Raid 10 – LSI MegaRAID Enterprise 1600 User Manual
Page 36
MegaRAID Enterprise 1600 Hardware Guide
22
RAID 10
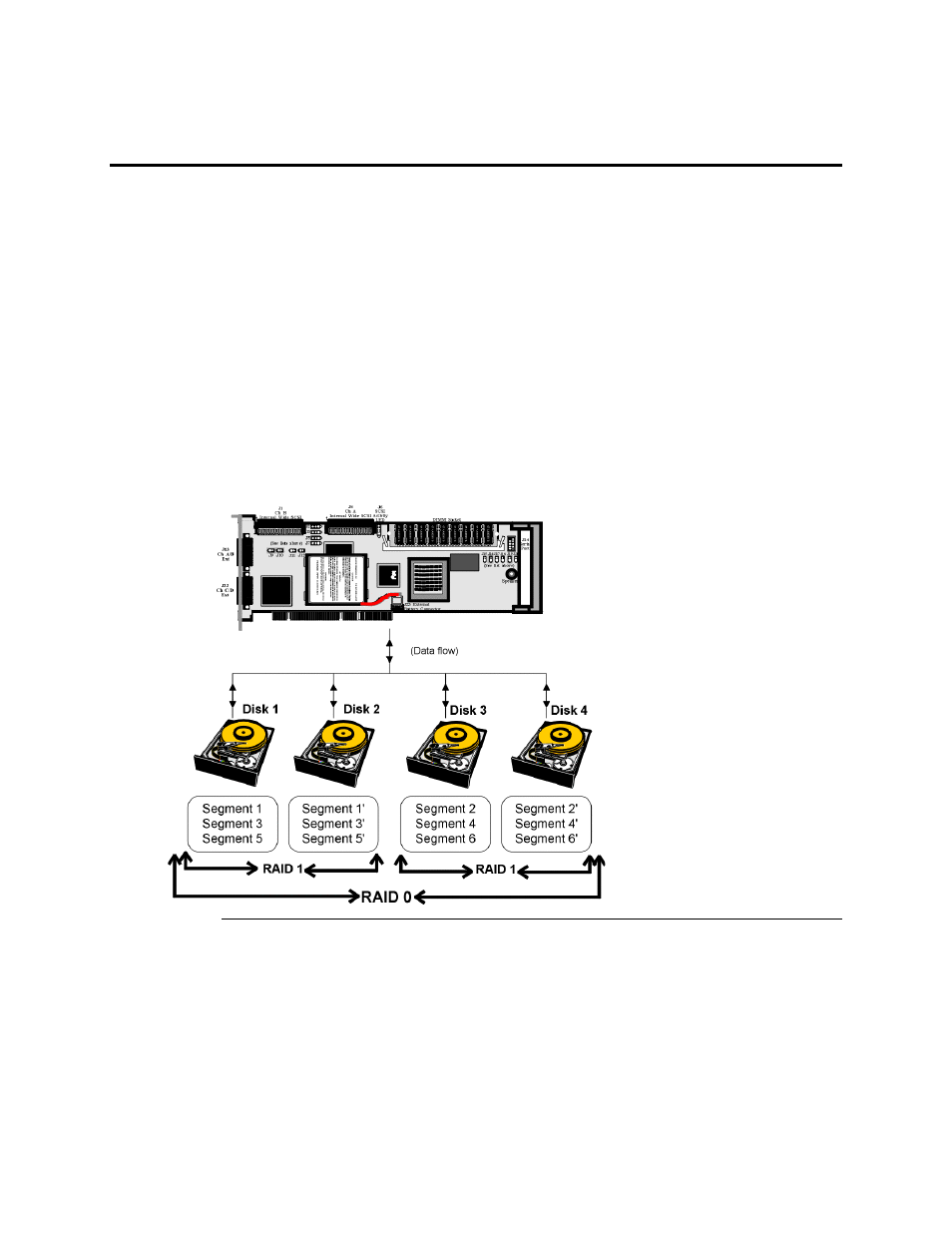
RAID 10 is a combination of RAID 0 and RAID 1. RAID 10 has mirrored drives. RAID 10 breaks
up data into smaller blocks, and then stripes the blocks of data to each RAID 1 raid set. Each
RAID 1 raid set then duplicates its data to its other drive. The size of each block is determined by
the stripe size parameter, which is set during the creation of the RAID set. RAID 10 can sustain
one to four drive failures while maintaining data integrity if each failed disk is in a different RAID
1 array.
Uses
RAID 10 works best for data storage that must have 100%
redundancy of mirrored arrays and that also needs the
enhanced I/O performance of RAID 0 (striped arrays).
RAID 10 works well for medium-sized databases or any
environment that requires a higher degree of fault tolerance
and moderate to medium capacity.
Strong Points
RAID 10 provides both high data transfer rates and
complete data redundancy.
Weak Points
RAID 10 requires twice as many drives as all other RAID
levels except RAID 1.
Drives
Four to 32 (must be a multiple of two)
