6 generating a stop, 7 transmitting a slave address, Figure 8-4 . slave address format -5 – Maxim Integrated MAX31782 User Manual
Page 73: 6generatingastop, 7transmittingaslaveaddress
MaximIntegrated 8-5
MAX31782 User’s Guide
Revision 0; 8/11
When the I2CSTART bit is set to a 1, the I
2
C controller starts its timeout timer if enabled (I2CTO_M
≠ 0) . If the timer
expires before the START can be generated, t h e I
2
C timeout interrupt flag (I2CTOI) will be set and an interrupt
generated if enabled . If a timeout occurs, the I
2
C master controller will reset to an idle state and the I2CSTART bit will
be cleared .
If the I2CSTART bit is set when the I
2
C controller is in the middle of a byte transfer (after the first bit rising edge), the
controller will wait for the current byte transfer to finish (after the 9th bit) before generating the START condition . In this
case, the timeout timer will not start counting until after the end of the 9th bit low time .
8.1.6GeneratingaSTOP
To end an I
2
C transfer, a STOP must be transmit . A STOP is generated by setting the I2CSTOP bit . The master I
2
C
controller’s flow when attempting to issue a STOP command is shown in
If the I2CSTOP bit is set when the I
2
C controller is in the middle of a byte transfer (after the first bit rising edge), it will wait
for the current byte transfer to finish (after the 9th bit) before generating the STOP condition .
Because the SDA line is feedback into the device, when the master generates a STOP, it will also detect the STOP
condition . When a STOP condition is detected, the I
2
C STOP interrupt flag (I2CSPI) will be set and an interrupt will
be generated enabled . The I2CBUS bit will be cleared to indicate that the I
2
C bus is now idle and the I2CSTOP bit will
be cleared .
When the master I
2
C controller attempts to generate the STOP condition, it will also start the timeout timer if this feature
is enabled . If a timeout is generated before the STOP condition is detected, a timeout will occur . When a timeout occurs,
the I2CTOI bit will be set, which can generate an interrupt if enabled, and the I2CSTOP bit will also be cleared to 0 .
8.1.7TransmittingaSlaveAddress
The first byte after an I
2
C start or restart condition is the slave address byte . This byte, which is transmit by the master,
contains seven bits of slave address followed by the R/W bit . The transmission of the slave address begins with writing
the address to I2CBUF_M .
The slave address written to I2CBUF_M is a seven-bit address that does not contain the R/W bit .
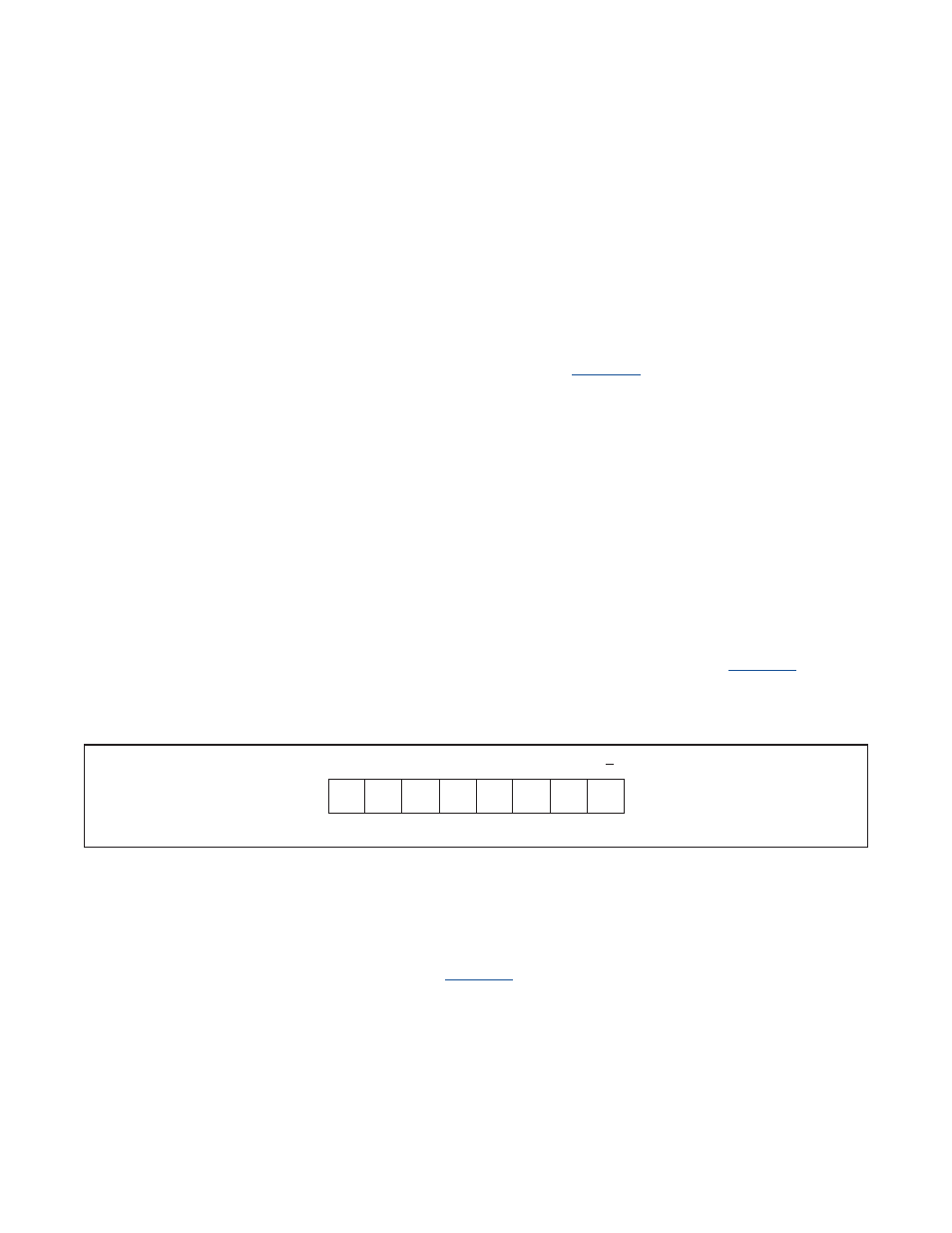
shows the
format for slave address 36h . The address bits A[6:0], which is the slave address excluding the R/W bit is written to
I2CBUF_M[6:0] . For example, to transmit slave address 36h, I2CBUF_M must be set to 1Bh . The I2CMODE bit will be
insert into the R/W bit when the slave address is transmit .
Figure 8-4. Slave Address Format
After the slave address has been written to I2CBUF_M, the I
2
C master controller will set the I2CBUSY bit to indicate the
controller is actively participating in a transaction . The seven bits in I2CBUF_M[6:0] will be transmit on SDA . The data
for the 8th bit transmit, which is the R/W bit, is the value of the I2CMODE bit . The I
2
C master then issues the 9th clock,
which is for the acknowledge bit, and reads SDA for an acknowledgment from a slave device . The I
2
C master controller
then performs the following steps . This is illustrated in
• Set the I2CNACKI bit with the value of the received acknowledgement .
• The I2CTXI bit will then be set to indicate a byte was transmit .
• Clear the I2CBUSY flag .
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
A6
A0
A1
A2
A3
A4
A5
R/W
SLAVE ADDRESS 36h SHOWN.
