NTi Audio Acoustilyzer AL1 User Manual
Page 91
90
91
STI, RASTI or STI-PA
STI, RASTI or STI-PA are the most established methods for measuring
speech intelligibility. All three of them basically apply the same principle,
whereby RASTI and STI-PA are a simplified version of STI. This article
explains the principles behind these methods.
Speech Model:
First of all, measuring the speech intelligibility requires a model for speech
signals. For instance, speech may be described as superposition of various
phoneme frequencies that are modulated (i.e. of which the amplitude is
varied).
Frequency Spectrum:
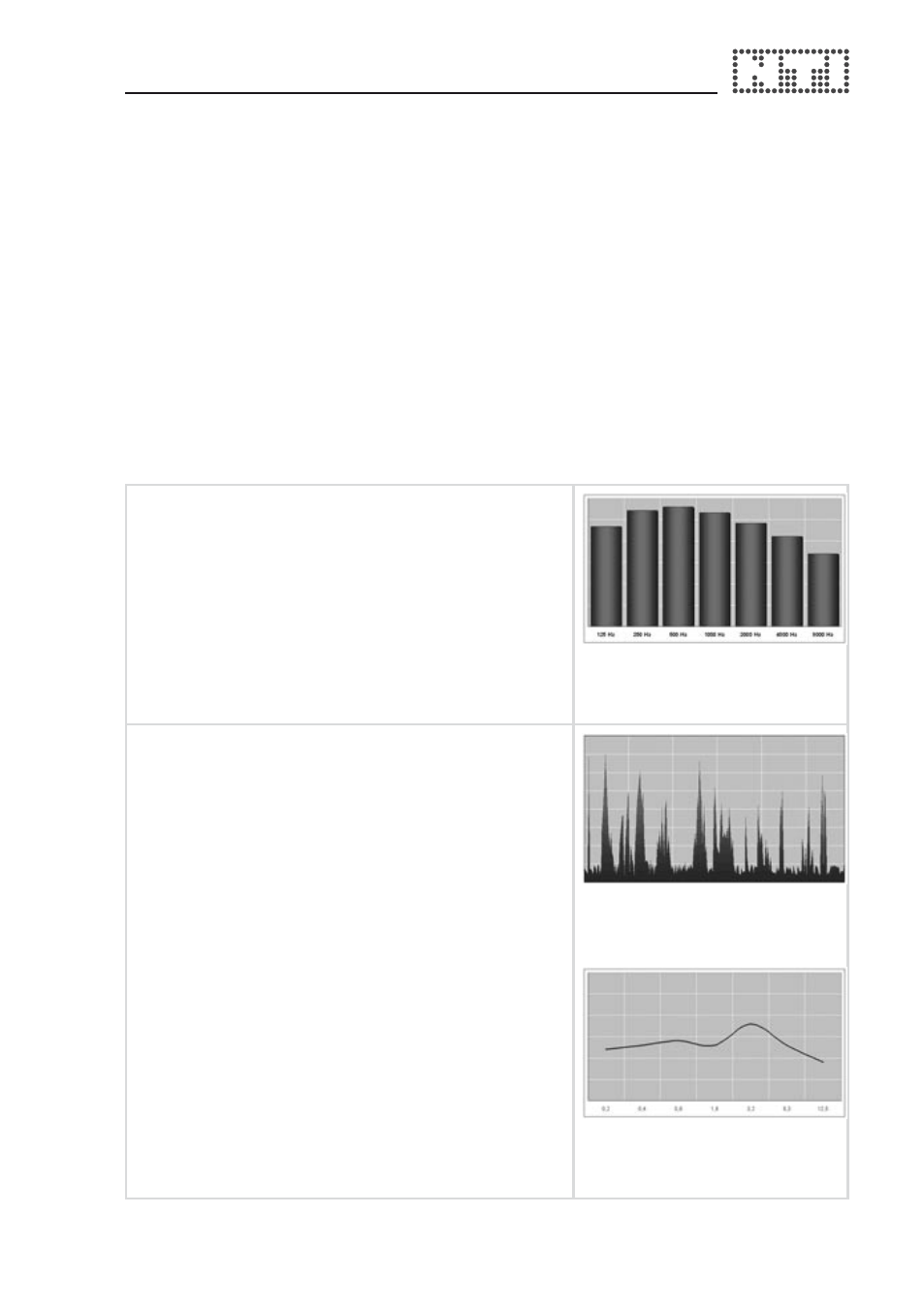
The frequency analysis of a male voice
over a certain period results in a typical
characteristic as shown in Figure 1.
Fig. 1: Averaged octave
band spectrum of a male
speaker.
Time Modulations:
Within each frequency band, the signal
level varies, i.e. it is “modulated” by the
speaker. Figure 2 shows the envelope of a
speech signal in the 250 Hz band, whereby
the shape of the envelope is given by the
speech contents.
By analyzing the spectra of envelope
sequences it can be shown that a speaker
modulates the individual frequency bands in
the range from 0.2 to 12.5 Hz.
Fig. 2: Envelope of a speech
signal (250 Hz band).
Fig. 3: frequency spectrum
of the envelope of a speech
signal (250 Hz band).
