Analysis, Data and calculations – PASCO SF-8616_8617 COILS SET User Manual
Page 17
scientific
15
012-03800A
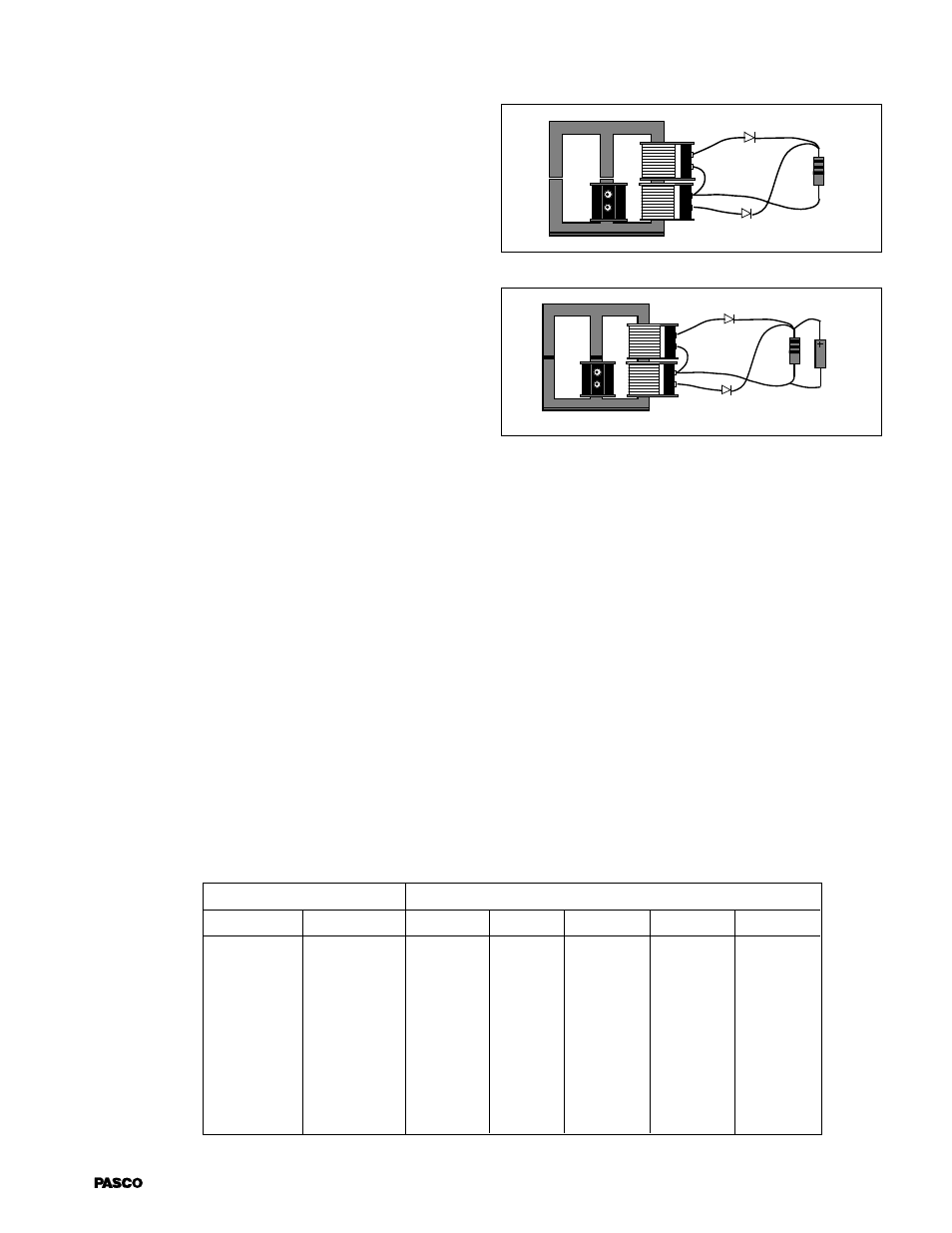
Primary
•
•
A
B
C
Load
Resistor
Diode
Diode
Figure 6
Capacitor
Primary
•
•
A
B
C
Load
Resistor
Diode
Diode
Figure 7
Analysis
1.
Answer the questions which have been posed along the way during the procedure.
2.
Why do you get such different results if you place the secondary coil(s) on the second or third
leg of the E-shaped core? Think about the magnetic circulation that must take place within
the core.
3.
Compare the results of lowering the load resistance on a half-wave rectified circuit with
lowering the load resistance on a full-wave rectified circuit. If you were to try to stabilize the
output of a power supply, which would be better, a half-wave or full-wave rectified signal?
4.
This experiment has introduced the concept of transformers and power supplies. Further
reading and experimentation can easily begin from here and lead to profitable new under-
standing.
15. The end result in step 14 is the produc-
tion of a full-wave rectified signal, one
which is directional in nature, although
it varyies in amplitude over time. We
will now add in a 470-
µ
F capacitor as
shown in Figure 7.
16. What is the new waveform across the
load resistor? Do you have d.c., yet?
What is the d.c. voltage you’ve pro-
duced?
17. Now replace the 1000-
Ω
load resistance
with a 10-
Ω
resistor. What is the effect
on the d.c. voltage compared to the
1000-
Ω
resistance? What is the effect
on the waveform?
Data and Calculations
Table 4.1
Number of Turns
Primary
Secondary
Input V
Input I
Load R
Output V
Output I
