Layer 3 forwarding mechanisms, Figure 4, Two equal-co – H3C Technologies H3C S6800 Series Switches User Manual
Page 12
5
at RB 4 select the link. For more information about pseudonode IDs, see Layer 3—IP Routing
Configuration Guide.
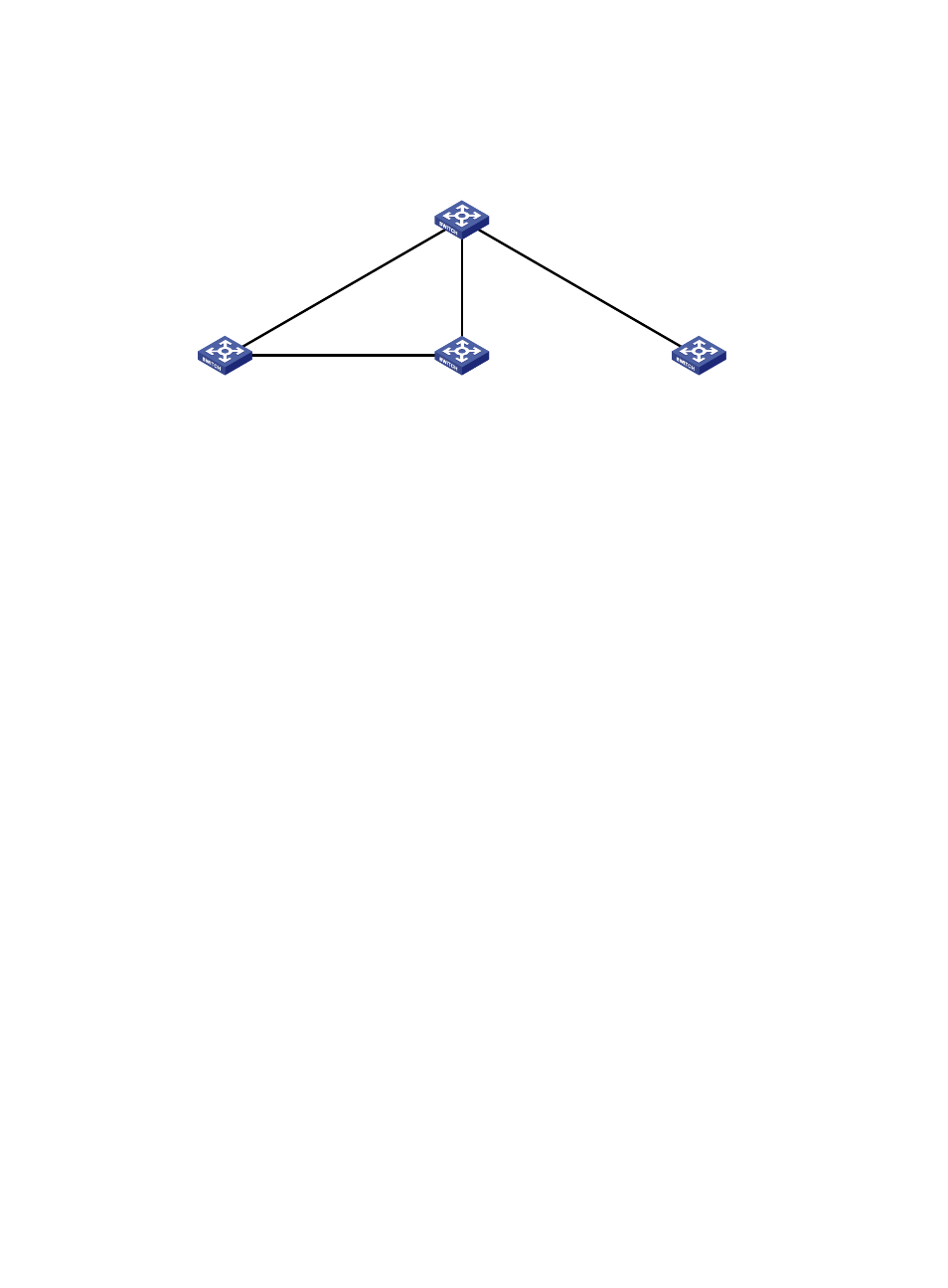
Figure 4 Multicast ECMP
TRILL distribution trees support Equal Cost Multiple Path (ECMP), also known as multicast ECMP.
When multicast ECMP is enabled, TRILL assigns equal-cost links to multiple TRILL distributions trees.
This improves the load sharing performance.
When N equal-cost links exist in the network, each TRILL distribution tree selects an equal-cost link
for forwarding packets through J mod N in root bridge priority order. J is the priority sequence
number of a TRILL distribution tree and starts from 0.
As shown in
{
The link directly connecting RB 1 to RB 3 is assigned to the TRILL distribution tree rooted at RB
3.
{
The link RB 1-RB 2-RB 3 is assigned to the TRILL distribution tree rooted at RB 4.
TRILL distribution trees support fast root switching. When an RB detects that the root of a
distribution tree is unreachable, the RB deletes the LSP of the root from its LSDB. This triggers
recalculation of all distribution trees in the TRILL network. Multidestination traffic is switched to new
distribution trees.
Layer 3 forwarding mechanisms
As shown in
, distribution layer devices RB 1 and RB 2 are gateways of a data center network.
Because of hardware limitations, RBs cannot perform Layer 3 forwarding before TRILL encapsulation or
after removing TRILL encapsulation.
To support Layer 3 forwarding, TRILL virtualizes the gateway RBs into a virtual router (VR). The VR
provides gateway services at a virtual IP address.
Co
st =
3
Cost = 2
Co
st
= 1
RB 1
RB 2
RB 3
RB 4
