Using collections to direct user searches – Google Search Appliance Configuring GSA Unification User Manual
Page 7
Google Search Appliance: Configuring GSA Unification
7
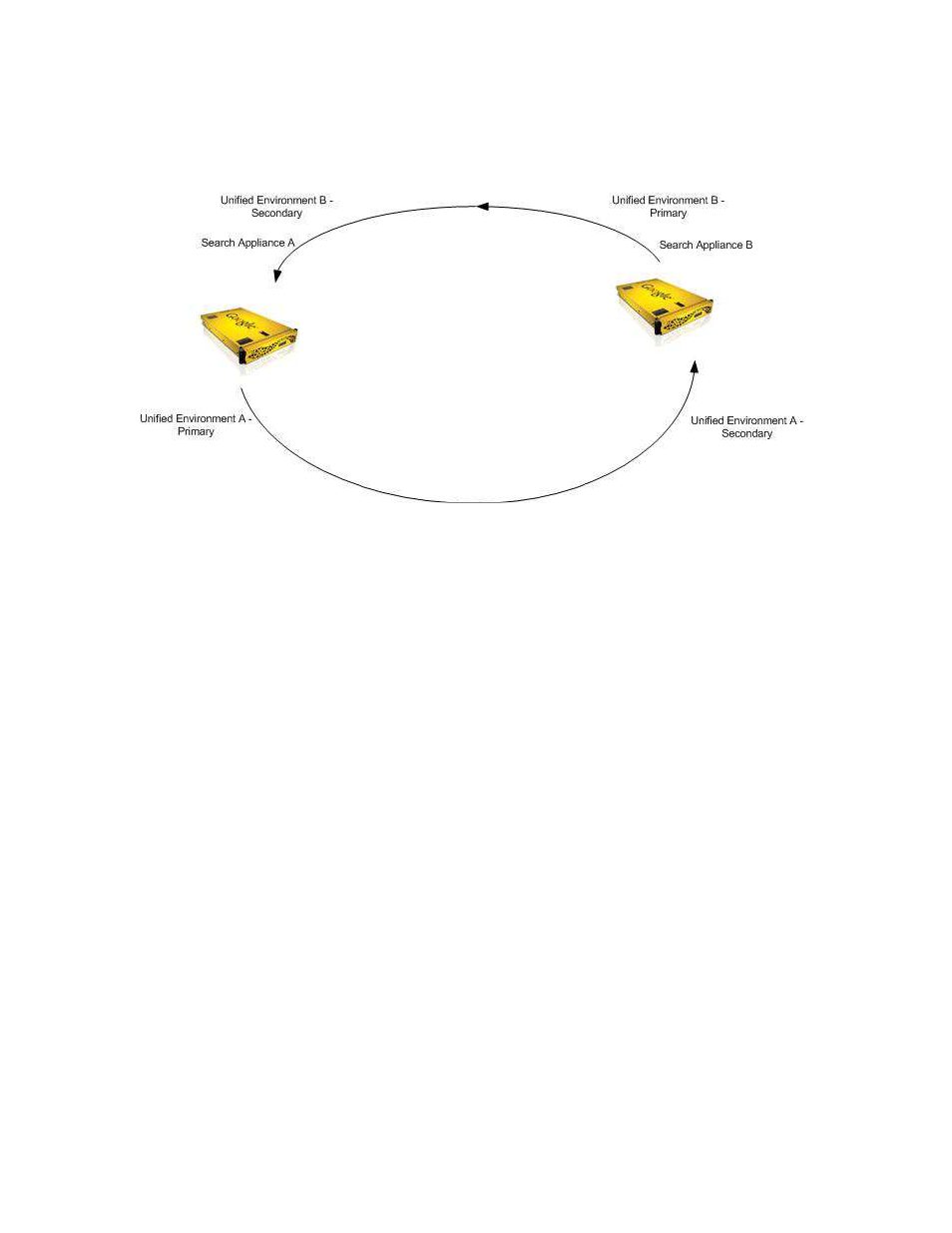
A particular search appliance is able to act as both a primary and secondary node in relation to another
search appliance. The following example illustrates a pair of unified environments consisting of two
search appliances. In unified environment A, Search Appliance A is the primary node and Search
Appliance B is the secondary node. In unified environment B, Search Appliance A is the secondary node
and Search Appliance B is the primary node.
A more complex use case involves search appliances that are physically located far away from one
another. For example, you might have search appliances in Tokyo, London, and Rio de Janeiro. Users in
those locations might sometimes need to search local content only, while at other times they would
need to search global content. To make these searches as efficient as possible, configure the unified
environment as follows.
•
Each search appliance is configured as a primary search appliance with the other search appliances
as secondary search appliances. In the example, Tokyo is configured as primary with London and
Rio de Janeiro as secondary; London is configured as primary with Tokyo and Rio de Janeiro as
secondary; Rio de Janeiro is configured as primary with Tokyo and London as secondary.
•
Use the composite collections feature to define both region-specific collections and a global
collection. When search users in Rio de Janeiro search local content, their search is conducted only
on content located on the Rio de Janeiro search appliance. For more information on composite
collections, see “Using Collections to Direct User Searches” on page 7 and “About Composite
Collections” on page 15.
Using Collections to Direct User Searches
A query to the primary search appliance in a unified environment returns results from all search
appliances in the configuration. By default, all collections on all search appliances are searched when a
query is directed to the primary search appliance. You can restrict which collections are searched in two
ways:
•
Use the site parameter of the query to define which collections are searched. For more
information on the site parameter, see the Search Protocol Reference.
•
Create composite collections on the primary search appliance, which are virtual collections
encompassing the specific collections to be searched on each search appliance in the unified
configuration. For more information on composite collections and how they work, see “About
Composite Collections” on page 15.
