Application – GW Instek GFC-8010H User Manual
Page 5
FREQUENCY COUNTER
USER MANUAL
7
5. APPLICATION
5-1. Sensitivity
The role of the SENSITIVITY (or attenuator) switch in a common
measuring instrument is to protect the input circuit and prevent the meter
from going off scale.
For a counter, SENSITIVITY is still one of the large roles. Generally,
hysteresis occurs in the waveshaping circuit of the counter. In order for the
instrument to put up resistance to noise, the circuit will not work even
when the noise is lower than the hysteresis applied. The waveshaping
circuit is a Schmitt circuit and the operation of this circuit is described
below:
Fig. 2 Operation of the Schmitt circuit
FREQUENCY COUNTER
USER MANUAL
8
As refer to Fig. 2, when input voltage is at V+, the output voltage is high
(V
OH
), while input voltage is at V
-
, the output voltage is low (V
OL
). The
difference between these two voltage V
H
=(V
+
)-(V
-
) is called the hysteresis
voltage.
But if both V
+
and V
-
don’t react each other, no output will be obtained
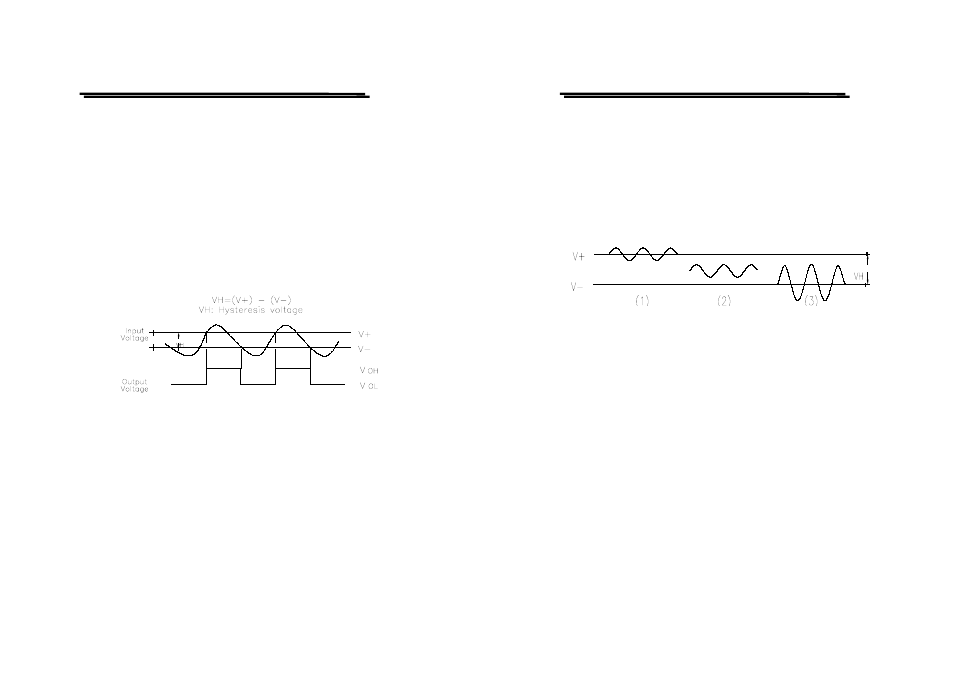
and the Schmitt circuit will not work out with the states of (1), (2) and (3)
of Fig. 3 shown as below.
Fig. 3 States under which the schmitt circuit doesn’t work
From above description, it can be easily understood whether or not the
Schmitt circuit works is attributed to the SENSITIVITY (Attenuator) to
determine the magnitude of the input voltage.
An example of preventing erroneous counting by correctly selecting the
SENSITIVITY shown as Fig. 4 below:
(a) Correctly counting a distortion signal by selecting suitable
SENSITIVITY. However, when the input voltage is too high, a
frequency doubles the unknown frequency will be indicated.
(b) Erroneous counting occurs when high frequency noise is
superimposed on the unknown signal and the input voltage of the
Schmitt circuit is too high. However, a correct counting can be
obtained by selecting suitable SENSITIVITY.
