High frequency measurements – Teledyne LeCroy ZS4000 User Manual
Page 16
ZS4000 High-Impedance, Active Probe
10
923360-00 Rev A
High Frequency Measurements
Probe Input Loading
When you touch a probe to the circuit under test, the probe will affect your
measurement because of the probe’s input impedance introduced into the
circuit. All probes present resistive, capacitive and inductive loading.
Inductive Loading (Lead Length)
A significant element in this circuit is the inductance shown in the input ground
leads of the oscilloscope probe.
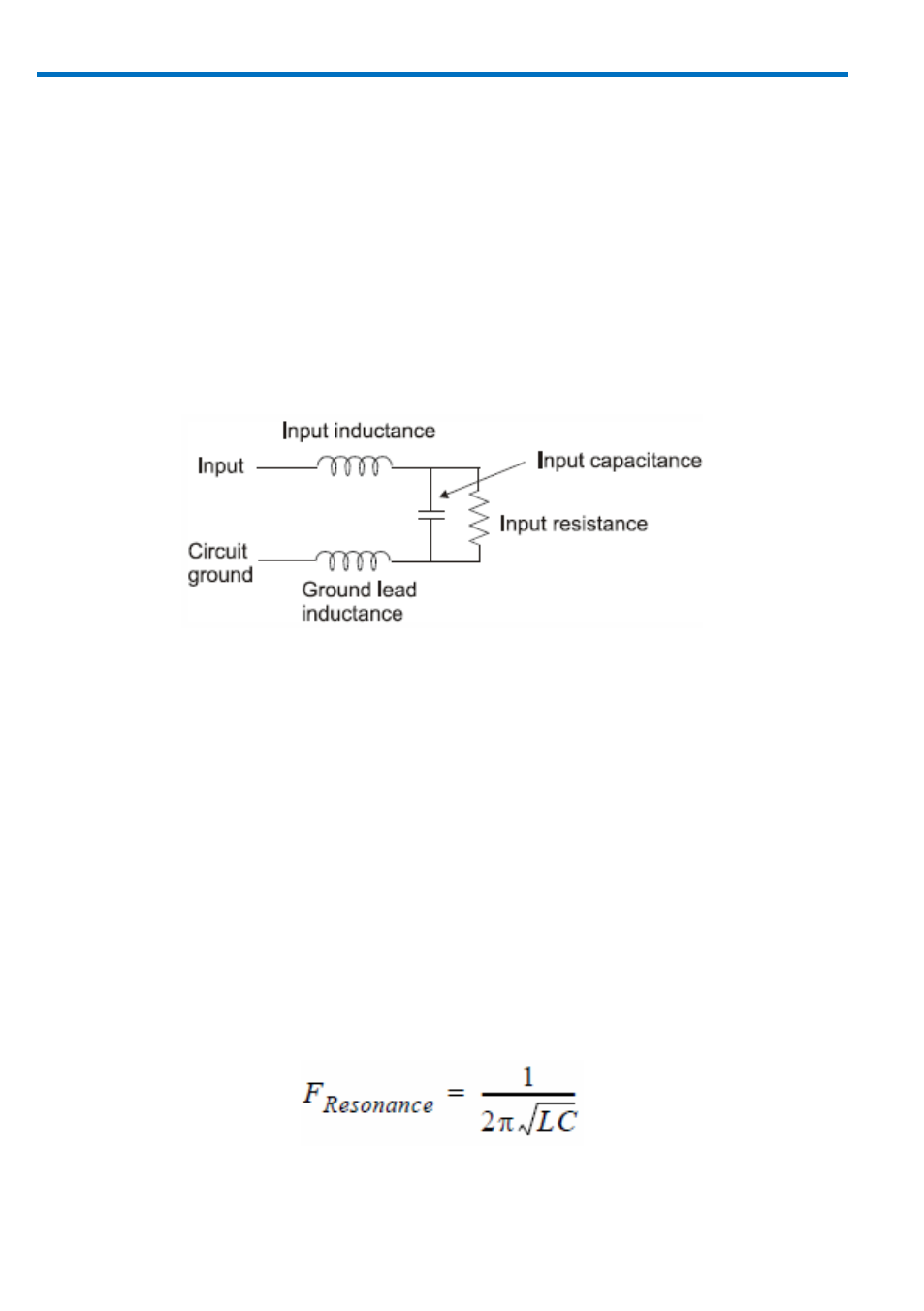
Probe input equivalent circuit
The ground lead is the primary return path for the current resulting from the
input voltage acting on the probe’s input impedance. The ground lead and input
lead inductances act with the probe’s input capacitance to form series L-C
network. The impedance of a series LC network drops dramatically at its resonant
frequency. This is the cause of the "ring" we often see after the leading edge of
pulses in measured waveforms.
This effect is referred to as ground lead corruption. Because it is impossible to
eliminate either the L or C from this circuit, the method to improve waveform
fidelity is to raise the resonant frequency beyond the bandwidth of interest in the
measurement.
The resonant frequency of a simple LC circuit can be represented by:
The resonant frequency of a series LC circuit can be raised by decreasing the
inductance, capacitance or both. Since the input capacitance is already very low
