6 position control – NORD Drivesystems BU0710 User Manual
Page 19
3 Functional characteristics
BU 0710 GB
19
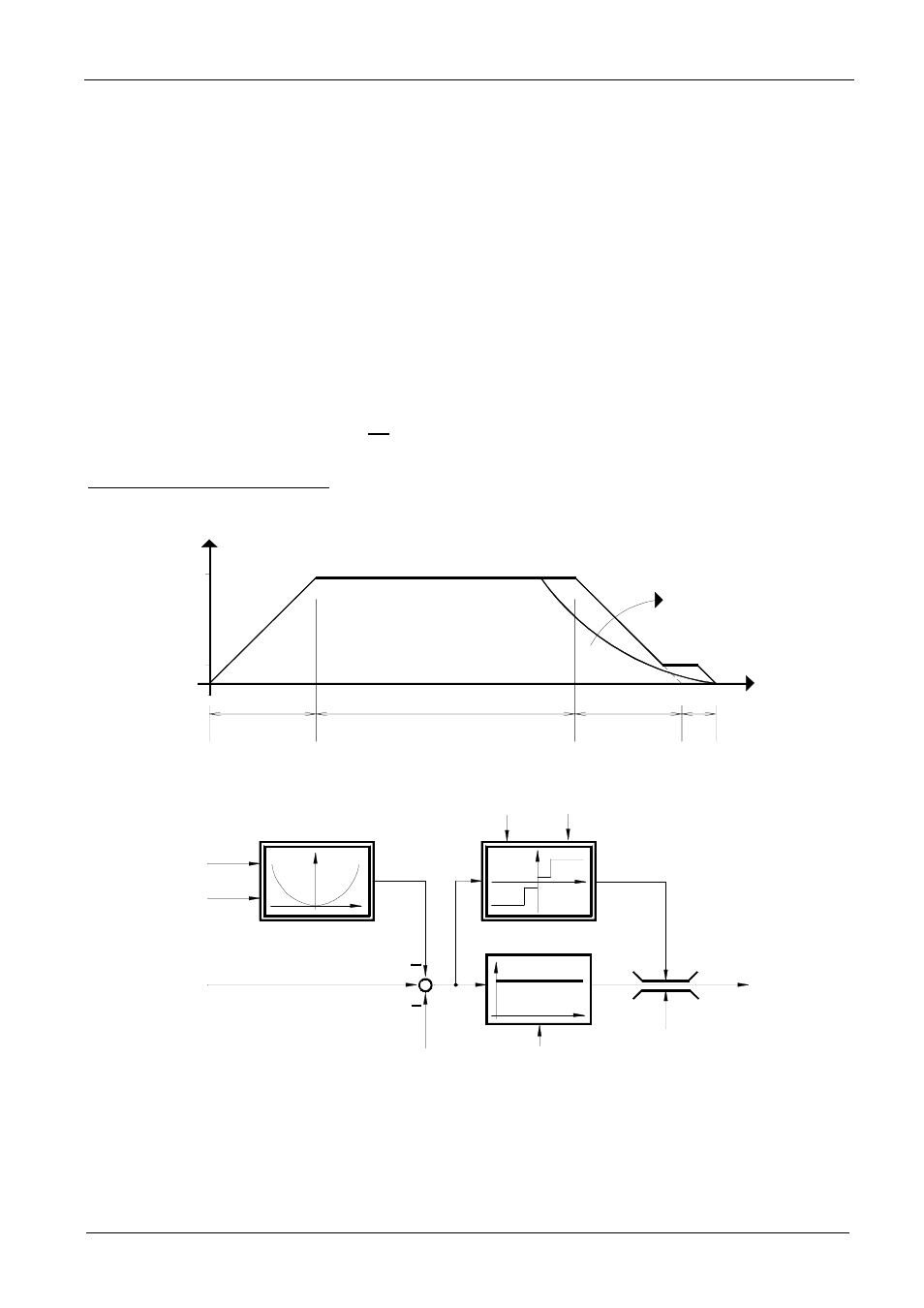
3.6 Position control
Position control is configured as a P control loop. Setpoint and actual position are constantly compared. The
setpoint frequency is calculated by multiplication of the position error with the value set in the "Position
controller P" parameter. Afterwards a maximum limit is determined which the setpoint frequency must not
exceed.
If the distance calculation function is activated, a derivative with respect to distance is calculated based on the
programmed braking time and the current speed. With braking time not being taken into account by distance
calculation, the speed would very probably be reduced too late, and the position be overshot. However braking
time is not a factor considered with highly dynamical systems where acceleration and deceleration periods are
extremely short, or with systems for which only very small displacement increments are defined.
Another parameter allows for the provision of settings for a destination window. In the destination window the
setpoint frequency is limited to minimum frequency (P104). In applications with varying loads and without
speed control, this parameter can be used to program a distance to be covered in crawling motion.
The destination window parameter does not affect the "Final position" relay signal.
Synoptical position control diagram:
max. frequency
P105
max.
min.
T_brake
P_set
frequency
N_act
P_act
(*) time depending on
"size of destination window"
P612
accel.time
P102
traveling with min.
frequency
N_set
time
size target window
P position controller
decel.time
P103
f_max
f_min
(*)
P position controller
