Operation, Inspection, Pulley alignment – COOK Duct Blower User Manual
Page 3: Final installation steps, Start up
3
All other fans
a. Loosen the pivoting motor base bolts and turn the
adjustment screws to lower the motor base so that the
belts can easily slip into the grooves on the pulleys.
Never pry, roll, or force the belts over the rim of the
pulley.
b. Adjust the motor plate until proper tension is reached.
For proper tension, a deflection of approximately 1/4”
per foot of center distance should be obtained by
firmly pressing the belt. Refer to Figure 1.
c. Lock the motor plate adjustment nuts in place.
d. Ensure pulleys are properly aligned. Refer to Figure 2.
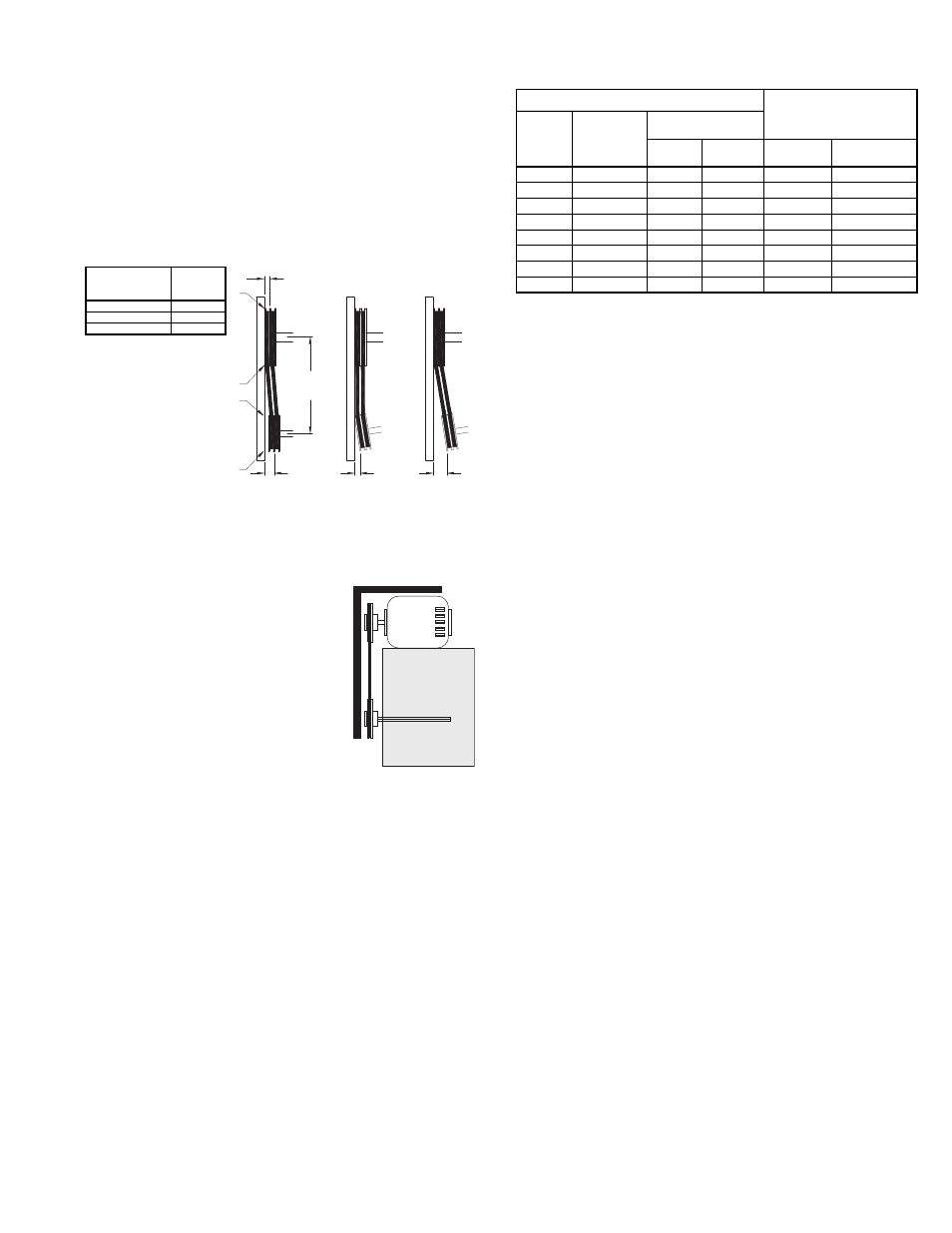
Pulley Alignment
Pulley alignment is adjusted by loosening the motor pulley
setscrew and by moving the motor pulley on the motor shaft.
Figure 2 indicates where to measure
the allowable gap for the drive align-
ment tolerance. All contact points
(indicated by WXYZ) are to have a
gap less than the tolerance shown in
the table. When the pulleys are not the
same width, the allowable gap must
be adjusted by half of the difference in
width. Figure 3 illustrates using a car-
penter’s square to adjust the position
of the motor pulley until the belt is par-
allel to the longer leg of the square.
Final Installation Steps
a. Inspect fasteners and setscrews, par-
ticularly fan mounting and bearing
fasteners, and tighten according to
the recommended torque shown in
the table, Recommended Torque for
Setscrews/Bolts.
b. Inspect for correct amperage and
voltage with an ammeter and voltme-
ter.
c. Ensure blower is secured to duct work.
d. Ensure all accessories are installed.
e. Inspect wheel-to-inlet clearance.
f. Test the fan to be sure the rotation is the same as indi-
cated by the arrow marked ‘rotation’.
NOTICE! Do not allow the fan to run in the wrong
direction. This will overheat the motor and cause seri-
ous damage. For 3-phase motors, if the fan is running
in the wrong direction, check the control switch. It is
Figure 2
Tolerance
Center Distance
Maximum
Gap
Up thru 12”
1/16”
12” up through 48
1/8”
Over 48”
1/4”
OFFSET
ANGULAR
OFFSET/ANGULAR
A
W
X
Y
Z
B
CENTER
DISTANCE
(CD)
GAP
GAP
possible to interchange two leads at this location so
that the fan is operating in the correct direction.
Operation
Pre-Start Checks
a. Lock out all the primary and secondary power sources.
b. Inspect fasteners and setscrews, particularly those
used for mounting the fan, and tighten if necessary.
c. Inspect belt tension and pulley alignment. (Remember,
if belt tension is correct, a loud squeal occurs as the
fan increases to full power.)
d. Inspect motor wiring.
e. Ensure the belt touches only the pulleys.
f. Ensure fan and ductwork are clean and free of debris.
g. Test the fan to ensure the rotation of the wheel is the
same as indicated by the rotation label.
h. Close and secure all access doors.
i. Restore power to unit.
Start Up
Turn the fan on. In variable speed units, set the fan to its
lowest speed. Inspect for the following:
• Direction of rotation.
• Excessive vibration.
• Unusual noise.
• Bearing noise.
• Improper belt alignment or tension (listen for a continu-
ous squealing noise).
• Improper motor amperage or voltage.
NOTICE! If a problem is discovered, immediately shut
off the fan. Lock out all electrical power and check for
the cause of the trouble. Refer to Troubleshooting,
page 5.
Inspection
Inspection of the fan should be conducted at the first 30
minute, 8 hour and 24 hour intervals of satisfactory opera-
tion. During the inspections, stop the fan and inspect as per
directions below.
30 Minute Interval
Inspect bolts, setscrews, and motor mounting bolts.
Adjust and tighten as necessary.
8 Hour Interval
Inspect belt alignment and tension. Adjust and tighten as
necessary.
24 Hour Interval
Inspect belt tension. Adjust and tighten as necessary.
Recommended Torque for Setscrews/Bolts (IN/LB.)
Setscrews
Hold Down Bolts
Size
Key Hex
Across
Flats
Recommended
Torque
Min.
Max.
Size
Wrench
Torque
No.10
3/32”
28
33
3/8”-16
240
1/4”
1/8”
66
80
1/2”-13
600
5/16”
5/32”
126
156
5/8”-11
1200
3/8”
3/16”
228
275
3/4”-10
2100
7/16”
7/32”
348
384
7/8”-9
2040
1/2”
1/4”
504
600
1”-8
3000
5/8”
5/16”
1104
1200
1-1/8”-7
4200
3/4”
3/8”
1440
1800
1-1/4”-7
6000
Figure 3
