Attachment b: bandwidth estimation – Asante Technologies Voyager II User Manual
Page 89
Attachment B: Bandwidth Estimation
Since the FPS is dependent on the bandwidth of the camera, the relationship between the size
of an image file and the bandwidth is always the major concern of the system construction
engineer.
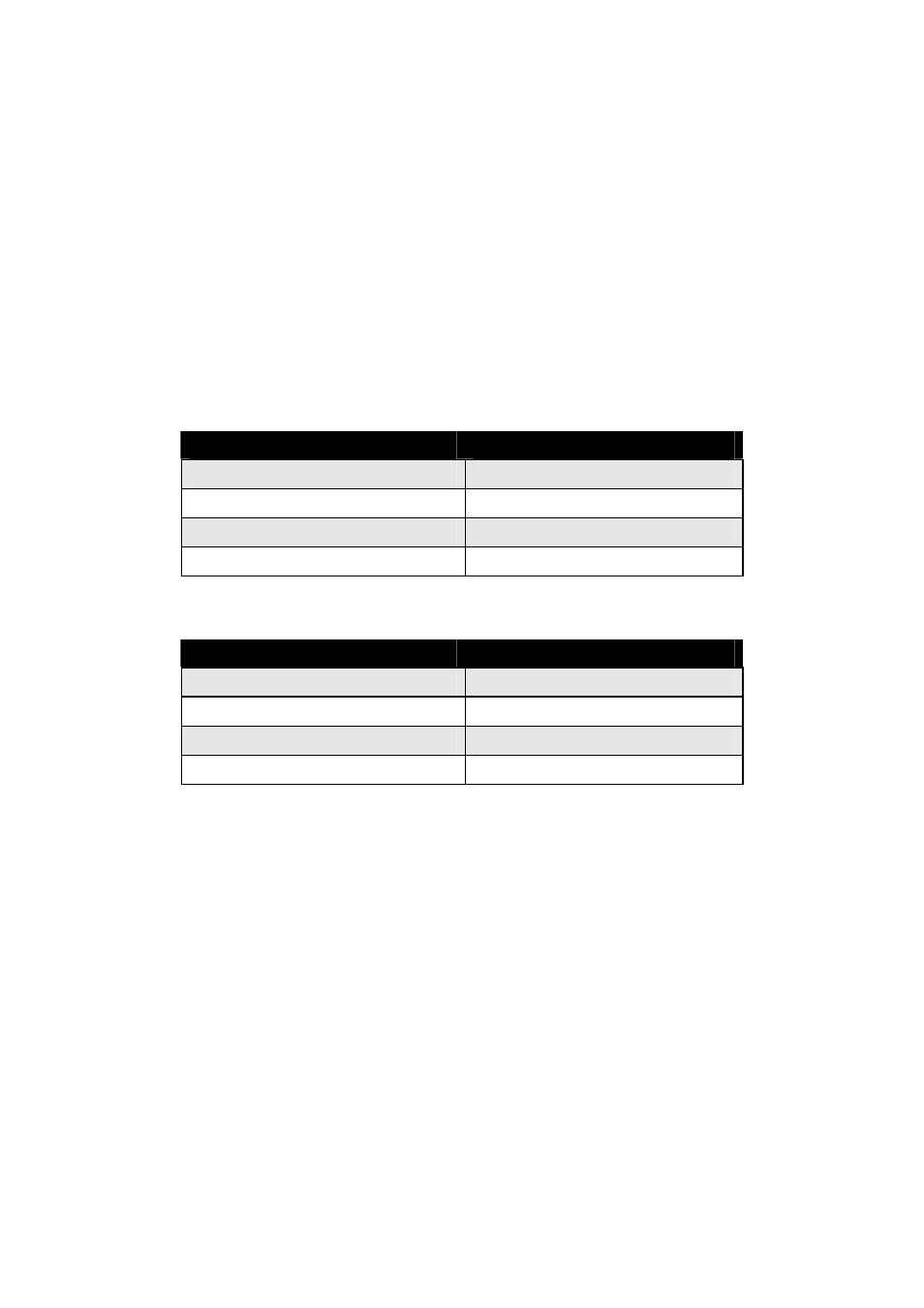
The table below shows the relation between the resolution and size of an MJPEG file in the
NTSC system. Please note that the values in the table are for reference only, because the size
of an image file is closely related to the complexity of the environment and the actual
situation of the place being monitored.
Image Resolution
Average range of Data Sizes
160 x 120 (QQVGA)
20k - 50k bit
320 x 240 (QVGA)
50k - 150k bit
640 x 480 (VGA)
150k - 350k bit
1280 x 1024 (SXGA)
400k – 900k bit
The table below shows the relation between the resolution and size of an MPEG4 file in the
NTSC system.
Image Resolution
Average range of Data Sizes
160 x 120 (QQVGA)
10k - 40k bit
320 x 240 (QVGA)
20k - 100k bit
640 x 480 (VGA)
60k - 210k bit
1024 x 768 (XGA)
100k – 300k bit
Ex.: The transmission speed on the Internet is 2fps under 320 x 240, i.e. 50k*2=100k to
150*2=300k per second. It is suggested to apply for 512K "upload" bandwidth.
Note 1: What the camera needs at the client end is the “upload” bandwidth. However, most
ISPs in Taiwan provide download bandwidth that is wider than the upload bandwidth.
Therefore, symmetrical bandwidth is a good choice for users who need wider upload
bandwidth. Ex. download/upload = 521K/512K
Note 2: 32 kbps to 64kbps is required for transmission of audio signals.
89
