Fig.3 fig.4 fig.5 – Sealey SM35CE User Manual
Page 3
4.3. HYDRAULIC FEED SELECTOR OPERATION.
4.3.1. The rate of descent of the main cutting arm is controlled by the
damping cylinder seen in fig.1. By turning the knob ‘F’ in fig.1
clockwise the rate of descent is slowed down. By turning the
knob anticlockwise the rate of descent is increased. The arm can
be locked in any position by turning the hydraulic flow off using
tap ‘G’ in fig.1. When the tap is at 90° to the cylinder the flow is
off and the arm will stop moving.
4.4. VICE SET UP & ADJUSTMENT.
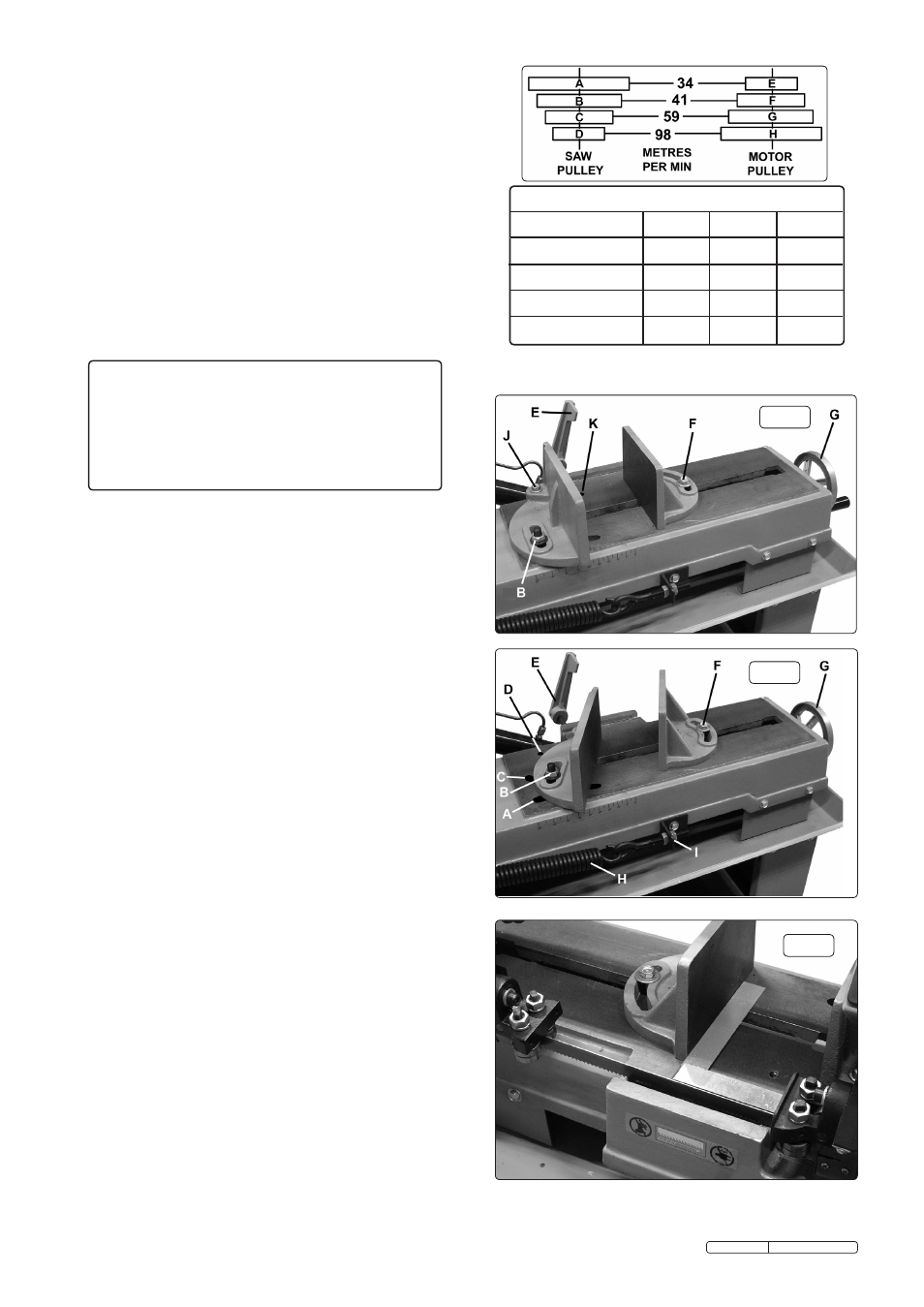
4.4.1. The vice has two adjustment positions. One specifically set at
90° degrees to the blade (see fig.3) and the other for variable
angle cutting (see fig.4).
4.4.2. For a non angled cut the vice should be set up as shown in fig.3.
Loosen pivot bolt ‘J’ and locking nut ‘B’ and adjust the vice face
to be 90° degrees to the blade by laying a set square onto the
machine bed as shown in fig.5. Tighten pivot bolt ‘J’ and locking
nut ‘B. When locking bolt ‘F’ is loosened the distance between
the vice faces can be adjusted by winding handle ‘G’. Adjust the
position of the stock stop ‘E’ as required. Lay the material to be
cut into the vice and wind handle ‘G’ until the material is firmly
clamped between the vice faces. Tighten locking bolt ‘F’.
4.4.3. To change the set up to an angled cut the vice should be
configured as shown in fig.4. Remove locking nut ‘B’ and its
associated bolt from straight slot ‘A’ and reassemble them into
the curved slot ‘C’. Referring back to fig.3 move the pivot bolt
‘J’ to position ‘K’ on the bed. The vice face will now pivot around
bolt ‘J’. Set the vice face to the desired angle using an adjustable
square and lock it at the set position with nut ‘B’ as shown in
fig.4. Lay the material to be cut into the vice and wind handle ‘G’
until the material is firmly clamped between the vice faces.
Tighten locking bolt ‘F’.
4.5. ADJUSTING BOW WEIGHT.
4.5.1. Bow weight is one of the most important adjustments on the saw.
Incorrect bow weight can result in poor performance including
crooked cuts, tooth stripping, stalling and the blade coming off the
blade wheels. The hydraulic feed rate unit will not compensate for
improper bow weight. Bow weight is factory set and should not
normally require adjustment. If performance problems are
encountered the bow weight can be adjusted as follows:
4.5.2. The bow weight spring, which acts on the main arm, can be seen
in fig.4.H as can the adjuster nuts fig.4.I
4.5.3. Disconnect the saw from the power supply.
4.5.4. Turn the hydraulic cylinder valve on and place the arm in the
horizontal position.Turn the feed rate valve on the cylinder
anticlockwise until it stops.
4.5.5. Hook a spring balance under the blade tension handle and lift the
saw arm. The scale should read 5-6kg. If this is not he case
adjust the tension until it does.
fig.3
fig.4
fig.5
Original Language Version
SM35CE.V4 Issue: 4 - 14/12/11
Recommended Pulley Selection for Various Metals
Material
Saw Pulley Motor Pulley Blade Speed
Tool, stainless or alloy steel.
Bearing bronze.
(A)
(E)
34m/min
Low carbon steel.
Medium carbon steel.
(B)
(F)
41m/min
Aluminium. Copper. Brass.
(C)
(D)
(G
)
(H
)
59m/min
98m/min
Recommended blade teeth per inch (tpi) for nominal cut length
Cut length Under 8mm
4-13mm
6-16mm
8-22mm
Tpi
32
24
18
14
Cut length 10-35mm
17-40mm
25-50mm
38-75mm
Tpi
10
8
6
4
Cut length 50-100mm 75-150mm 114-225mm >200mm
Tpi
3
2
1.25
0.75
Cutting Chart for Flat and Round Bar
4.2. CHANGING BLADE SPEED.
4.2.1. Disconnect the machine from the power supply.
4.2.2. Remove the pulley cover screw and hinge up the cover to access the
pulleys and belt.
4.2.3. Loosen the lock bolt on the rear of the motor plate as shown in
fig.2.3.
4.2.4. Loosen the locking nut on the tensioning screw as shown in fig.2.2.
4.2.5. Loosen the tensioning screw itself (see fig.2.1) and slacken it off in
order to allow the motor plate to move inwards to shorten the
distance between the two pulleys. It may be necessary to tap the
edge of the motor plate with a soft faced hammer to get the plate to
move inwards to the point where the belt position can be changed.
Refer to the adjacent diagrams to decide on the best position for
the belt for the job in hand.
4.2.6. When the belt is repositioned, retension it ensuring that it is not too
tight and tighten the motor plate lock bolt. Close the pulley cover
and replace the cover screw.
