Hanna Instruments HI 83208-2008 User Manual
Page 17
32
33
Iron HR
IRON HIGH RANGE
SPECIFICATIONS
Range
0.00 to 5.00 mg/L
Resolution
0.01 mg/L
Accuracy
±0.04 mg/L ±2% of reading
Typical EMC
±0.01 mg/L
Deviation
Light Source
Tungsten lamp with narrow band interference filter @ 525 nm
Method
Adaptation of the
EPA Phenantroline method 315B, for natural and treated waters.
The reaction between iron and reagents causes an orange tint in the sample.
REQUIRED REAGENTS
Code
Description
Quantity
HI 93721-0
Powder Reagent 1 packet
REAGENT SETS
HI 93721-01 Reagents for 100 tests
HI 93721-03 Reagents for 300 tests
For other accessories see page 73.
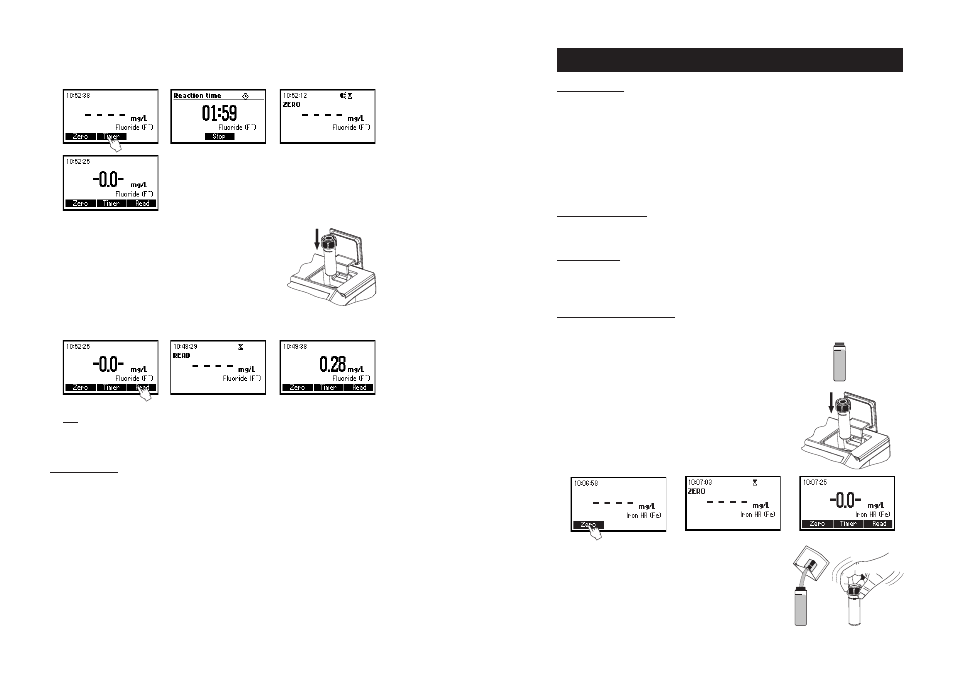
MEASUREMENT PROCEDURE
• Select the
Iron HR method using the procedure described
in the
Method Selection section (see page 12).
• Fill the cuvette with 10 mL of unreacted sample (up to
the mark) and replace the cap.
• Place the cuvette into the holder and close the lid.
• Press ZERO key. The display will show “-0.0-” the meter
is zeroed and ready for measurement.
• Remove the cuvette and add the content of one packet of
HI 93721-0 reagent. Replace the cap and shake until
dissolution is complete.
10 mL
• Press TIMER and the display will show the countdown prior to zeroing or, alternatively, wait for two
minutes and press ZERO. The display will show “-0.0-” when the meter is zeroed and ready for
measurement.
• Remove the cuvette.
• Insert the other cuvette (# 2) with the reacted sample into the
instrument.
• Press READ to start reading. The instrument displays the results in mg/L of fluoride.
Note: For wastewater or seawater samples, before performing measurements, distillation is required.
For most accurate results, use two graduated pipettes to deliver exactly 8 mL of distilled water and 8
mL of sample.
Fluoride
# 2
INTERFERENCES
Interferences may be caused by:
Alkalinity (as CaCO
3
) above 5000 mg/L
Aluminum above 0.1 mg/L
Iron, ferric above 10 mg/L
Chloride above 700 mg/L
Phosphate, ortho above 16 mg/L
Sodium hexametaphosphate above 1.0 mg/L
Sulfate above 200 mg/L
Highly colored and turbid samples may require distillation
Highly alkaline samples can be neutralized with nitric acid.
