3 signal extraction tab, 1 extraction example – Soft dB Opus Suite Data Logger Module User Manual
Page 47
46
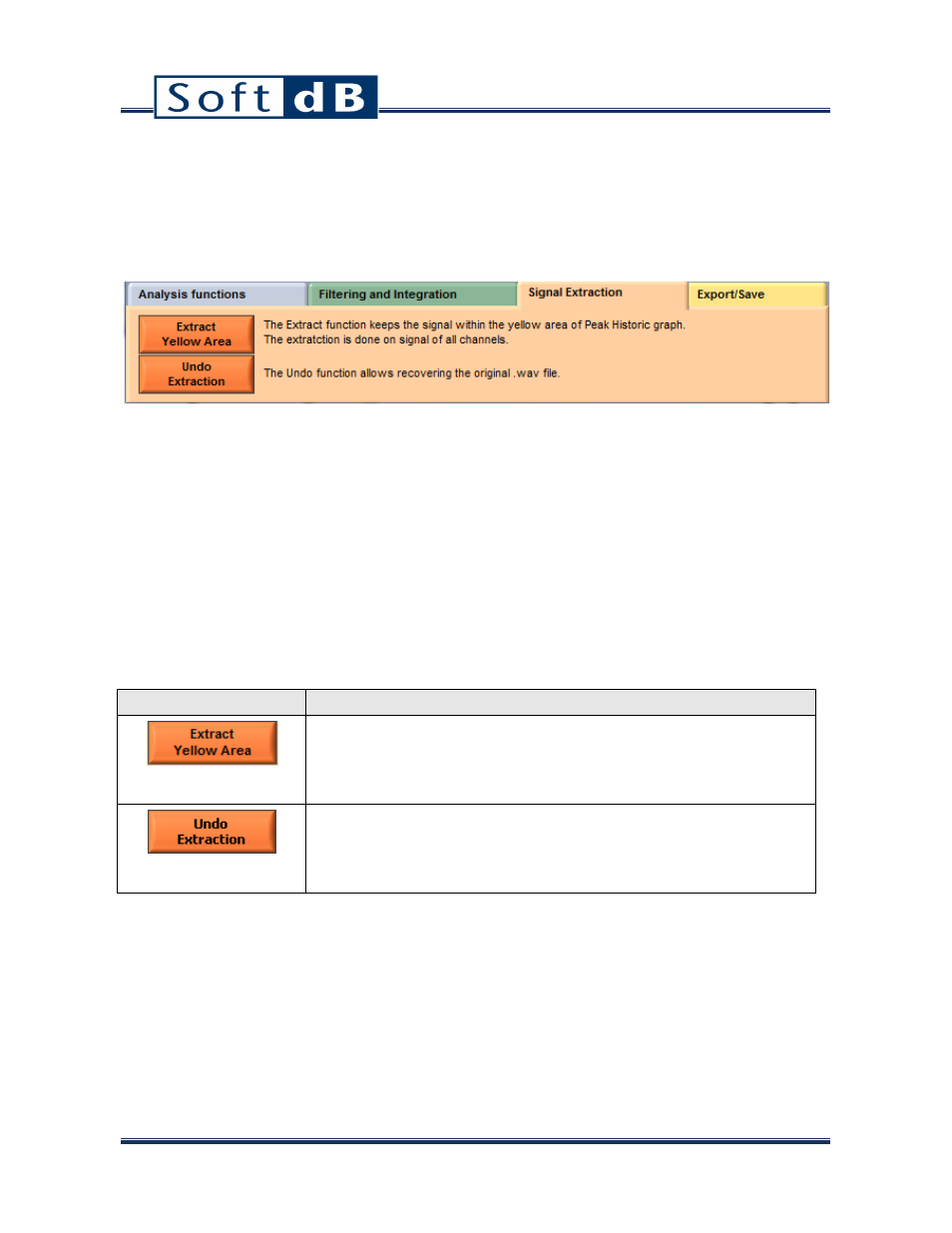
9.3 Signal Extraction Tab
The signal extraction tab includes a function for extracting a portion of the signal. This feature is very
useful for analyzing a portion of the wave file and for removing the beginning of a wave file after a
filtering operation. Also, a saturated portion of the signal can be excluded for better analysis.
The extraction can be cancelled at any time, and the entire framework of the original wave file will
be recovered. The extraction technique is based on the use of file pointers. This means that the start
and end-points of the selected framework are sample numbers in the wave file. This way, the original
wave file is never changed and an Undo operation is always available.
When an extraction has been done using the Extract Yellow Area function, all functions and modules
of the post-processing interface will work with the new start and end-points of the framework. The
save .wav function will also take into account the starting point and the ending points. After saving
for instance, the new wave file will contain only the selected portion of the signal of the original
wave file.
Here is the detail of the extraction functions:
Functions
Description
This function changes the start and end-points of the framework
following the yellow area on the peak value. The start and end points
are changed for all channels. Use the Undo Extraction function to
cancel the extraction.
This function cancels the extraction(s) and resets the start point to
zero and the end point to the end of the wave file. For multiple
extractions, the undo operation always retrieves the entire wave file
signal and not the preceding selection.
9.3.1
Extraction example
The objective of this example is to keep the signal between time 00:03:50 and 00:06:00. First, the
blue and green cursors are moved to the desired start and end-points:
