Arcmaster, 300 s, 02 stick welding problems – Tweco 300 S Arcmaster User Manual
Page 41
ARCMASTER
®
300 S
March 31, 2006
10-3
10.02 Stick Welding Problems
Description
Possible Cause
Remedy
1. Gas pockets or voids in weld metal
(Porosity).
A.
B.
C.
Electrodes are damp.
Welding current is too high.
Surface impurities such as oil,
grease, paint, etc.
A.
B.
C.
Dry electrodes before use.
Reduce welding current.
Clean joint before welding.
2. Crack occurring in weld metal soon
after solidifi cation commences
A.
B.
C.
Rigidity of joint.
Insuffi cient throat thickness.
Cooling rate is too high.
A.
B.
C.
Redesign to relieve weld joint
of severe stresses or use crack
resistance electrodes.
Travel slightly slower to allow
greater build up in throat.
Preheat plate and cool slowly.
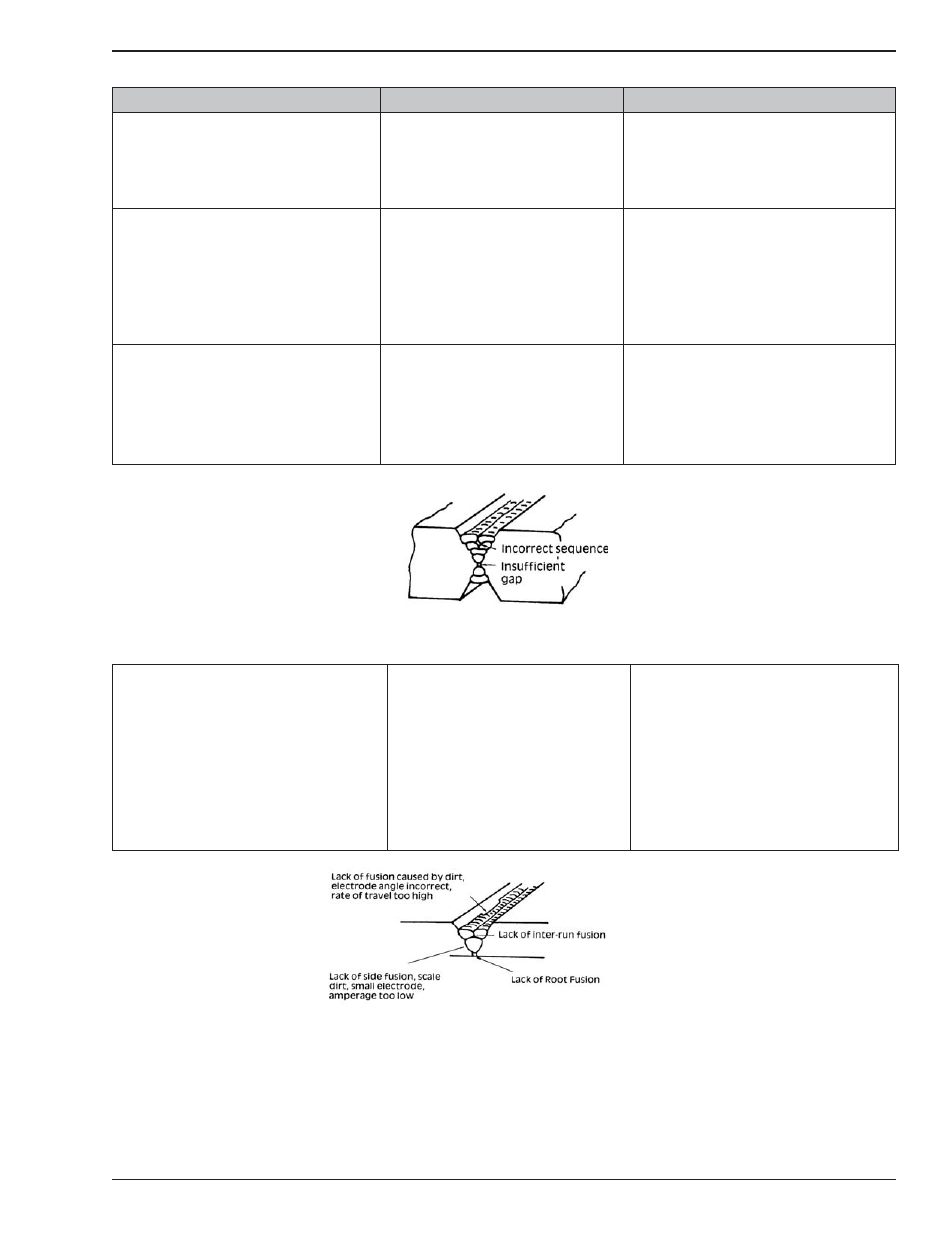
3. A gap is left by failure of the weld
metal to fi ll the root of the weld.
A.
B.
C.
Welding current is too low.
Electrode too large for joint.
Insuffi cient gap.
A.
B.
C.
Increase welding current
Use smaller diameter
electrode.
Allow wider gap.
D. Incorrect sequence.
D.
Use correct build-up sequence.
Figure 8 – Example of insuffi cient gap or incorrect sequence
4. Portions of the weld run do not fuse
to the surface of the metal or edge of
the joint.
A .
B.
Small electrodes used on heavy
cold plate.
Welding current is too low.
A.
B.
Use larger electrodes and pre-heat
the plate.
Increase welding current
C. Wrong electrode angle.
C.
Adjust angle so the welding arc is
directed more into the base metal
D. Travel speed of electrode is too
high.
D. Reduce travel speed of electrode
E.
Scale or dirt on joint surface.
E.
Clean surface before welding.
Figure 9 – Example of lack of fusion
