration time, and for the duration of the integration
time, electrical charges are generated at the pixel level.
3.3
Analog-to-digital Converter/ Reconstructing an 8-bit Fingerprint Image
An analog-to-digital converter (ADC) is used to convert the analog signal coming from the pixel
into digital data that can be used by a processor.
As the data rate for the parallel port and the USB is in the range of 1 MB per second, and at least
a rate of 500 frames per second is needed to reconstruct the image with a fair sweeping speed
of the finger, two 4-bit ADCs have been used to output two pixels at a time on one byte.
3.4
Start Sequence
A reset is not necessary between each frame acquisition.
The start sequence must consist in:
1.
Setting the RST pin to high.
2.
Setting the RST pin to low.
3.
Sending 4 clock pulses (due to pipe-line).
4.
Sending clock pulses to skip the first frame.
Note that after a reset it is recommended to skip the first 200 slices to stabilize the acquisition.
Figure 3-7.
Start Sequence
8
latches
Chip
temperature
sensor
Column selection
Line sel
Odd
Even
8 lines of 280 columns of pixels
4-bit
ADC
ADC
8
1 dummy column
4
4
Amp
De0-3
Do0-3
1
2
3
4
4-bit
1
4
3
1
2
1
1124
Clock PCLK
Reset RST
4 + 1124 clock pulses to skip the first frame
