Mobile – Google Networking Best Practices for Large Deployments User Manual
Page 34
34
Networking Best Practices for Large Deployments
For Google Apps, we support the latest version of Google Chrome (which automatically
updates whenever it detects that a new version of the browser is available). We also support
the current and some previous major releases of Mozilla Firefox, Microsoft Internet Explorer,
and Apple Safari. Check th
for more information about
supported versions of browsers.
Offline Access
Offline access can dramatically affect overall network bandwidth. Offline access causes
network behavior for email and other applications to become similar to traditional email clients,
since offline access uses data synchronization instead of immediate direct access. This
behavior can cause load problems if all users have offline access enabled. If possible, enable
offline access in Google Apps only for those users who require it.
Mobile
In most cases, mobile clients have very little effect on your network load. This varies based on
your specific mobile solution. See the sections below for details.
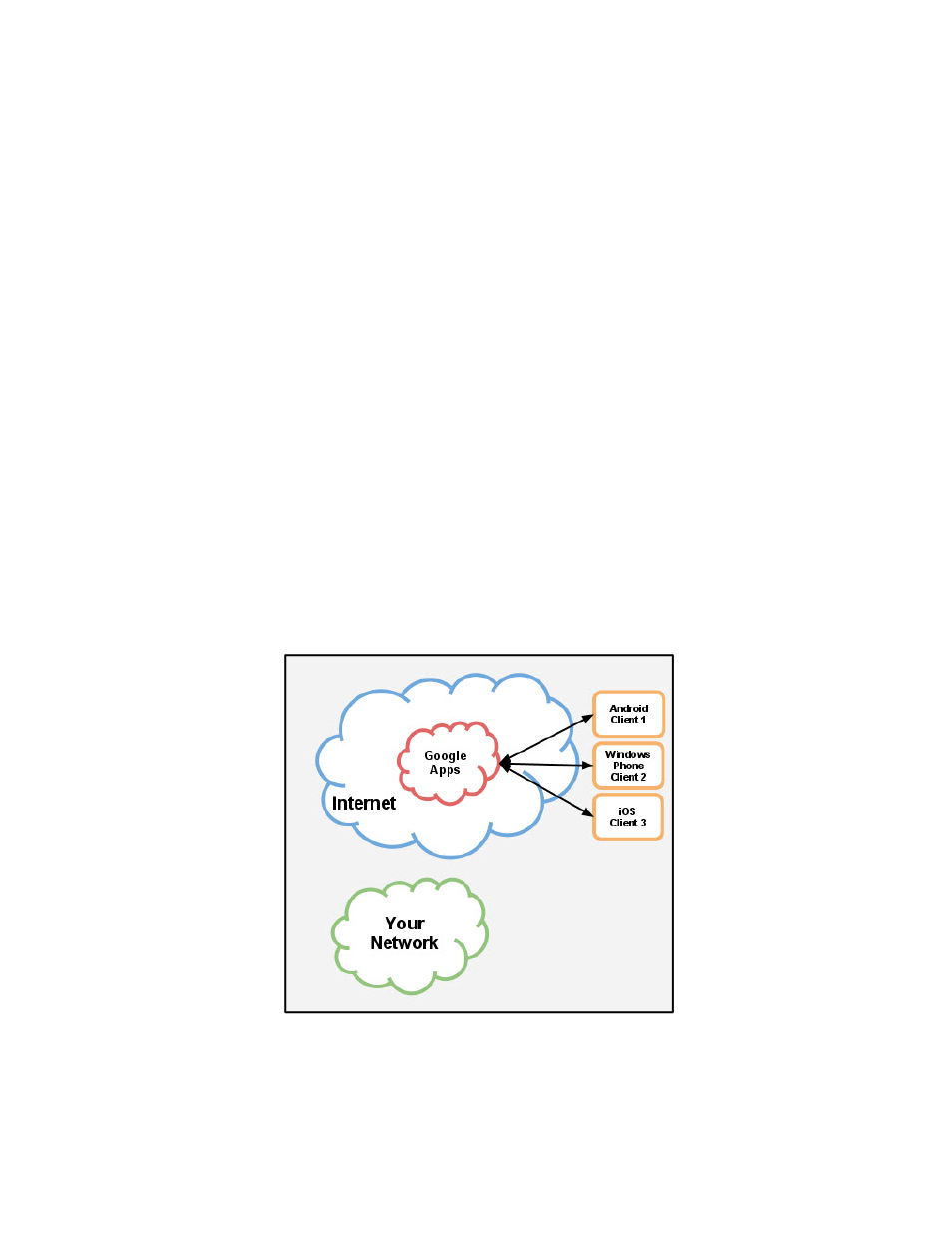
Android, iOS, and Windows Phone
Android devices (which use the Google Sync protocol) and Windows Phone and Apple iOS
devices (which use the ActiveSync protocol) communicate directly to Google servers without
using your network resources.
See the chart below for an illustration.
These devices do not access your network when using Google Apps. With ActiveSync or
Google Sync, Google Apps delivers this mail directly to the user’s device.
