Rockwell Automation TLAR Electric Cylinders Replacement User Manual
Page 15
MP-Series and TL-Series Electric Cylinders Replacement Parts 15
Rockwell Automation Publication MPAR-IN002B-EN-P - September 2012
9.
Hold the pulleys with a wrench and tighten the collar by turning the hex key
counter-clockwise to the torque shown in this table.
10.
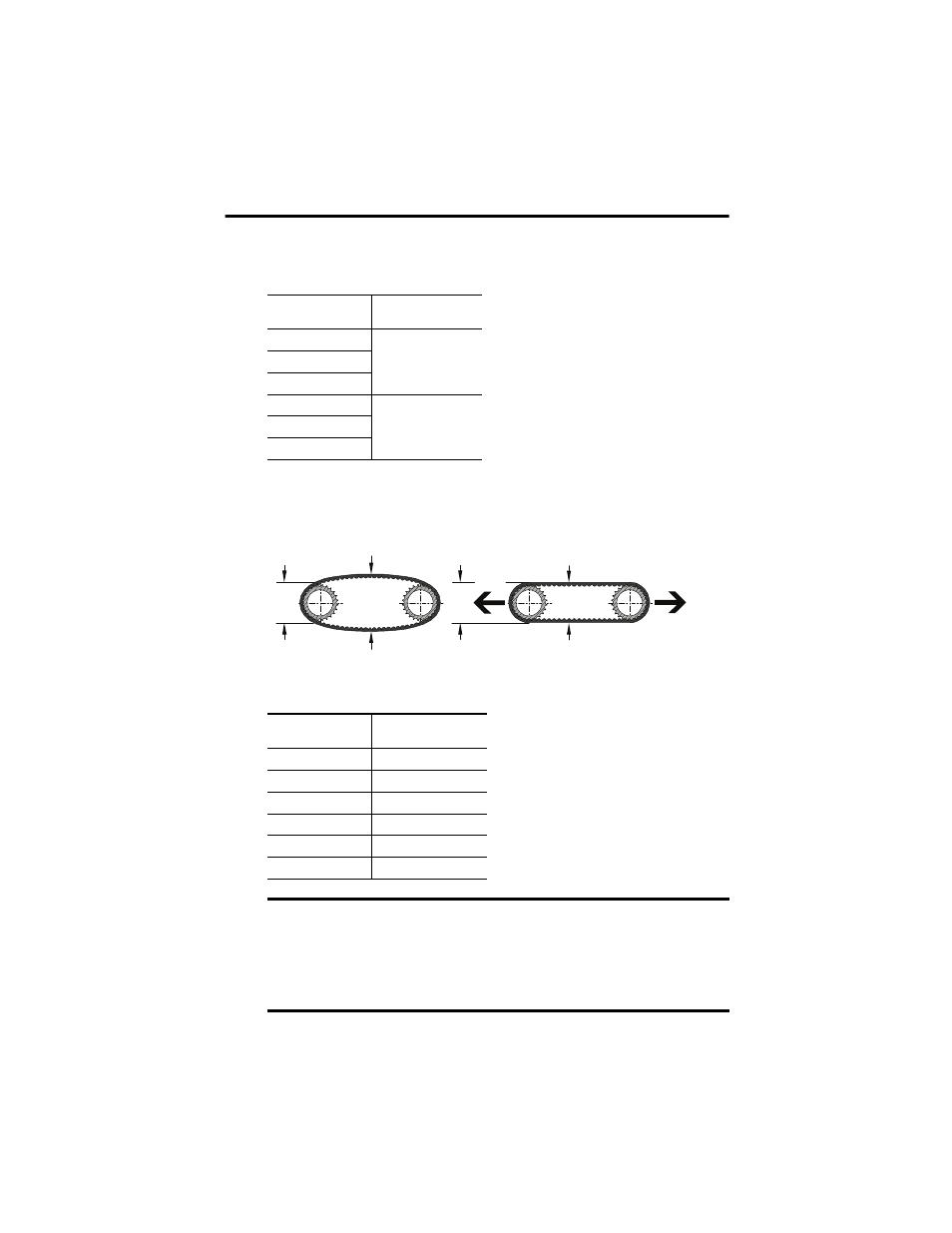
Apply pressure to the base of the motor to tension the belt.
Observe the distance a X and Y and determine this transition precisely.
This table shows the recommend belt tension values.
Cat. No.
Torque
N•m (lb•ft)
MPAR-x1xxxB-xxB/D/E
16.95 (13)
MPAR-x1xxxE-xxB/D/E
MPAR-x2xxxC-xxB/D/E
MPAR-x2xxxF-xxB/D/E
67.79 (50)
MPAR-x3xxxE-xxB/D/E
MPAR-x3xxxH-xxB/D/E
Cat. No.
Recommend Belt Tension
N (lb)
MPAR-x1xxxB-xxB/D/E
30 (6.75)
MPAR-x1xxxE-xxB/D/E
61 (13.73)
MPAR-x2xxxC-xxB/D/E
67 (15.10)
MPAR-x2xxxF-xxB/D/E
90 (20.23)
MPAR-x3xxxE-xxB/D/E
162 (36.4)
MPAR-x3xxxH-xxB/D/E
224 (50.4)
IMPORTANT
A low pretension force is better than a high pretension force.
Excessive pretension on the belt results in:
•
impermissible radial loads causing shaft to break
•
increased wear in the axis and motor gearings
•
reduction of the service life of the belt
X
Y
X
Y
Fv
Fv
Untensioned: X Tensioned: X = Y
