Woodstock SHOP FOX W1816 User Manual
Page 34
-32-
W1816 Owner's Manual (Mfg. Since 10/09)
O
PE
R
ATIO
NS
In most small/medium shops it is only necessary to
calculate the line with the longest duct length or the
most fittings (operating under the assumption that if the
line with the highest resistance works, the others will be
fine).
To calculate the static pressure of any given line in the
system, do these steps:
1. Make a list of each size duct in the line, including
the length, and multiply those numbers by the static
pressure value given in
Figure 46.
2. List each type of elbow or branch and multiply the
quantity (if more than one) by the static pressure
loss given in
Figure 46.
3. Add the additional factors from Figure 47 to your
list.
4. Total your list as shown in the example in Figure 48
to come up with your overall static pressure loss
number for that line.
Note: Always account for a seasoned filter, so you
don't end up with a system that only works right
when the filter is clean.
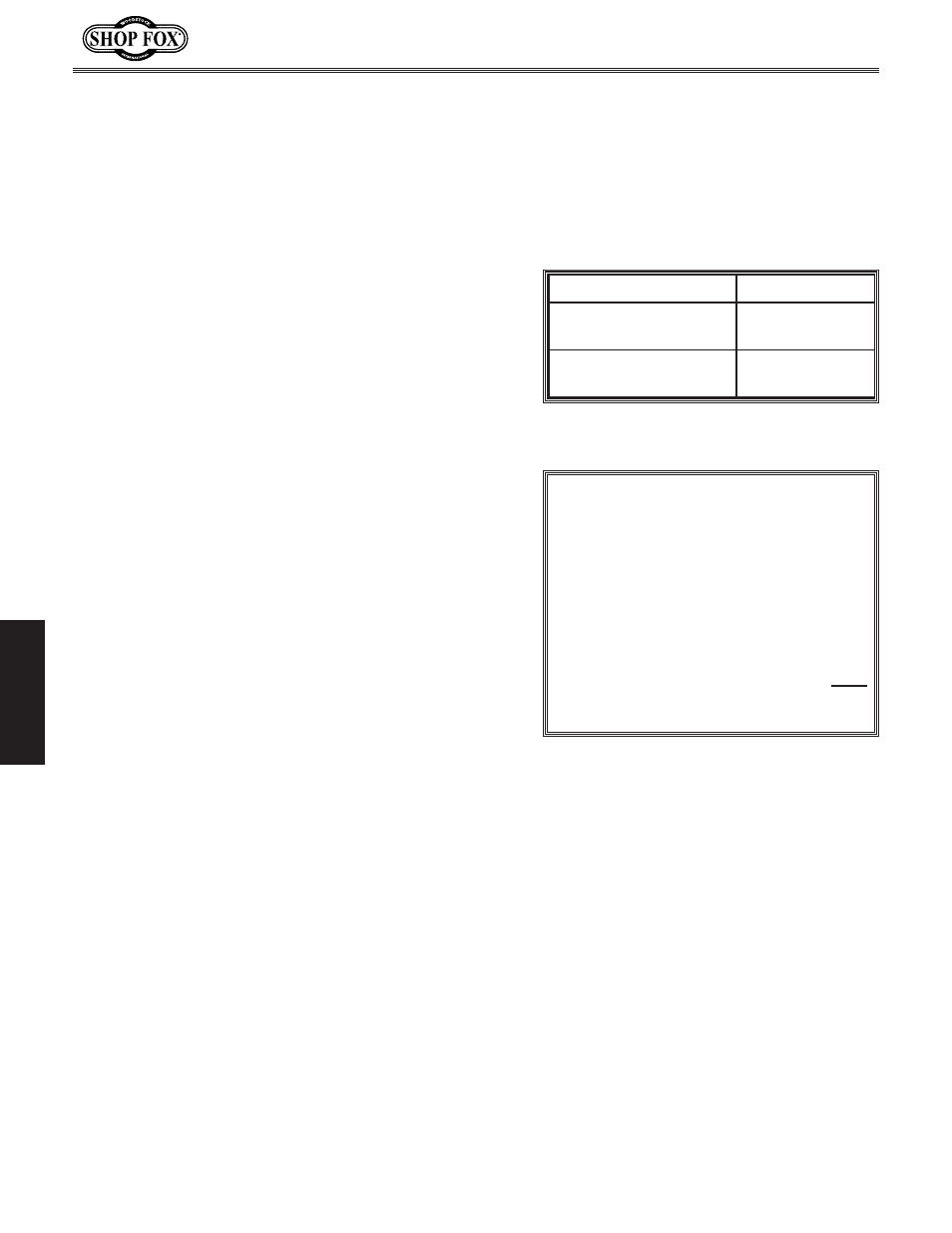
Additional Factors
Static Pressure
Seasoned (well used)
Dust Collection Filter
1"
Entry Loss at Large
Machine Hood
2"
Figure 47. Additional factors that affect
static pressure loss (airflow resistance).
Main Line
6" Rigid Pipe (0.037) at 20'................0.740
Branch Line
4" Rigid Pipe (0.075) at 10'................0.750
4" Flex Pipe (0.28) at 5'....................1.400
Elbows/Branches
6" 45˚ Y-Branch..............................0.329
4" 45˚ Elbow.................................0.225
Additional Factors
Seasoned Filter..............................1.000
Total Static Pressure Loss................4.444
Figure 48. Example of calculating the
total static pressure loss.
