IKA C 7000 Grundausstattung Set 2 User Manual
Page 24
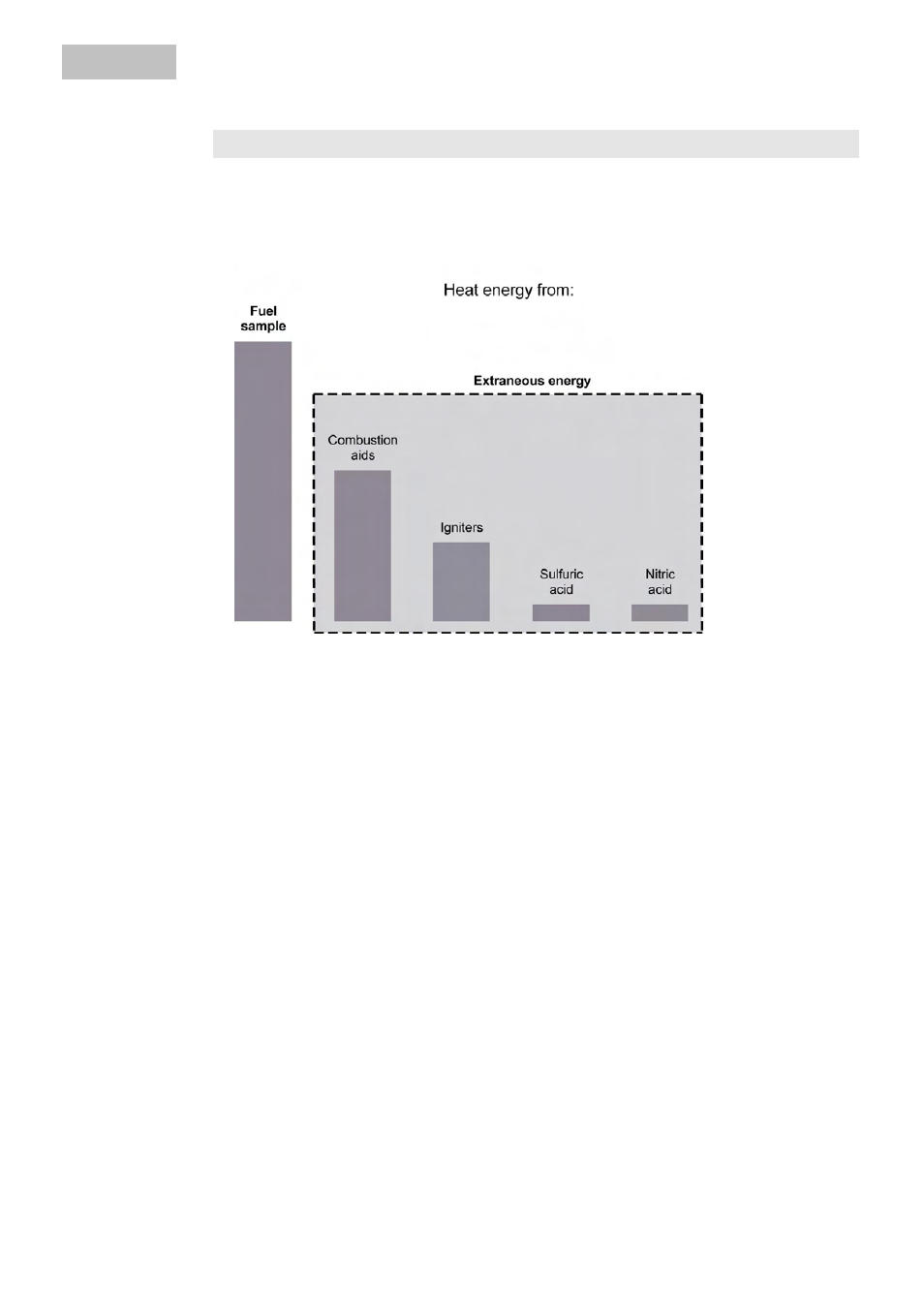
3ULQFLSOHV RI &DORULPHWULF 0HDVXUHPHQW
IKA
-WERKE C 7000
Ver. 07 09.07
3DJH
&RUUHFWLRQV
It is intrinsic to the method that during a combustion test heat is released from ex-
ternal sources as well as from the sample.
The ratio of heat from external sources to heat from the sample can vary considerably.
The heat of combustion of the cotton thread used to ignite the sample, and the
electrical ignition energy would falsify the result. In the calculation, a correction
must be applied to compensate for them.
Substances that are difficult to ignite and those with low flammability are burnt to-
gether with a combustion aid. The combustion aid is first weighed and then added to
the sample in the crucible. The quantity of heat resulting from it can be determined
from its mass and its known gross calorific value. The test result must be corrected
by deducting this quantity of heat.
A combustible crucible C 14 can be used in place of a conventional crucible. The
combustible crucible burns completely to leave no residue. When a combustible
crucible is used, a cotton thread is not required for ignition. The crucible makes di-
rect contact with the fixed ignition wire in the decomposition vessel, which ignites it.
The purity of the material used for combustible crucibles prevent chemical contami-
nation of the sample.
Decomposition vessels in which combustible crucibles are to be used must be fitted
with an additional part (Support C 5010.4, see Accessories). The sample is weighed
in the combustible crucible in the usual way. In most cases, an additional combus-
tion aid is not required, because the crucible itself fulfils this role.
&RQEXVWLRQ DLG
&RPEXVWLEOH
FUXFLEOH &
+HDW RI
FRPEXVWLRQ DQG
H[WHUQDO HQHUJ\
