Common-mode signal rejection considerations, Signal sources -12, Common-mode signal rejection considerations -12 – National Instruments NI PCI-6110 User Manual
Page 42
Chapter 4
Connecting Signals
4-12
ni.com
Differential Connections for Nonreferenced or
Floating Signal Sources
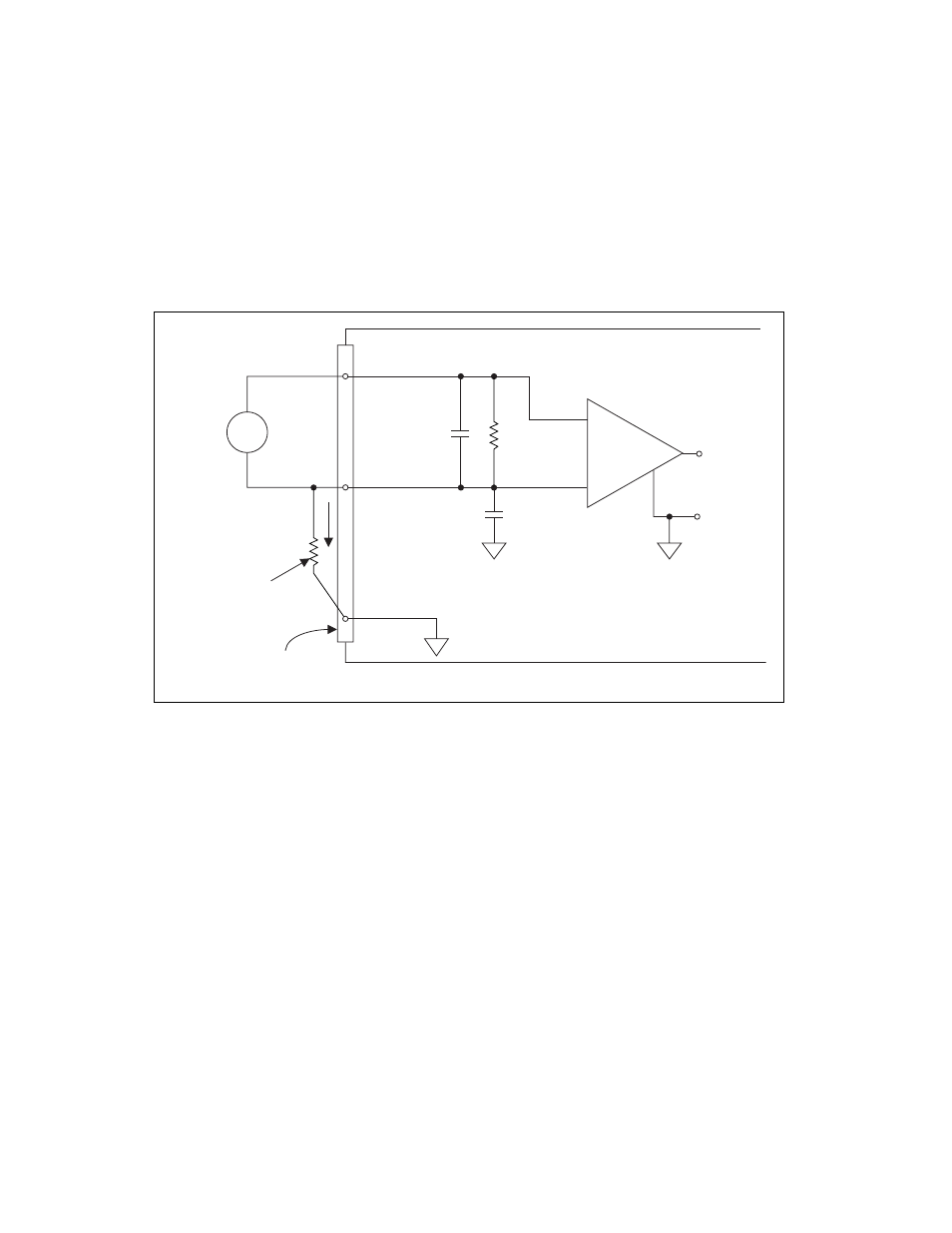
Figure 4-5 shows how to connect a floating signal source to a channel on
the NI PCI-6110/6111.
Figure 4-5. Differential Input Connections for Nonreferenced Signals
Figure 4-5 shows a bias resistor connected between ACH0– and the
floating signal source ground. If you do not use the resistor and the source
is truly floating, the source often floats outside the common-mode signal
range of the PGIA, and the PGIA saturates, causing erroneous readings.
You must reference the source to the respective channel ground.
Common-Mode Signal Rejection Considerations
Figure 4-4 shows connections for signal sources that are already referenced
to some ground point with respect to the NI PCI-6110/6111. In theory,
the PGIA can reject any voltage caused by ground-potential differences
between the signal source and the device. In addition, with
pseudodifferential input connections, the PGIA can reject common-mode
noise pickup in the leads connecting the signal sources to the device.
+
+
Floating
Signal
Source
Instrumentation
Amplifier
V
m
Measured
Voltage
I/O Connector
ACH0GND
Bias
Current
Return
Paths
ACH0–
ACH0+
ACH0 Connections Shown
PGIA
1M
Ω
100pf
10nf
Bias
Resistor
(see text)
V
s
–
+
–
–
