1 buffered mode, Buffered mode, Figure 22: syncmanager buffer allocation – BECKHOFF EtherCAT Technology Section I User Manual
Page 62: Figure 23: syncmanager buffered mode interaction
SyncManager
I-42
Slave Controller
– Technology
8.1
Buffered Mode
The buffered mode allows writing and reading data simultaneously without interference. If the buffer is
written faster than it is read out, old data will be dropped. The buffered mode is also known as 3-
buffer-mode.
Physically, 3 buffers of identical size are used for buffered mode. The start address and size of the
first buffer is configured in the SyncManager configuration. The addresses of this buffer have to be
used by the master and the local application for reading/writing the data. Depending on the
SyncManager state, accesses to the first buffer
’s (0) address range are redirected to one of the 3
buffers. The memory used for buffers 1 and 2 cannot be used and should be taken into account for
configuring other SyncManagers.
One buffer of the three buffers is allocated to the producer (for writing), one buffer to the consumer (for
reading), and the third buffer keeps the last consistently written data of the producer.
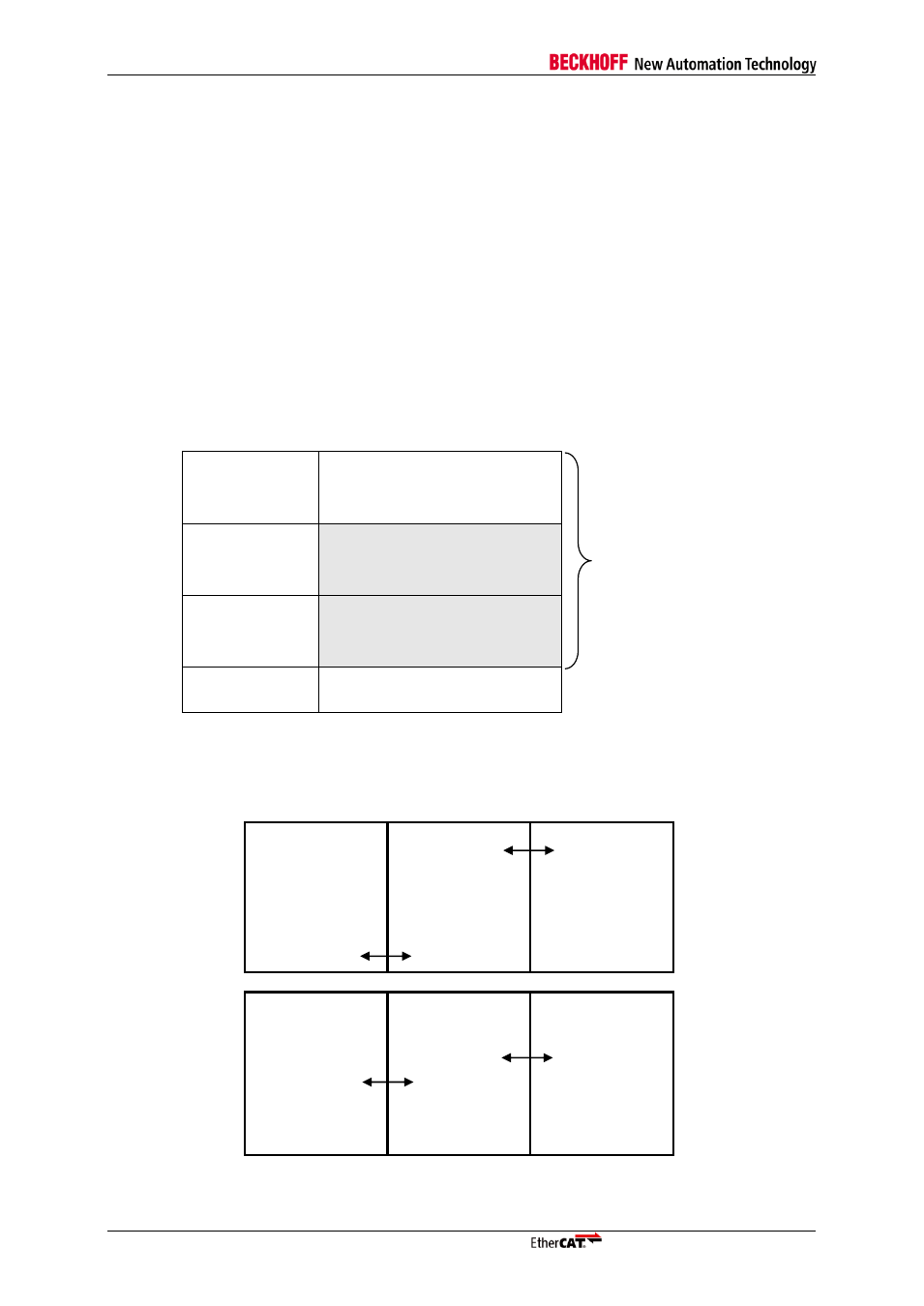
As an example, Figure 22 demonstrates a configuration with start address 0x1000 and Length 0x100.
The other buffers shall not be read or written. Access to the buffer is always directed to addresses in
the range of buffer 0.
0x1000
-
0x10FF
Buffer 0
(visible)
All buffers are
controlled by the
SyncManager.
Only buffer 0 is
configured by the
SyncManager and
addressed by
ECAT and
µController.
0x1100
-
0x11FF
Buffer 1
(invisible shall not be used)
0x1200
-
0x12FF
Buffer 2
(invisible shall not be used)
0x1300
…
Next usable RAM space
Figure 22: SyncManager Buffer allocation
The buffer interaction is shown in Figure 23:
Master
ECAT
NEXT
PDI
µController
Write begin
Load next buffer
if new data
available
Read begin
Write end
Exchange buffer
(if frame is ok)
Read end
Exchange buffer
Write begin
Write end
Read begin
Read end
Load next buffer
if new data
available
Figure 23: SyncManager Buffered Mode Interaction
