5 rapid spanning tree protocol status – ZyXEL Communications GS-2750 User Manual
Page 113
Chapter 11 Spanning Tree Protocol
GS-2750 User’s Guide
113
11.5 Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol Status
Click Advanced Application > Spanning Tree Protocol in the navigation panel to display
the status screen as shown next. See
for more information on RSTP.
"
This screen is only available after you activate RSTP on the Switch.
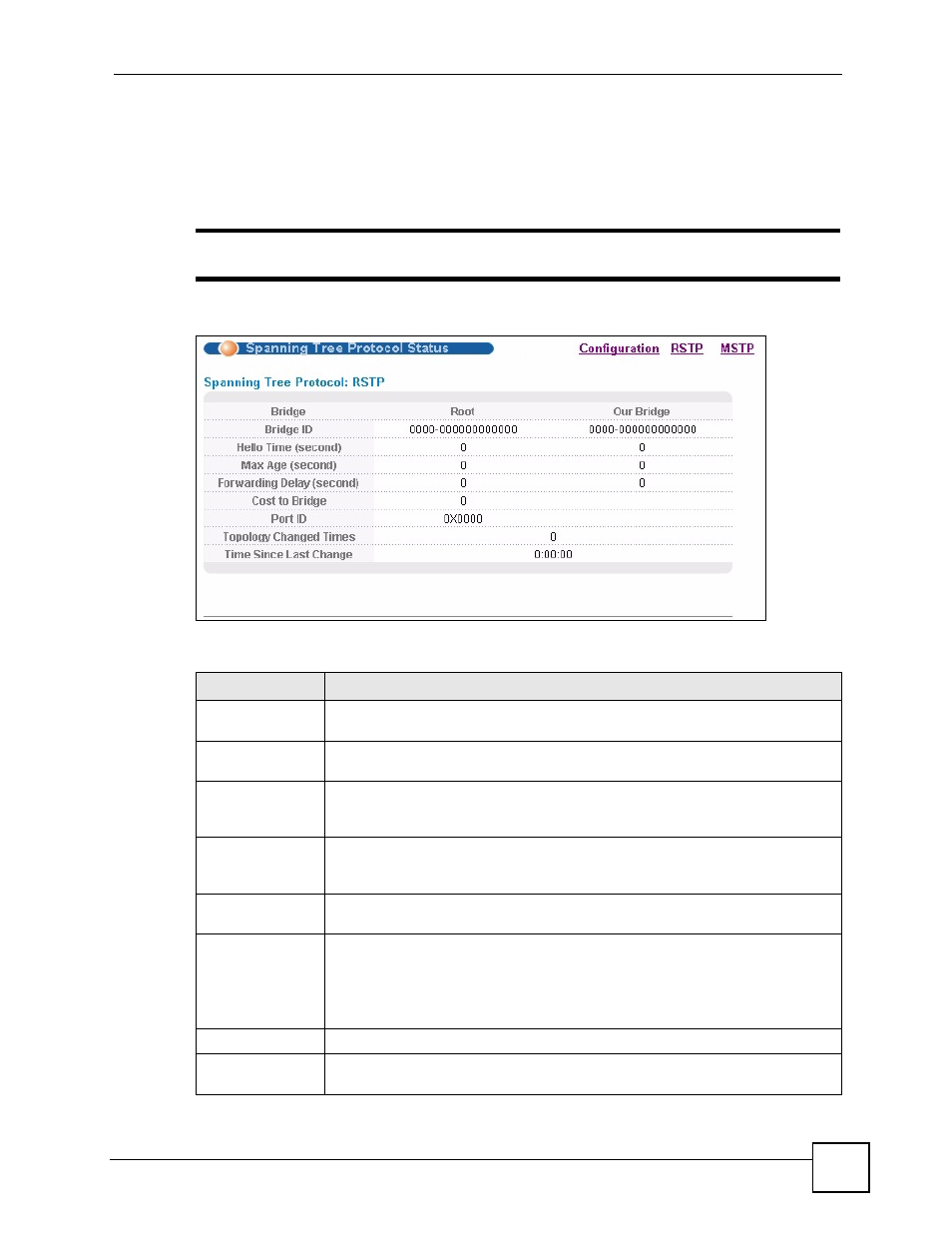
Figure 51 Advanced Application > Spanning Tree Protocol > Status: RSTP
The following table describes the labels in this screen.
Table 28 Advanced Application > Spanning Tree Protocol > Status: RSTP
LABEL
DESCRIPTION
Configuration
Click Configuration to specify which STP mode you want to activate. Click RSTP
to edit RSTP settings on the Switch.
Bridge
Root refers to the base of the spanning tree (the root bridge). Our Bridge is this
Switch. This Switch may also be the root bridge.
Bridge ID
This is the unique identifier for this bridge, consisting of the bridge priority plus the
MAC address. This ID is the same for Root and Our Bridge if the Switch is the
root switch.
Hello Time
(second)
This is the time interval (in seconds) at which the root switch transmits a
configuration message. The root bridge determines Hello Time, Max Age and
Forwarding Delay.
Max Age (second) This is the maximum time (in seconds) a switch can wait without receiving a
configuration message before attempting to reconfigure.
Forwarding Delay
(second)
This is the time (in seconds) the root switch will wait before changing states (that
is, listening to learning to forwarding). See
information on port states.
Note: The listening state does not exist in RSTP.
Cost to Bridge
This is the path cost from the root port on this Switch to the root switch.
Port ID
This is the priority and number of the port on the Switch through which this Switch
must communicate with the root of the Spanning Tree.
