Amplifier – Waldorf Lector User Manual
Page 26
The Controls in Detail
Lector User´s Manual
26
Ringmod Level
0...100%
Volume of the ring modulation between Oscillator 1 and
2. From a technical point of view ring modulation is the
multiplication of two oscillators’ signals. The result of this
operation is a waveform that contains the sums and the
differences of the source frequency components. Since the
ring modulation generates disharmonic components, it
can be used to add metallic distorted sound
characteristics. This is useful e.g. when generating synth
percussion. Please note that in a complex waveform all
harmonic components behave like interacting sine waves,
resulting in a wide spectral range of the ring modulated
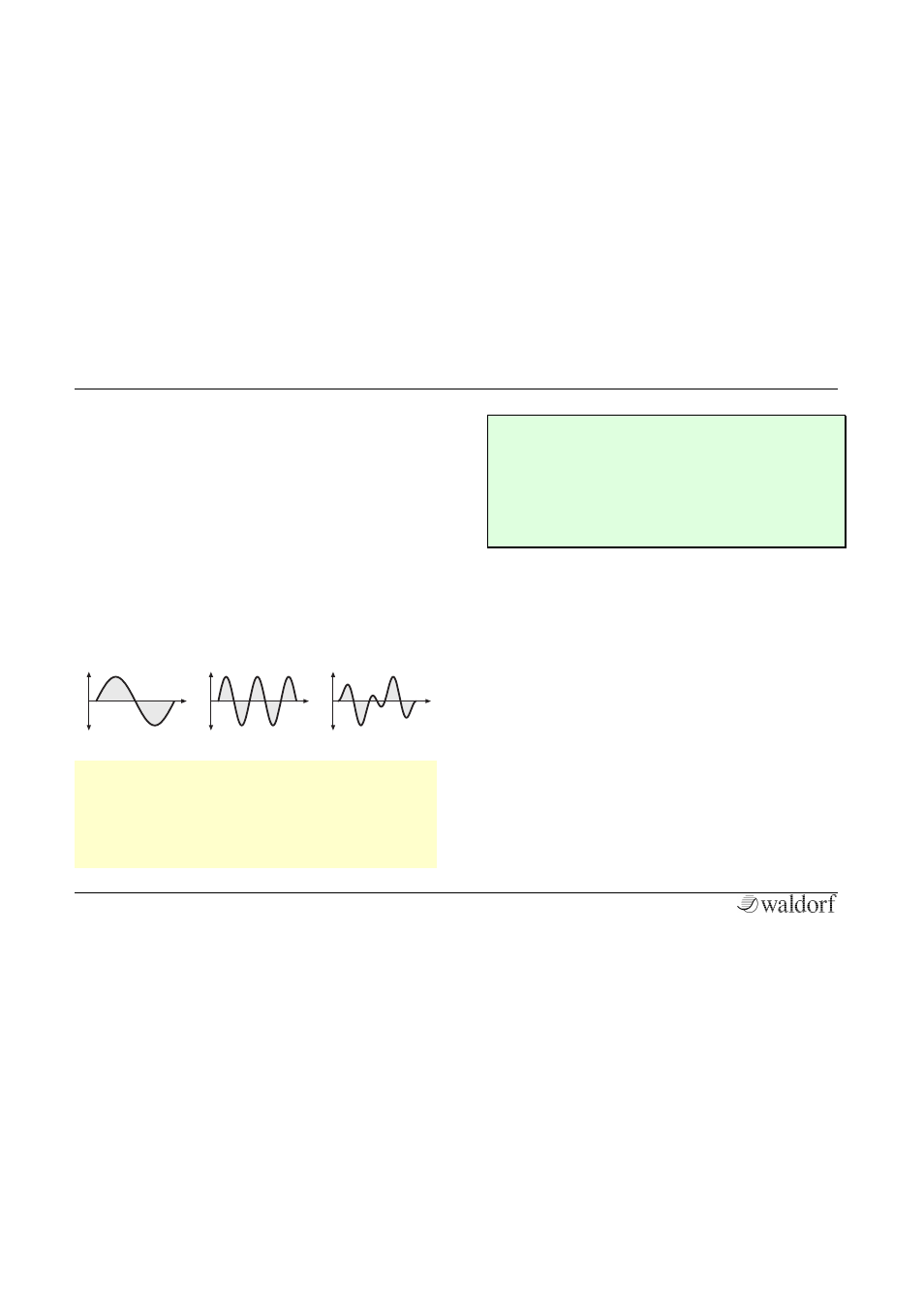
sound. The following pictures show the results of two
ringmodulated sine waves:
w
Ring Modulation can result in unwanted low
frequencies when the pitches of oscillator 1 and 2
don’t differ very much. This is logical because when
you use i.e. one oscillator set to 100 Hz and the
second set to 101 Hz, the resulting ring modulation is
201 Hz and 1 Hz.
✻
Ring Modulation can be very interesting when a
slow pitch modulation is applied to one oscillator.
This creates spacy effect sounds.
✻
If you turn down the pitch of one oscillator
markedly, you can get an effect very similar to
Amplitude modulation. Use this for sounds with a
periodic element if you wish.
Amplifier
Attack
0...60s
Determines the attack rate or amount of time it takes for
the signal volume to go from zero to maximum level.
Decay
0...60s
Determines the decay rate or amount of time it takes for
the signal volume to reach the sustain level.
Velocity
Off / On
-64…+63
Specifies if volume will be affected by keyboard velocity.
Use this feature to give more expression to the sound.
Trigger
Normal / Single / Latch
A Sine wave with frequency 1 ringmodulated with a Sine wave with
frequency 2.5 (1 octave + 4 semitones)
results in this wave
