Changing from priority mode to bind mode – HP XP Array Manager Software User Manual
Page 8
priority mode, write operations do not have to wait for available cache segments, and there will
be no backend contention caused by destaging data.
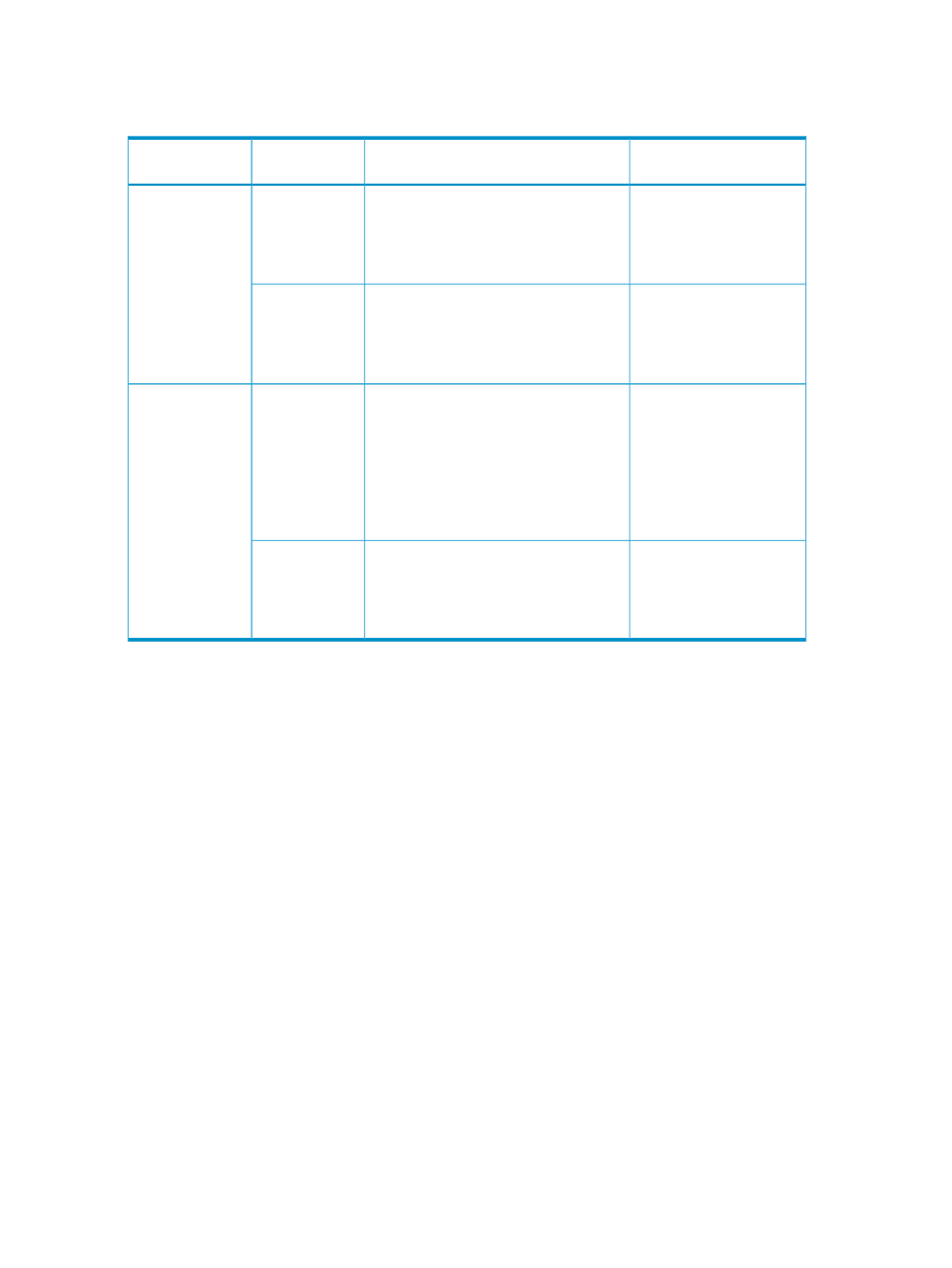
Table 2 Bind Mode Cache Residency Cache Requirements
Cache Residency Cache
Requirement
Capacity Specifications
RAID Level or
Volume Type
System Type
3 times the space required
for user data: 1 slot = 3 x
264 KB = 792 KB = 48
cache segments
Slot capacity: 264 KB
Cache segment capacity: 16.5 KB
Cache segments needed per slot: 48 (slot
capacity / cache segment capacity)
RAID 5 (3390)
or RAID 6
OPEN Systems
2 times the space required
for user data: 1 slot = 2 x
264 KB = 528 KB = 32
cache segments
Slot capacity: 264 KB
Cache segment capacity: 16.5 KB
Cache segments needed per slot: 32 (slot
capacity / cache segment capacity)
RAID 1, or
external volumes
3 times the space required
for user data: 1 slot = 3 x
66 KB = 198 KB = 12
cache segments
Slot capacity: 66 KB
Cache segment capacity: 16.5 KB
Cache segments needed per slot: 12 (slot
capacity / cache segment capacity)
Note: Even though a track for mainframe
is 56 KB, because cache is divided into
16.5 KB segments, it requires 4 segments.
RAID 5 zSeries
and S/390 or
RAID 6
Mainframe (for
example, 3390-3,
3390-9, z/OS,
etc.)
2 times the space required
for user data: 1 slot = 2 x
66 KB = 132 KB = 8 cache
segments
Slot capacity: 66 KB
Cache segment capacity: 16.5 KB
Cache segments needed per slot: 8 (slot
capacity / cache segment capacity)
RAID 1 zSeries
and S/390, or
external volumes
Cache Residency bind data that has write attributes is normally not de-staged. However, this data
will be de-staged in the following cases:
•
During cache blockage that is caused by certain maintenance operations (for example, cache
upgrades) or that is caused by cache failure.
•
If the subsystem is powered off.
•
If the volume is deleted from Cache Residency bind mode.
•
If a fixed or customized volume that is partly or wholly assigned to Cache Residency is
converted into free space by the Virtual LVI/LUN Volume-to-Space function.
•
If a VDEV containing volumes that are assigned to Cache Residency is initialized by the Virtual
LVI/LUN Volume Initialization function.
For further information on Virtual LVI/LUN, see the HP StorageWorks XP24000/XP20000
Virtual LVI/LUN (VLL) and Volume Shredder User Guide.
Changing from Priority Mode to Bind Mode
Changing the mode without cache extension requires a Cache Residency re-configuration.
Using Pre-staging for Immediate Data Access in Priority and Bind Modes
You can use the pre-staging function to make data available from the Cache Residency cache the
first time the host accesses the data. Both priority mode and bind mode permit pre-staging.
8
About Cache Residency Manager Operations
