Fibre address conversion tables – HP XP RAID Manager Software User Manual
Page 53
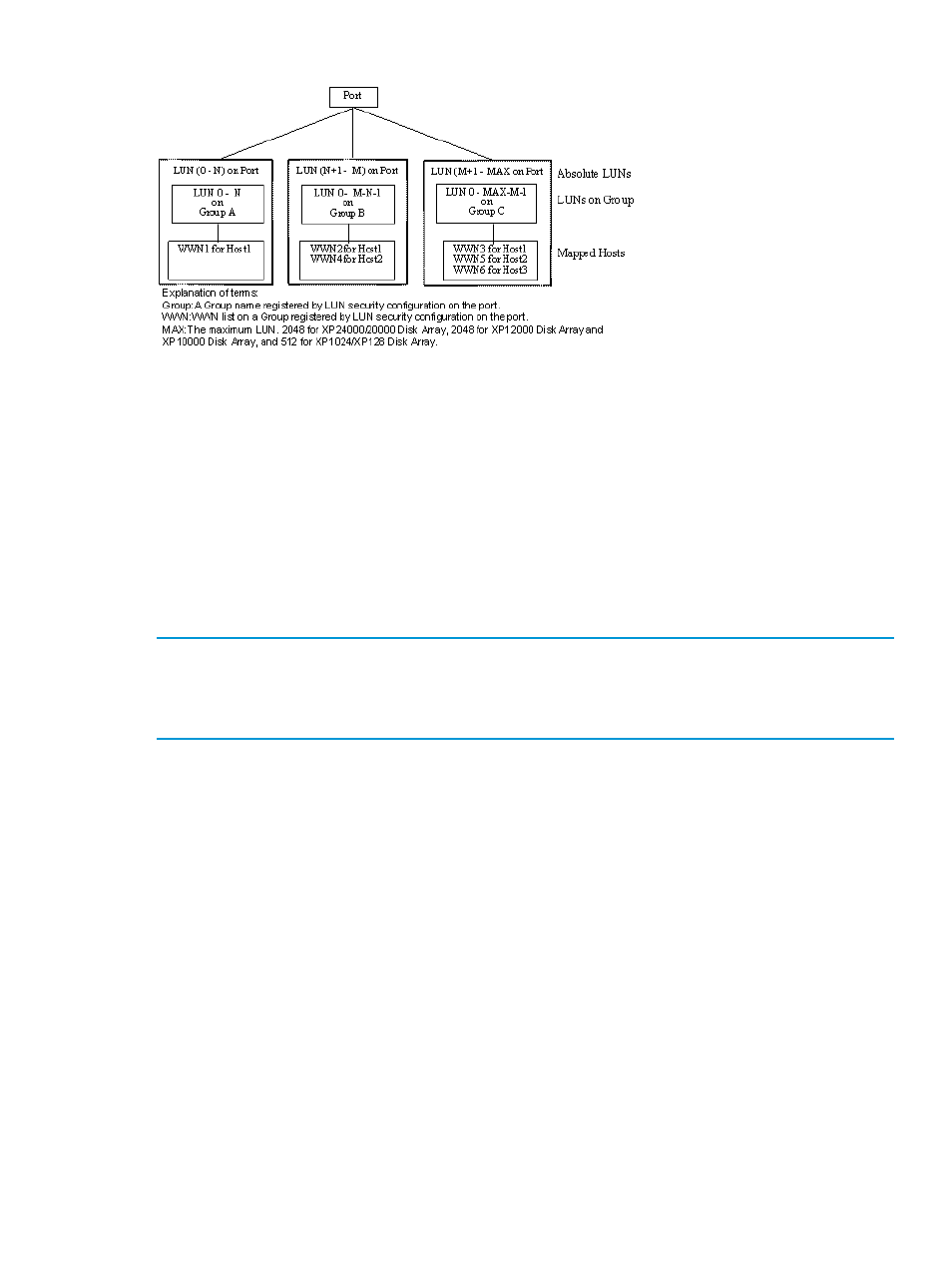
Figure 10 LUN configuration
RAID Manager uses absolute LUNs to scan a port, whereas the LUNs on a group are mapped for
the host system so that the target ID & LUN, that is indicated by the raidscan command, is different
from the target ID & LUN shown by the host system. In this case, the target ID & LUN indicated by
the raidscan command should be used.
In this case, you must start HORCM without a description for HORCM_DEV and HORCM_INST
because target ID & LUN are unknown. Use the port, target ID, and LUN displayed by the raidscan
-find or raidscan -find conf command for HORCM_DEV (see
Example 8 “Displaying the port, TID,
).
For details on LUN discovery based on a host group, see Host Group Control in the HP P9000
RAID Manager User Guide.
Example 8 Displaying the port, TID, and LUN using raidscan
# ls /dev/rdsk/* | raidscan -find
DEVICE_FILE UID S/F PORT TARG LUN SERIAL LDEV PRODUCT_ID
/dev/rdsk/c0t0d4 0 S CL1-M 0 4 31168 216 OPEN-3-CVS-CM
/dev/rdsk/c0t0d1 0 S CL1-M 0 1 31168 117 OPEN-3-CVS
/dev/rdsk/c1t0d1 - - CL1-M - - 31170 121 OPEN-3-CVS
UID: displays the Unit ID for multiple RAID configuration. If UID appears as ‘-’ then the command
device for HORCM_CMD is not found.
S/F: displays that a PORT is SCSI or Fibre.
PORT: displays the RAID storage system port number.
TARG: displays the target ID (converted by the Fibre conversion table, see
).
LUN: displays the Logical Unit Number (converted by the Fibre conversion table).
SERIAL: displays the production number (serial#) of the RAID storage system.
LDEV: displays the LDEV# within the RAID storage system.
PRODUCT_ID: displays product-id field in the STD inquiry page.
Fibre address conversion tables
,
and show the Fibre address
conversion tables:
•
Table number 0 = HP-UX systems (see
)
•
Table number 1 = Solaris and IRIX systems (see
)
•
Table number 2 = Windows systems (see
Fibre address conversion tables
53
