Napt – H3C Technologies H3C SecPath F1000-E User Manual
Page 10
3
NAPT
Network Address Port Translation (NAPT) is a variation of basic NAT. It allows multiple internal addresses
to be mapped to the same public IP address, which is called multiple-to-one NAT or address
multiplexing.
NAPT mapping is based on both the IP address and the port number. With NAPT, packets from multiple
internal hosts are mapped to the same external IP address with different port numbers.
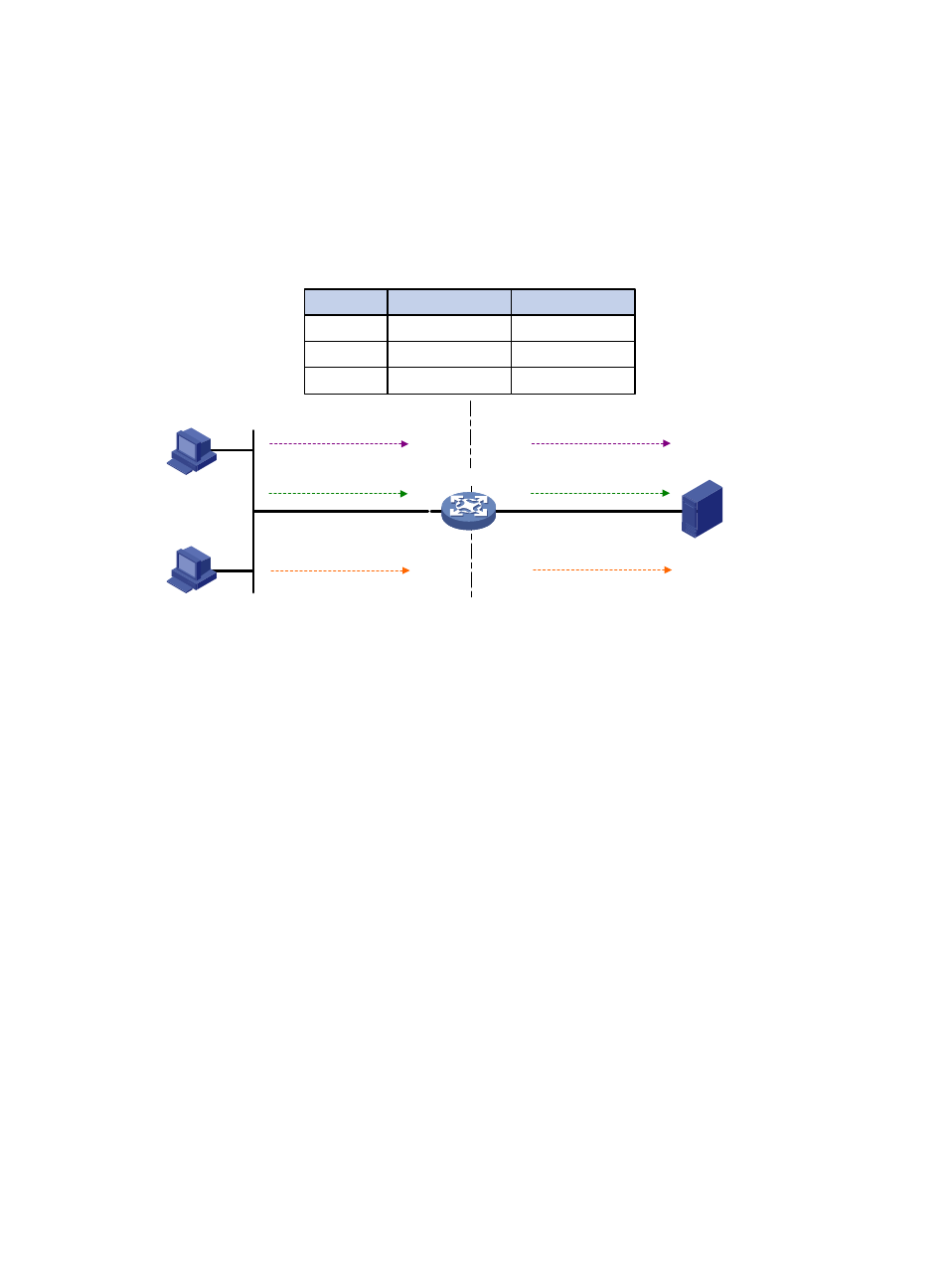
Figure 2 Diagram for NAPT operation
As shown in
, three IP packets arrive at the NAT device. Packets 1 and 2 are from the same
internal address but have different source port numbers. Packets 1 and 3 are from different internal
addresses but have the same source port number. NAPT maps the three IP packets to the same external
address but with different source port numbers. Therefore, the packets can still be differentiated. When
receiving the response packets, the NAT device forwards them to the corresponding hosts according to
the destination addresses and port numbers.
NAPT can better utilize IP address resources, enabling more internal hosts to access the external network
at the same time.
NAPT supports the following NAT mapping behavior modes:
•
Endpoint-Independent Mapping—In this mode, the NAT device uses entries, each of which
comprises the source IP address, source port number, and protocol type to translate addresses and
filter packets. The same NAPT mapping applies to packets sent from the same internal IP address
and port to any external IP address and port. The NAT device also allows external hosts to access
the internal network by using the translated external addresses and port numbers. This mode
facilitates communication among hosts that connect to different NAT devices.
•
Address and Port-Dependent Mapping—In this mode, the NAT device uses entries each comprising
the source IP address, source port number, protocol type, destination IP address, and destination
port number to translate addresses and filter packets. For packets with the same source address and
source port number but different destination addresses and destination port numbers, different
NAPT mappings apply so that the source address and port number are mapped to the same
external IP address but different port numbers. The NAT device allows the hosts only on the
corresponding external networks where these destination addresses reside to access the internal
network. This mode is secure but inconvenient for communication among hosts that connect to
different NAT devices.
192.168.1.1
20.1.1.1
1.1.1.2
Server
NAT
Intranet
Internet
192.168.1.2
Host A
192.168.1.3
Host B
Packet 1
Src : 192.168.1.2:1111
Packet 2
Src : 192.168.1.2:2222
Packet 3
Src : 192.168.1.3:1111
Packet 1
Src : 20.1.1.1:1001
Packet 2
Src : 20.1.1.1:1002
Packet 3
Src : 20.1.1.1:1003
Before NAT
192.168.1.2:1111
After NAT
20.1.1.1:1001
Direction
Outbound
192.168.1.2:2222
20.1.1.1:1002
Outbound
192.168.1.3:1111
20.1.1.1:1003
Outbound
