Jitter parameters – Teledyne LeCroy SDA III-CompleteLinQ User Manual
Page 49
Operator's Manual
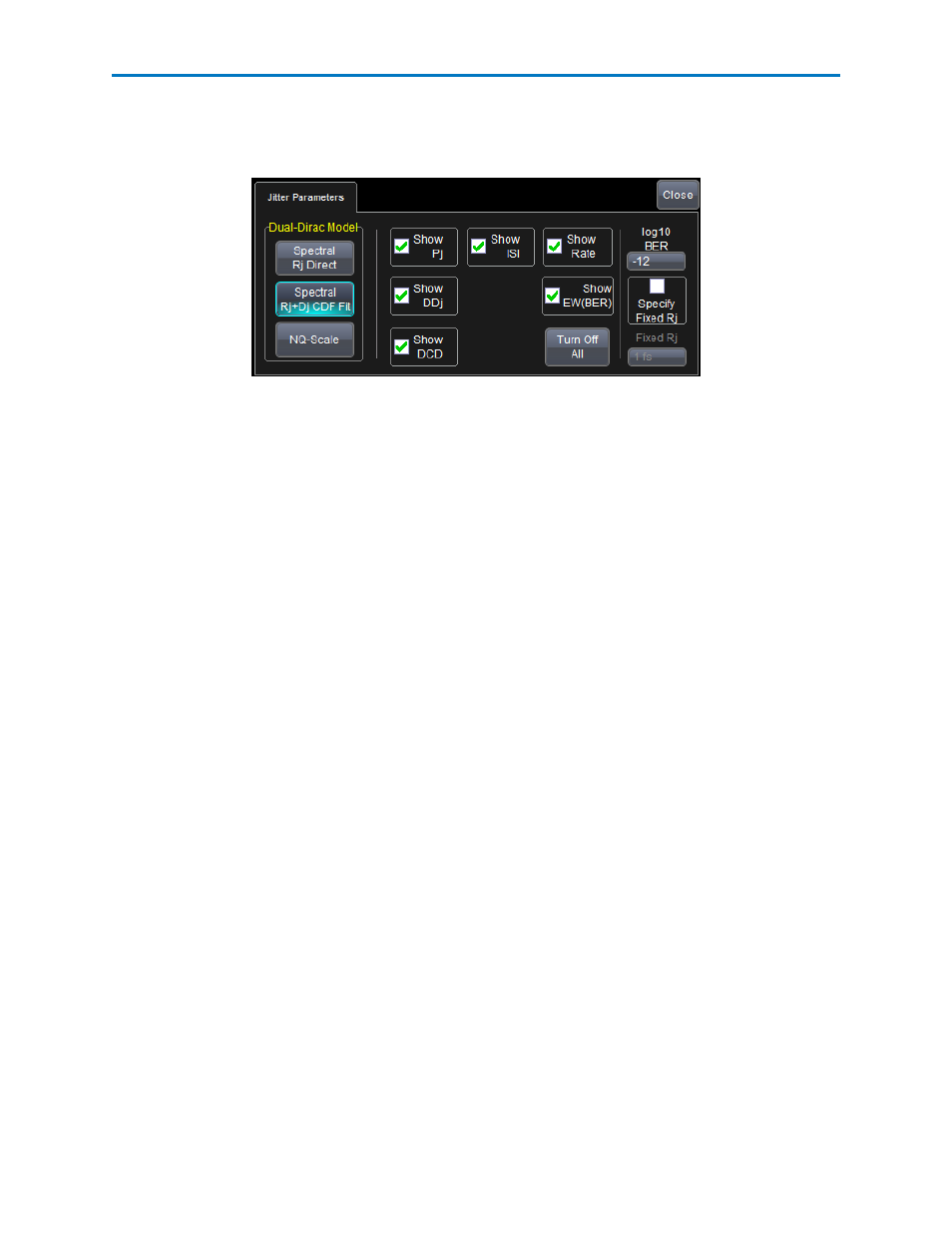
Jitter Parameters
Touch the Jitter Parameters button on the Jitter Measurement dialog to display the Jitter
Parametersdialog and select the parameters to display on the readout table.
Dual-Dirac Spectral Rj Direct - If Spectral is selected, then the Rj(sp) from the Jitter spectrum analysis is
used as the sigma of the fit Gaussians, and the positions of the right and left Gaussians, mu_left and mu_
right are obtained from a best fit. This technique gives the fastest convergence and is the right one to use
except in cases where crosstalk or other kinds of deterministic jitter exist that can masquerade as ran-
dom jitter. In those cases NQ-Scale should be used. In general if the 2 techniques are close, use the spec-
tral to take advantage of it's rapid convergence, if they differ by more than a little, then the assumptions
of the spectral model are probably being stretched and it would be better to use the NQ-Scale.
Dual-Dirac Spectral Rj+Dj CDF Fit - If Spectral is selected, then spectral analysis is used to determine a
sigma value to fit the tails of RjBUjHist, and the positions of the right and left Gaussians, mu_left and
mu_right are obtained from a best fit. This technique gives the fastest convergence and is the right one
to use except in cases where crosstalk or other kinds of deterministic jitter exist that can masquerade as
random jitter. In those cases NQ-Scale should be used. In general if the 2 techniques are close, use the
spectral to take advantage of it's rapid convergence, if they differ by more than a little, then the assump-
tions of the spectral model are probably being stretched and it would be better to use the NQ-Scale.
Dual-Dirac NQ-Scale - If NQ-Scale is selected, then there are 3 free parameters that are fit to obtain each
tail Gaussian: (1) the mean or mu, (2) the sigma, and (3) the population. A separate Gaussian is fit for
both the left and right side of the distributions, so there are 6 parameters in all. Use this technique in
cases where deterministic jitter can masquerade as random jitter, such as when non-repetitive crosstalk
is present. If the NQ-scale is showing significantly less Rj than the Spectral method, the NQ-scale tech-
nique will give a more accurate measure because the Spectral method is probably misidentifying Dj as Rj.
Log10 BER - This control sets the BER at which the Tj is reported, 10^-12 by default.
Show Pj - The p-p value of all the periodic jitter obtained from the IFFT of the spectral Pj peaks.
Show DDj - The range (max-min) of the DDj distribution for both positive and negative edges (and
includes the DCD effect).
Show DCD - The difference in the means of the histograms for the positive and negative edges.
Show ISI - The larger of the range (max-min) of the 2 subsets of the DDJ histogram for negative edges or
positive edges.
Show Rate - Displays the Jitter Rate.
Turn Off All - Touch this button to turn off all jitter parameters.
921143 Rev A
47
