6 using cli command history, 7 using the no and default forms of commands – Asante Technologies 35516 User Manual
Page 33
- 33 -
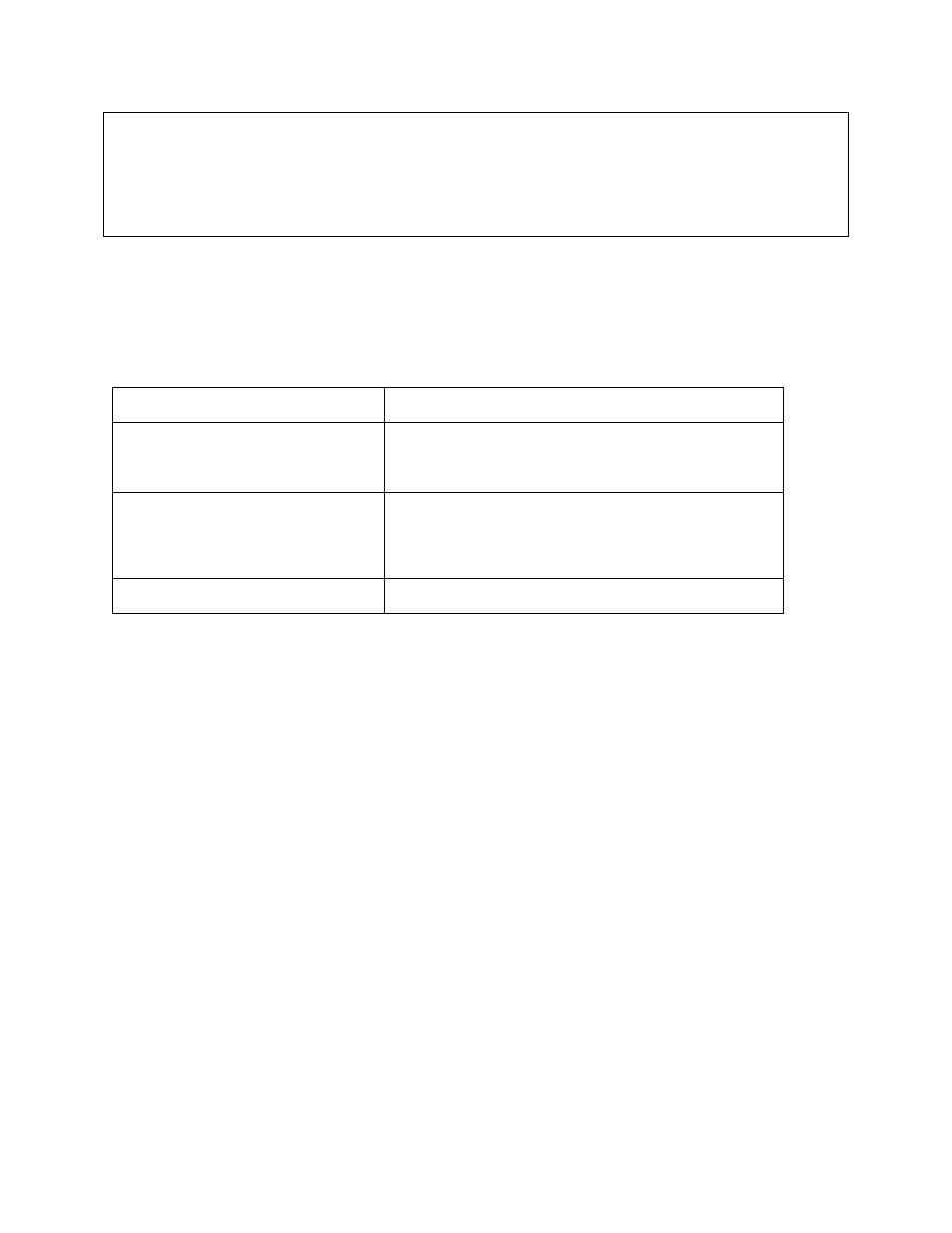
Router(config)# router ?
bgp BGP information
ospf Open Shortest Path First
rip Routing Information Protocol (RIP)
Router(config)# router
Router(config)#router rip
Router(config-rip-router)#
3.6 Using CLI Command History
The CLI user interface provides a history or record of commands that you have entered. This feature is particularly
useful for recalling long or complex commands or entries, including access lists. To recall commands from the history
buffer, use one of the following commands:
Keystrokes/Command Purpose
Press Ctrl-P or the up arrow key
Recall commands in the history buffer, beginning with the
most recent command. Repeat the key sequence to recall
successively older commands.
Press Ctrl-N or the down arrow key
Return to more recent commands in the history buffer after
recalling commands with Ctrl-P or the up arrow key. Repeat
the key sequence to recall successively more recent
commands.
show history
While in EXEC mode, list the last several commands entered.
3.7 Using the No and Default Forms of Commands
Almost every router configuration command has an opposite no form that negates or reverses a command. In
general, the no form is used to disable a function that has been enabled. To re-enable a disabled function, or to
enable a function that is disabled by default, use the command without the no keyword. For example, Address
Resolution Protocol (ARP) is enabled by default. Specify the command no arp to disable the ARP table; to re-enable
the ARP table, use the arp command.
3.8 Using Command-Line Editing Features and Shortcuts
A variety of shortcuts and editing features are enabled for the CLI command-line interface. The following subsections
describe these features:
•
Moving Around on the Command Line
•
Completing a Partial Command Name
•
Editing Command Lines that Wrap
• Deleting
Entries
•
Scrolling Down a Line or a Screen
•
Redisplaying the Current Command Line
