Warning – ZOLL M Series Defibrillator Rev YH User Manual
Page 54
M S
ERIES
O
PERATOR
’
S
G
UIDE
8-2
3
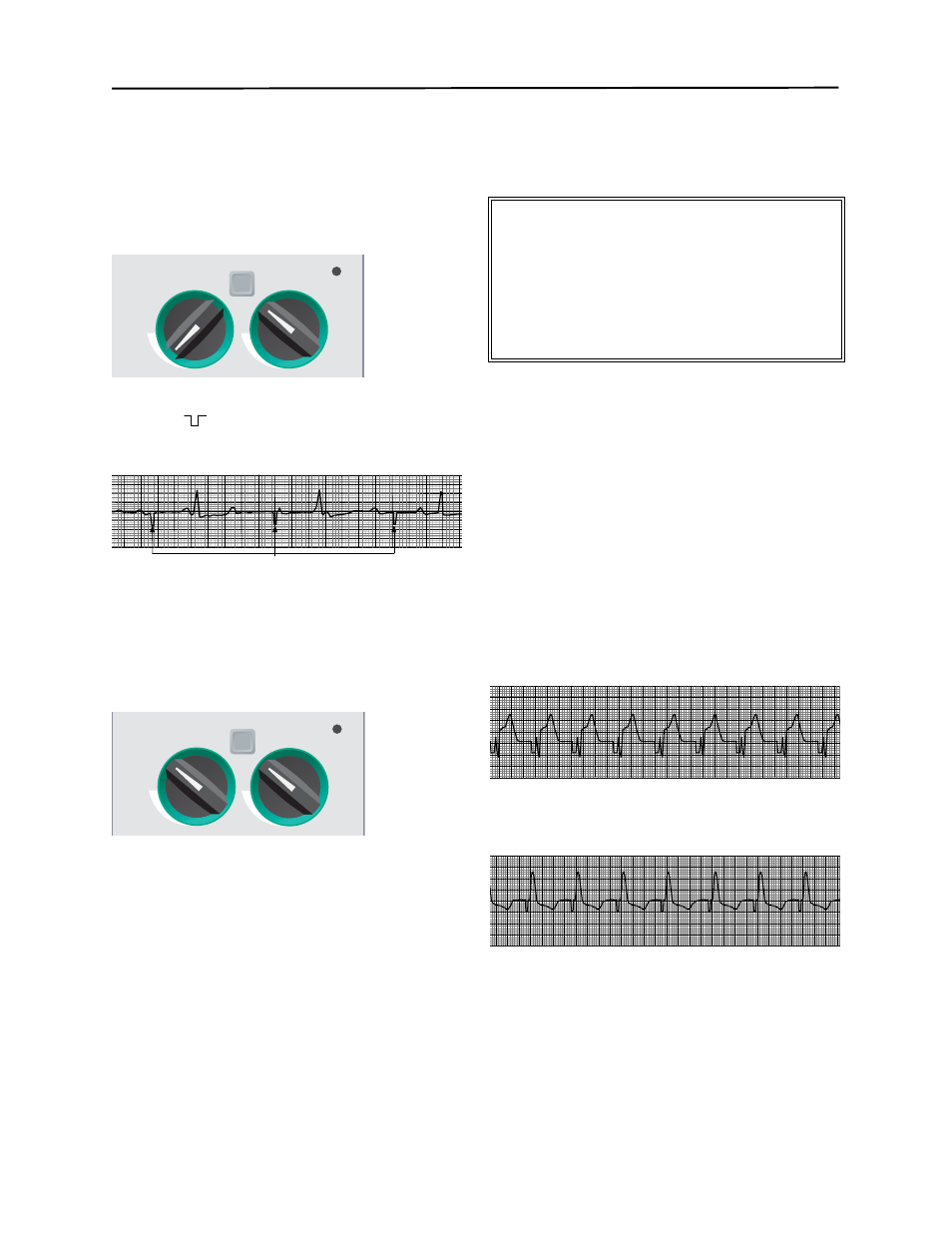
Set Pacer Rate
Set PACER RATE to a value 10-20 ppm higher than
patient’s intrinsic rate. If no intrinsic rate exists, use
100 ppm.
The pacer rate will increment or decrement by a value of
2 ppm on the display when the knob is turned.
Observe the pacing stimulus marker on the display or
stripchart (
) and verify that it is well-positioned in
diastole.
4
Set Pacer Output
Increase PACER OUTPUT mA until stimulation is
effective (capture). Output mA value is displayed.
The pacer output will increment or decrement by a value
of 2 mA on the display when the knob is turned.
Note: When the device is switched out of Pacer mode
into Defib or Monitor mode and then switched
back to Pacer mode, the Pacer settings will
remain unchanged.
If the unit is turned off for more than 10 seconds, the
pacer default settings will be restored.
5
Determine Capture
It is important to recognize when pacing stimulation has
produced a ventricular response (capture).
Determination of capture must be assessed both
electrically and mechanically in order to assure
appropriate circulatory support of the patient.
Electrical capture is determined by the presence of a
widened QRS complex, the loss of any underlying
intrinsic rhythm, and the appearance of an extended,
and sometimes enlarged, T-wave.
Mechanical capture is assessed by palpation of
peripheral pulse.
In order to avoid mistaking muscular response to pacing
stimuli for arterial pulsations, the following are the ONLY
recommended locations for palpating pulse during
pacing:
•
femoral artery
•
right brachial or radial artery.
Ventricular response is normally characterized by
suppression of the intrinsic QRS complex.
Effective Pacing
The following ECG tracings are typical of effective
pacing:
•
Negative R-wave and large T-waves.
•
Widened positive QRS, which looks like an ectopic beat.
A paced beat is by definition a ventricular ectopic beat.
•
Inverted T-waves and the absence of P-waves.
Changing ECG leads and size can sometimes be helpful
in determining capture.
Note: Shape and size of the paced ECG waveforms
can vary depending on the ECG lead
configuration chosen; variation from patient to
patient can be expected.
PACER
RATE
ppm
PACER
OUTPUT
mA
4:1
Pacing Stimuli
PACER
RATE
ppm
PACER
OUTPUT
mA
4:1
WARNING
•
Determination of electrical capture should only be
performed by viewing the ECG on the screen with its ECG
cable directly attached to the patient.
•
Use of other ECG monitoring devices may provide
misleading information due to the presence of pacer
artifacts.
