Match, Forward peak power, Peak average power – Bird Technologies VPM3 User Manual
Page 34: Burst average power
26
Match
Match measures the relation between forward and reflected average power.
The health of the feedline and antenna systems can be monitored using Match,
or VSWR, measurement under full power operating conditions. High VSWR is an
indicator of feed line damage, overtightened cable or feed line clamps, or
antenna changes/damage due to weather conditions, icing, or structural dam-
age to the tower.
Rho and Return Loss are also the same measurement, but in different units:
Rho -
Rho
P
R
P
F
=
VSWR -
VSWR
1
p
+
1
p
–
-------------
=
Return Loss (dB) -
ReturnLoss dB
20
log
=
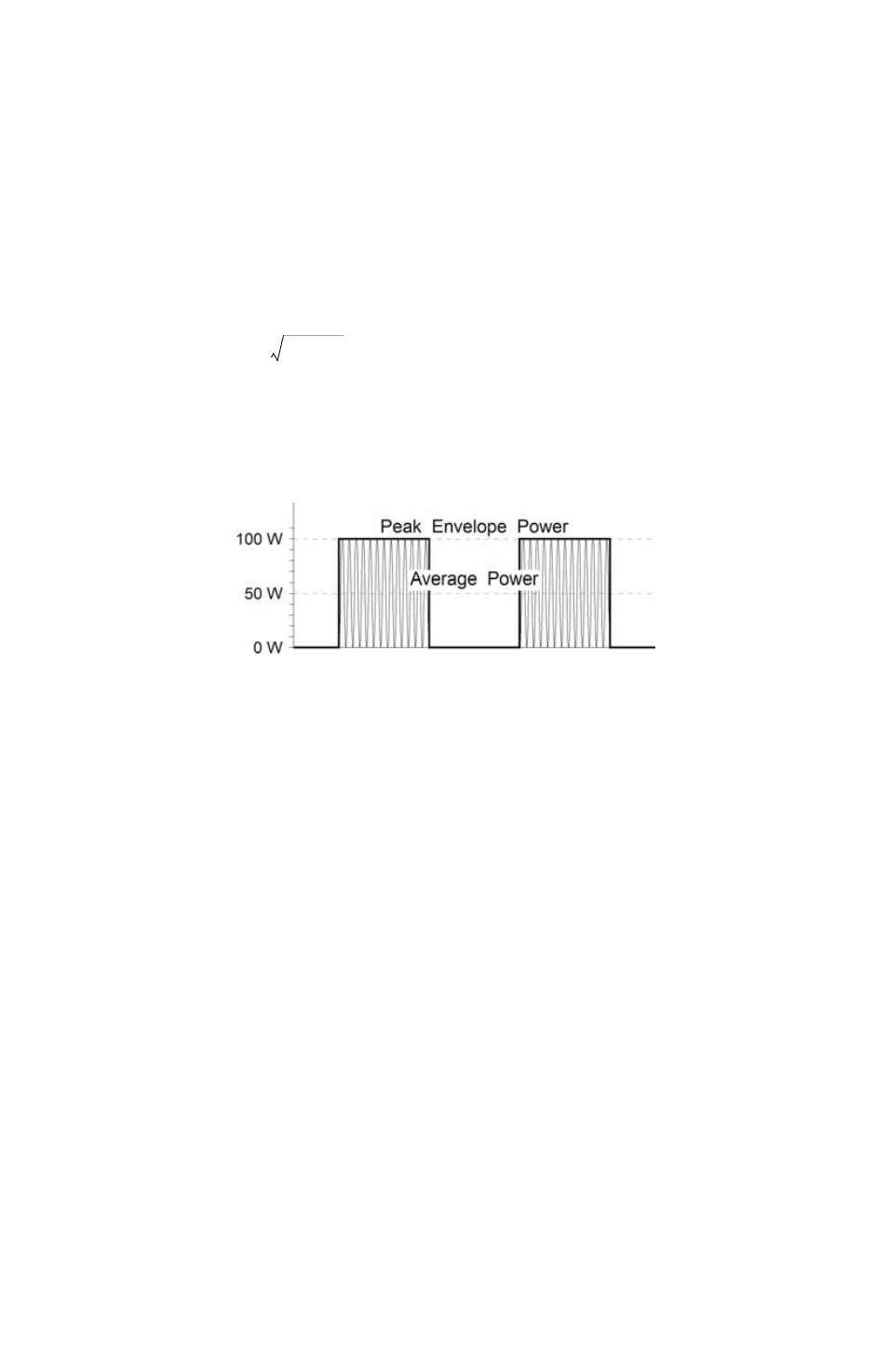
Figure
22
Average and Peak Envelope Power, Square Wave Signal
Forward Peak Power
Peak power measurements detect amplitude changes as a signal modulates the
carrier envelope.
Transmitter overdrive can be detected with peak measurements. Common
problems are overshoot at the beginning of burst packets, amplitude modula-
tion, and excessive transients. These damage system components with exces-
sive peak power and also cause data degradation, increasing the Bit Error Rate.
For TDMA applications, Peak and Burst Power measurements are used to detect
overshoot in single timeslots. Other timeslots must be turned off for this test.
Peak Average Power
This displays the average of the positive and negative peak power readings.
Burst Average Power
Burst width (BW) is the duration of a pulse. Period (P) is the time from the start
of one pulse to the start of the next pulse. Duty cycle
(D) is the percentage of
time that the transmitter is on. To calculate the duty cycle simply divide the
burst width by the period (D = BW / P). Low duty cycles mean that the burst
width is much less than the period; a large amount of dead time surrounds each
burst. For low duty cycles, the burst average power will be much larger than the
average power.
After peak power is measured, a threshold of ½ the peak is set. The sampled
power crosses that threshold at the beginning and end of each burst. The time
between crossings is used to calculate the duty cycle. Burst Average Power is
calculated by dividing the Average Power by the Duty Cycle.
