Google Networking Best Practices for Large Deployments User Manual
Page 37
Client Configuration
37
If you plan to set up Single Sign-On authentication, consider the following suggestions:
•
Set up SSO servers in distributed network locations, rather than a central location.
•
Set up internal DNS servers to redirect SSO traffic to the nearest SSO server, and ensure
that alternate SSO servers are in place for redundant service in case of disruptions that
prevent users from accessing the SSO server in a particular location.
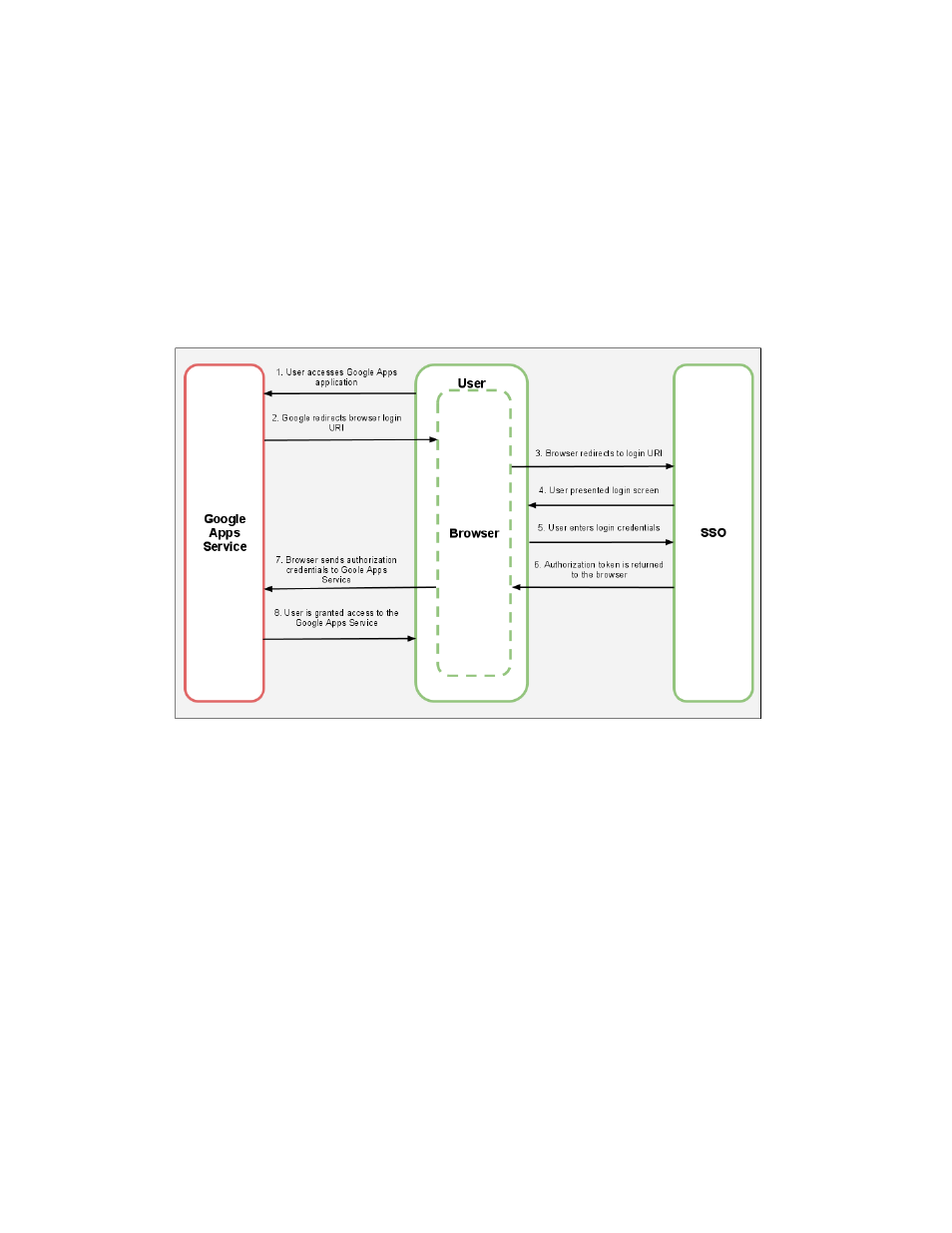
Single Sign-On Process
When an unauthenticated user logs into Google Apps, and an SSO URI is configured for the
domain, authentication takes several steps. See the chart below.
The process of SSO Authentication is as follows:
1. The user makes a request for a Google Apps service.
2. The Google Apps Authentication System redirects the user’s browser to the configured
URI for the SSO System. If the SSO/SAML server is not available, the user is unable to
authenticate to the service.
3. The browser redirects to the login URI.
4. The SSO server displays a login screen.
5. The user enters login credentials and authenticates to the SSO System.
6. The SSO System passes an authorization token to the user’s browser.
7. The user’s browser sends the authorization credentials to the Google Apps Service.
8. The user is granted access to the Google Apps service.
