Hanna Instruments HI 83208-2008 User Manual
Page 11
20
21
FREE CHLORINE
FREE CHLORINE
FREE CHLORINE
FREE CHLORINE
FREE CHLORINE
SPECIFICATIONS
Range
0.00 to 2.50 mg/L
Resolution
0.01 mg/L
Accuracy
±0.03 mg/L ±3% of reading
Typical EMC
±0.01 mg/L
Deviation
Light Source
Tungsten lamp with narrow band interference filter @ 525 nm
Method
Adaptation of the
EPA DPD method 330.5. The reaction between free chlorine and the
DPD reagent causes a pink tint in the sample.
REQUIRED REAGENTS
POWDER
:
Code
Description
Quantity
HI 93701-0
DPD
1 packet
LIQUID:
Code
Description
Quantity
HI 93701A-F
DPD1 Indicator
3 drops
HI 93701B-F
DPD1 Buffer
3 drops
REAGENT SETS
HI 93701-F Reagents for 300 tests (liquid)
HI 93701-01 Reagents for 100 tests (powder)
HI 93701-03 Reagents for 300 tests (powder)
For other accessories see page 73.
MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
• Select the
Free Chlorine method using the procedure
described in the
Method Selection section (see page 12).
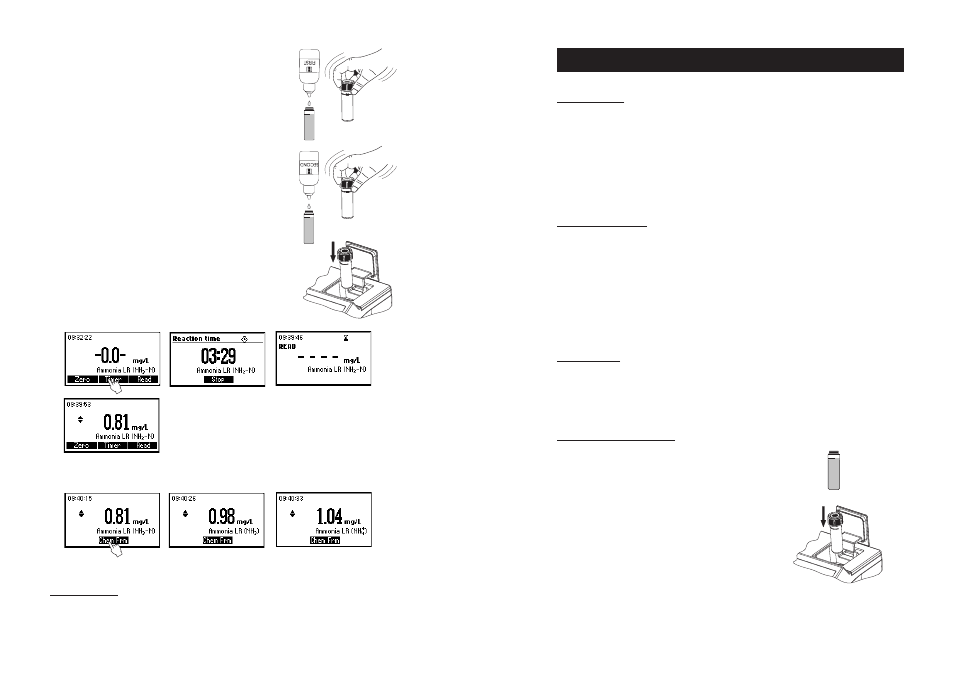
• Fill the cuvette with 10 mL of unreacted sample (up
to the mark) and replace the cap.
• Place the cuvette into the holder and close the lid.
Free Chlorine
FREE CHLORINE
10 mL
Ammonia LR
• Remove the cuvette.
• Add 4 drops of HI 93700A-0 First reagent (6 drops for seawater
analysis). Replace the cap and mix the solution.
• Add 4 drops of HI 93700B-0 Second reagent (10 drops for seawater
analysis). Replace the cap and mix the solution.
• Reinsert the cuvette into the instrument.
• Press TIMER and the display will show the countdown prior to the
measurement or, alternatively, wait for 3 minutes and 30 seconds and
press READ. When the timer ends the meter will perform the reading.
The instrument displays the results in mg/L of ammonia nitrogen
(NH
3
-N).
• Press the or to access the second level of functions.
• Press the Chem Frm functional key to convert the result in mg/L of ammonia (NH
3
) and ammonium (NH
4
+
).
• Press the or to go back to the measurement screen.
INTERFERENCES
Interference may be caused by: acetone, alcohols, aldehydes, glycine, hardness above 1 g/L, iron, organic
chloramines, sulfide, various aliphatic and aromatic amines.
x 4
x 4
