Hanna Instruments HI 83208-2008 User Manual
Page 28
54
55
pH
pH
SPECIFICATIONS
Range
6.5 to 8.5 pH
Resolution
0.1 pH
Accuracy
±0.1 pH
Typical EMC
±0.1 pH
Deviation
Light Source
Tungsten lamp with narrow band interference filter @ 525 nm
Method
Adaptation of the Phenol Red method. The reaction with the reagent causes a yellow
to red tint in the sample.
REQUIRED REAGENTS
Code
Description
Quantity
HI 93710-0
Phenol Red Indicator
5 drops
REAGENT SETS
HI 93710-01 Reagents for 100 pH tests
HI 93710-03 Reagents for 300 pH tests
For other accessories see page 73.
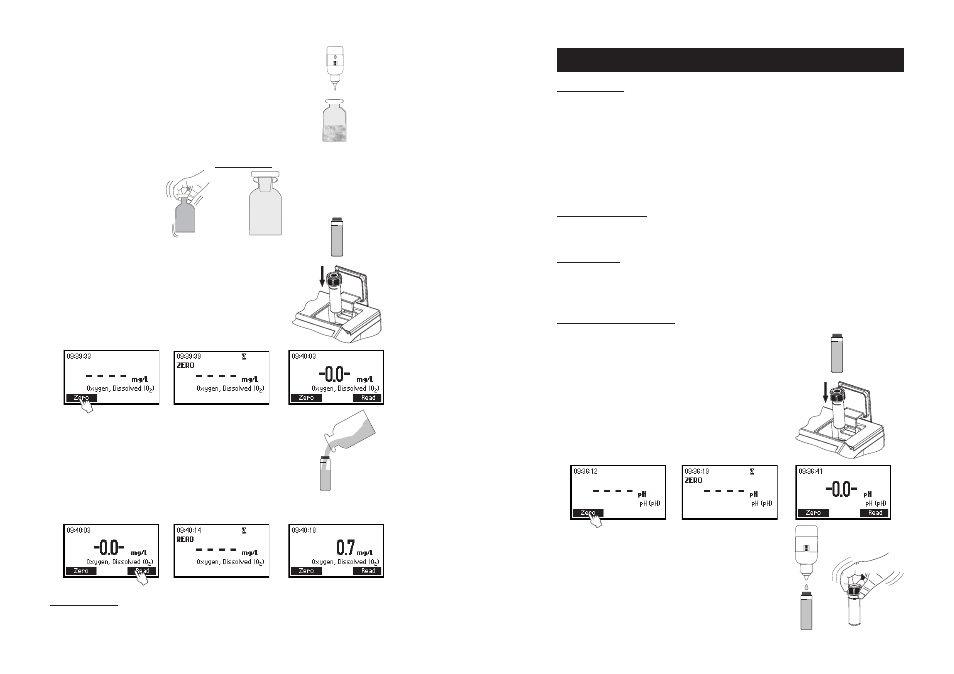
MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
• Select the
pH method using the procedure described in the
Method Selection section (see page 12).
• Fill the cuvette with 10 mL of unreacted sample (up to the
mark) and replace the cap.
• Place the cuvette into the holder and close the lid.
• Press ZERO key. The display will show “-0.0-” when the meter
is zeroed and ready for measurement.
• Remove the cuvette and add 5 drops of HI 93710-0 Phenol
Red Indicator. Replace the cap and mix the solution.
10 mL
x 5
Dissolved Oxygen
• Let the sample stand and the flocculent agent will start to settle.
• After approximately 2 minutes, when the upper half of the bottle becomes
limpid, add 10 drops of HI 93732C-0.
• Replace the cap and invert the bottle until the settled flocculent dissolves completely. The sample is
ready for measurement when it is yellow and completely limpid.
• Fill the cuvette up to the mark with 10 mL of the unreacted (original)
sample, and replace the cap. This is the blank.
• Place the cuvette into the holder and close the lid.
• Press ZERO key. The display will show “-0.0-” when
the meter is zeroed and ready for measurement.
• Remove the cuvette.
• Fill another cuvette up to the mark with 10 mL of the reacted sample and
replace the cap.
• Reinsert the cuvette into the instrument.
• Press READ to start the reading. The instrument will display the results in mg/L of dissolved oxygen.
10 mL
x 10
INTERFERENCES
Interferences may be caused by reducing and oxidizing materials.
